Angular 17 Structural Directives (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 23 Jul, 2025
Structural directives in Angular 17 are a special type of directives that allow you to dynamically manipulate the DOM (Document Object Model) by adding, removing, or replacing elements based on certain conditions. These directives are prefixed with an asterisk (*) in the template syntax.
In this article, we will learn more about Structural Directive.
Table of Content
- What are Structural Directives?
- Features of Structural Directives
- Uses of Structural Directives
- Types of Structural Directives
- 1. @ngIf
- 2. @switch
- 3. @for
Prerequisites:
- Angular and it's core concepts
- Angular components and templates
- Familiarity with Angular directives
- HTML and CSS
- TypeScript
What are Structural Directives?
Structural directives are Angular directives that control the structure of the DOM by adding, removing, or manipulating elements based on conditions. They allow to create dynamic and interactive templates by conditionally rendering or repeating elements.
**Syntax:
Features of Structural Directives
- **Conditional Rendering: Structural directives like
*ngIfallow to conditionally render elements based on the evaluation of an expression. The element is added to the DOM if the expression evaluates to true and removed if it evaluates to false. - **Iteration: Structural directives like
*ngFor provideiteration over lists or collections and generate multiple instances of a template element for each item in the list. - **Template Switching: Structural directives like
ngSwitchallow to conditionally switch between multiple template options based on the evaluation of a matching expression. This is useful for implementing conditional logic and rendering different views or components.
Uses of Structural Directives:
- **Conditional Rendering: Showing or hiding elements based on user authentication status, permission levels, or application state.
- **Dynamic Lists: Rendering dynamic lists of items fetched from APIs or databases, such as news articles, product listings, or user profiles.
- **Conditional Template Switching: Implementing tabbed interfaces, accordion menus, or wizard-like navigation where different views are displayed based on user interactions.
Types of Structural Directives:
**There are basically 3 built in structural directives available in Angular 17
- NgIf (@ngIf)
- NgSwitch (@ngSwitch)
- NgFor (@ngFor)
1. @ngIf
NgIf is a structural directive in Angular used to conditionally render or remove an element from the DOM based on the evaluation of a given expression. The angular directive NgIf is used to add an element subtree for the expression's **true value. The element subtree in this instance will not be added to the DOM if the "expression" value is either **false or **null.
- NgIf conditionally includes a template based on the value of expression.
- The HTML element in the DOM layout can be added or removed.
- The basic syntax of the ngIf directives is simple and effective , all we need to do prefix the directive name with @ and add it anywhere inside our template.
**Syntax :
@if(condition){text}
**Example :
HTML `
Welcome To learn about Structural Directives
@if(isLoggedIn){
<div>User is LoggedIn</div>
}JavaScript
// app.component.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core'; import { RouterOutlet } from '@angular/router';
@Component({ selector: 'app-root', standalone: true, imports: [RouterOutlet], templateUrl: './app.component.html', styleUrl: './app.component.css', preserveWhitespaces: true }) export class AppComponent { title = 'Structuraldirectives';
isLoggedIn: boolean = true}
`
**Output:

2. @switch
NgSwitch is a structural directive in Angular used for conditional rendering of elements based on a given value. It is similar to a switch statement in programming languages.
Switch uses **Case and **Default . Switch uses **Case keyword to define a set of possible element trees and **Default is used to define default value when expression condition does not match to any element tree defined by Case. @switch is used to switch a set of directives among alternative views.
**Example :
HTML `
Welcome To learn about Structural Directives
Enter Your name :@switch(txtname.value) { @case('Ram'){ Hello Ram } @case('Shyam'){ Hello Shyam } @case('Mohan'){ Hello Mohan }@default{ No data matched } }
JavaScript
// app.component.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core'; import { RouterOutlet } from '@angular/router';
@Component({ selector: 'app-root', standalone: true, imports: [RouterOutlet], templateUrl: './app.component.html', styleUrl: './app.component.css', preserveWhitespaces: true }) export class AppComponent { title = 'Structuraldirectives'; name = "Shyam" }
`
**Output :
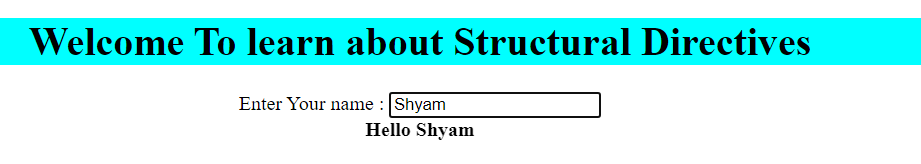
**Note : In Angular 17 you can create duplicate cases.
3. @for
NgFor is a structural directive in Angular used to render a template for each item in a collection. It iterates over each item in the collection and creates a new instance of the template for each item.
**Syntax :
@for(i of items ; track i.name){
**Note : In Angular 17 , the track concept has been defaulted. you must write.
**Example :
HTML `
Welcome To learn about Structural Directives
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>EMPLOYEE ID</th>
<th>EMPLOYEE NAME</th>
</tr>
@for(emp of employee;track emp.id){
<tr>
<td>{{emp.id}}</td>
<td>{{emp.name}}</td>
</tr>
}@empty{
<tr>
<td colspan="2">No Data Found</td>
</tr>
}
</table>JavaScript
// app.component.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core'; import { RouterOutlet } from '@angular/router';
@Component({ selector: 'app-root', standalone: true, imports: [RouterOutlet], templateUrl: './app.component.html', styleUrl: './app.component.css', preserveWhitespaces: true }) export class AppComponent { title = 'Structuraldirectives';
employee: any[] = [
{ id: 100, name: "Tina" },
{ id: 101, name: "Shyam" },
{ id: 102, name: "Meena" },
{ id: 103, name: "Rohan" },
{ id: 104, name: "Rajesh" },
{ id: 101, name: "Sita" }
]}
`
**Output :
