Angular Interview Questions and Answers (original) (raw)
Angular is a popular open-source framework that simplifies web development by creating interactive single-page applications (SPAs). Unlike traditional websites that load new pages for each click, SPAs offer a smoother user experience by updating content on the same page.
- Syncs model and view in real-time, minimizing DOM manipulation.
- Organizes code for scalability and maintainability in SPAs.
- Simplifies dynamic UI creation with reusable HTML components.
Angular Basics Interview Questions
In this section, we will discuss basic Angular questions asked in the interview suitable for the freshers.
1. **Why was a client-side framework introduced?
Client-side frameworks were introduced to handle the growing complexity of modern web applications. Earlier, with plain JavaScript or jQuery, developers had to manually update the DOM, which became messy and hard to maintain as applications grew.
Frameworks like Angular and React solved this by:
- Supporting Single Page Applications (SPAs) for smooth, fast user experiences without full page reloads.
- Providing features like two-way data binding (Angular) or virtual DOM (React) to keep UI and data in sync automatically.
- Offering a component-based architecture so code is reusable, organized, and easier to maintain.
- Giving built-in tools (routing, forms, state management) that increased developer productivity.
2. How does an Angular application work?
An Angular app is a Single Page Application (SPA) that runs in the browser. It bootstraps the root module, builds the UI with components and templates, uses services for logic, manages navigation with the router, and keeps the UI updated through data binding and change detection.
- App bootstraps from
main.tswithAppModuleandAppComponent. - Modules group app features.
- Components build UI with logic, template, and styles.
- Data binding links view and logic.
- Directives modify DOM.
- Services share reusable logic via DI.
- Routing handles navigation.
- Change detection updates DOM on data change.
- Compiler renders templates into JavaScript.
3. How are Angular expressions different from JavaScript expressions?
- JavaScript expressions are evaluated by the browser’s JS engine directly.
- Angular expressions are written inside
{{ }}in templates and evaluated by Angular.
| **Angular Expressions | **JavaScript Expressions | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Used inside Angular templates ({{ }}, *ngIf, *ngFor). | Used in .js/.ts files or
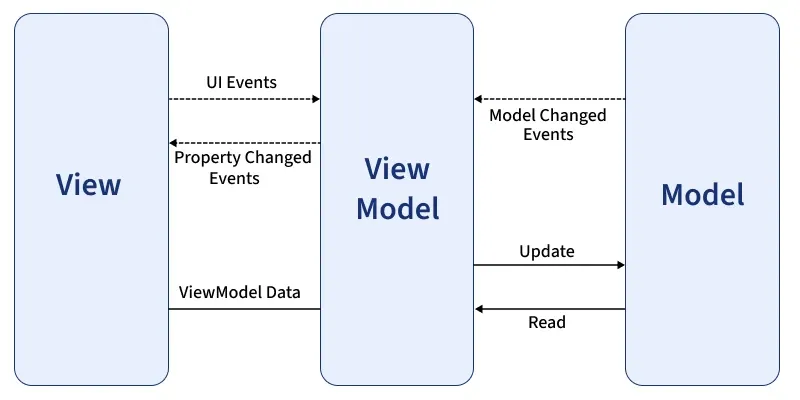
29. How can you pass data between components in Angular?Data can be passed between components using Input and Output decorators, services, or router state. Passing data from a parent component to a child component using @Input decorator. JavaScript ` //child.component.ts import { Component, Input } from '@angular/core'; @Component({ selector: 'app-child', templateUrl: './child.component.html', styleUrls: ['./child.component.css'] }) export class ChildComponent { @Input() childData: string; // Declare the input property } //Child.component.html Data from parent: {{ childData }} //parent.component.ts import { Component } from '@angular/core'; @Component({ selector: 'app-parent', templateUrl: './parent.component.html', styleUrls: ['./parent.component.css'] }) export class ParentComponent { parentData: string = 'Hello from Parent Component!'; } //parent.component.html //App.module.ts import { NgModule } from '@angular/core'; import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser'; import { AppComponent } from './app.component'; import { ParentComponent } from './parent/parent.component'; import { ChildComponent } from './child/child.component'; @NgModule({ declarations: [ AppComponent, ParentComponent, ChildComponent ], imports: [ BrowserModule ], providers: [], bootstrap: [AppComponent] }) export class AppModule { } ` 30. Explain lazy loading in Angular?Lazy loading in Angular is a technique used to improve the performance of an application by loading feature modules only when they are needed, rather than loading all modules upfront. This reduces the initial load time of the application and speeds up the startup process. 31. What is MVVM architecture in Angular?MVVM (Model-View-ViewModel) is a software architectural pattern that is commonly used in Angular applications, providing a clean separation of concerns between different components of an application. This ensures that changes in one part of the application (like in the logic or data) do not directly affect or interfere with the user interface.
**Here's how MVVM works in Angular: **Model:
**View:
**ViewModel:
32. What are Angular lifecycle hooks?Angular lifecycle hooks are methods that allow you to tap into key moments in a component's lifecycle. Here are the main lifecycle hooks:
33. What is a pipe in Angular?A pipe is a way to transform data in the template. It allows you to format or manipulate data before displaying it to the user. Angular provides several built-in pipes like DatePipe, UpperCasePipe, and CurrencyPipe, and you can also create custom pipes. Pipes are typically used to modify the display of data without altering the original data itself. 34. **What is Angular Universal?**Angular Universal is a technology that enables **server-side rendering (SSR) for Angular applications, improving performance, initial load times, and **search engine optimization (SEO) by pre-rendering the application on the server before sending it to the client. This results in faster, more interactive user experiences and better indexing by search engines. 35. How do you optimize Angular applications?To optimize Angular applications, you can:
36. What are Angular interceptors?Angular interceptors are services that intercept and modify HTTP requests and responses. They allow you to perform actions such as adding headers (e.g., authentication tokens), logging, or handling errors globally. Interceptors are useful for managing HTTP communication centrally in Angular applications. 37. Explain the purpose of NgZone in Angular?NgZone in Angular is a service that helps Angular know when to update the view by tracking asynchronous operations. It runs change detection whenever an asynchronous operation, like a setTimeout or HTTP request, completes. NgZone ensures that Angular is aware of changes in the application state and triggers the necessary updates to the view. 38. What is the difference between |
| Decorator | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| @Input() | Pass data from parent to child component | |
| @Output() | Emit events from child to parent component |
39. How do you implement authentication in Angular?
Authentication can be implemented using JWT tokens, Angular guards, and interceptors to manage login and secure routes.
Securing a route with an AuthGuard.
JavaScript `
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
@Injectable({ providedIn: 'root' }) export class AuthService {
constructor() { }
isLoggedIn(): boolean {
return !!localStorage.getItem('userToken');
}}
`
40. What are Standalone Components in Angular 19?
In Angular 19, standalone components provide a simpler and more flexible way to build applications without depending on NgModules. They reduce complexity, improve optimization through better tree-shaking, and make components easier to manage, test, and reuse. This leads to cleaner code, improved performance, and a streamlined development workflow.
- No need for complex NgModule dependencies.
- Better tree-shaking: Optimized bundle size.
- Easier to develop, test, and reuse components independently.
- Cleaner code and improved flexibility in application architecture.
41. How do you use Typed Forms?
Typed Forms in Angular 19 provide enhanced type safety for reactive forms. By defining strict types for FormGroup, FormControl, and FormArray, developers can prevent runtime errors, ensure consistency, and handle form data more robustly. This improves maintainability and the overall developer experience.
- Strong type-checking for form controls to prevent runtime errors.
- Easier management and access to form values with proper type support.
- More robust and maintainable reactive forms for large applications.
42. What is the purpose of the Signal API?
The Signal API in Angular simplifies state management by providing reactive signals that automatically track changes and update the view. This reduces the need for manual change detection, improves performance, and makes applications more responsive and efficient.
- Automatic tracking of state changes and dependencies.
- Updates the view without manual change detection.
- Reduces complexity in managing reactivity.
- Optimizes performance by minimizing unnecessary updates.
43. How does the inject() function work?
The inject() function simplifies the process of dependency injection (DI). It allows developers to access and inject services or dependencies directly within the component’s constructor or lifecycle methods without the need for constructor injection.
44. What improvements have been made to standalone testing?
Standalone components can now be tested directly, reducing boilerplate code and enhancing tree-shaking by avoiding unnecessary module dependencies. The testing framework has been optimized for better performance and developer experience. Angular 19 also improves integration with testing libraries like Jasmine and Karma, allowing for more straightforward configuration, faster tests, and a smoother testing process.
45. Explain the use of Functional Components?
Functional components focus purely on rendering UI based on inputs and outputs, without requiring a class structure. This approach brings a more functional programming style to Angular, making it easier to write and test components with better performance, especially for simple and reusable components.
46. What is Ahead-of-Time (AOT) compilation in Angular?
Ahead-of-Time (AOT) compilation in Angular is the process of compiling Angular templates and TypeScript code into efficient JavaScript code during the build process, before the application is run in the browser. This reduces the size of the application, improves startup performance, and allows for earlier detection of template errors, resulting in faster rendering and better overall performance in production.
47. What is Ivy in Angular?
Ivy is Angular's next-generation rendering engine, introduced to improve performance and reduce bundle sizes. It offers faster compilation, more efficient rendering, and enhanced debugging capabilities. Ivy's advanced tree-shaking features eliminate unused code, leading to smaller and faster applications. Additionally, Ivy provides better backward compatibility, making it easier to update and maintain Angular applications.
**48. Explain the purpose of Angular Elements.
- **Web Component Integration: Allows Angular components to be packaged as custom elements (web components) that can be used in any HTML page or framework.
- **Reusability: Enables the reuse of Angular components across different projects and frameworks, providing code sharing and consistency.
- **Interoperability: Provides the integration of Angular components into non-Angular applications, enhancing flexibility and compatibility.
- **Encapsulation: Provides encapsulated, self-contained components that encapsulate their logic, styles, and templates, reducing the risk of conflicts in larger applications.
49. **What is a Resolver in Angular?
A Resolver in Angular is a service that pre-fetches data before a route is activated, ensuring that the necessary data is available when the route is accessed. This is particularly useful for loading important data that a component depends on, thereby enhancing user experience by avoiding loading indicators or incomplete views.
**Angular Advanced Interview Questions
In this set we will be covering Angular interview question for experienced developers with over 5 years of experience.
50. What is difference between Angular and React?
| Angular | React |
|---|---|
| Full-fledged framework | Library for building user interfaces |
| TypeScript (JavaScript superset) | JavaScript (JSX syntax) |
| MVC (Model-View-Controller) / MVVM (Model-View-ViewModel) | Component-based architecture |
| Suitable for large-scale applications with complex requirements | Best for building interactive UIs and SPAs (Single Page Applications) |
51. How are Angular expressions are different from JavaScript expressions?
Angular Expressions are a simplified version of JavaScript expressions designed for use within templates and for data binding, while JavaScript Expressions are more flexible and can be used to perform various operations in the logic layer of an application.
52. What is the purpose of NgModule in Angular?
The purpose of NgModule in Angular is to organize an application into cohesive blocks of functionality by grouping related components, directives, pipes, and services. NgModule defines a compilation context for these elements, providing modularity and maintainability.
53. **What is the difference between Template-driven and Reactive Forms?
| Template-driven Forms | Reactive Forms |
|---|---|
| Based on directives | Based on explicit creation |
| Asynchronous | Synchronous |
| Simple forms | Complex forms |
| Two-way data binding | Immutable data model |
54. What are Angular Guards?
Angular Guards are services that control access to routes in an Angular application. They are used to protect routes from unauthorized access or to prevent unwanted navigation. Common types of guards include:
- **CanActivate: Determines if a route can be activated.
- **CanDeactivate: Checks if a route can be deactivated.
- **CanLoad: Determines if a module can be loaded lazily.
55. How do you create custom validators in Angular?
Custom validators can be created by implementing the ValidatorFn interface and using it in the form controls.
Creating a custom validator to check if a username is available.
JavaScript `
import { AbstractControl, ValidationErrors, ValidatorFn } from '@angular/forms'; import { Injectable } from '@angular/core'; import { Observable, of } from 'rxjs'; import { map } from 'rxjs/operators';
@Injectable({ providedIn: 'root' }) export class UsernameValidatorService { private takenUsernames = ['admin', 'user', 'guest'];
checkUsername(username: string): Observable<boolean> {
return of(this.takenUsernames.includes(username)).pipe(
map(isTaken => !isTaken)
);
}}
`
56. What is the purpose of Angular animations?
The purpose of Angular animations is to add dynamic visual effects to applications, improving user experience by making transitions, **state changes, and movements more engaging. They enable smooth animations for elements such as **fading, sliding, or resizing, triggered by user interactions or state changes in the application.
57. Explain dynamic components in Angular.
**Dynamic components in **Angular are components that are created and inserted into the application at runtime, rather than being statically declared in the template. This allows for greater flexibility and responsiveness in applications.
58. What is Angular Material?
**Angular Material is a UI component library for **Angular applications that provides pre-built, reusable, and customizable user interface components, following Google’s Material Design principles. It offers components like buttons, dialogs, form controls, and navigation elements, helping developers create modern, responsive, and visually appealing applications quickly.
**59. What is Eager?
In AngularJS, eager loading refers to the process where modules, services, and controllers are loaded at the start of the application, even if they are not immediately needed. Eager loading is typically used when the developer expects all parts of the application to be used early on.
60. What is the purpose of Angular's Renderer2?
- **Platform Agnostic:
Renderer2provides a platform-agnostic way to manipulate the DOM, ensuring that the application can run consistently across different environments, such as server-side rendering with Angular Universal or web workers. - **Security: It helps prevent XSS (Cross-Site Scripting) attacks by sanitizing inputs and ensuring safe interactions with the DOM.
- **Abstraction:
Renderer2abstracts away direct DOM manipulation, making the code more testable and maintainable by allowing developers to focus on logical rather than low-level DOM operations. - **Consistency: Ensures consistent behavior across various browsers and platforms.
61. What is the difference between AOT and JIT?
| AOT (Ahead-of-Time) Compilation | JIT (Just-in-Time) Compilation |
|---|---|
| Compilation occurs at build time | Compilation occurs at runtime |
| Faster startup time, as the code is already compiled | Slower startup time, as the code is compiled in the browser |
| Errors are detected at build time, allowing for earlier fixes | Errors are detected at runtime, which may affect the user experience |
| Smaller bundle size, as the compiler is not included in the bundle | Larger bundle size, as the compiler is included in the bundle |
| Better suited for production environments, including server-side rendering | Often used in development environments for faster iteration and debugging |
62. What are the benefits of using Web Workers in Angular?
- **Improved Performance: Web Workers allow for offloading heavy computations and tasks to background threads, freeing up the main thread and ensuring smoother and more responsive user interfaces.
- **Enhanced User Experience: By running complex operations in the background, Web Workers prevent the UI from becoming unresponsive, providing a seamless and uninterrupted user experience.
- **Parallel Processing: Web Workers enable parallel processing of tasks, which can significantly speed up operations that are computationally intensive or involve large datasets.
- **Better Scalability: Utilizing Web Workers can help scale applications more effectively by distributing the workload, leading to more efficient resource utilization and improved performance under high load conditions.
63. What is Data Binding in Angular?
Data binding in Angular is a mechanism that allows communication between the component and the view (HTML template). It synchronizes the data between the model (component) and the view, making it easy to reflect changes in the UI whenever data changes in the component.
There are the 4 types of the data binding in Agular:
- Interpolation (One-way Binding)
- Property Binding (One-way Binding)
- Event Binding (One-way Binding)
- Two-way Binding
64. What are impure pipes in angular?
Impure pipes in Angular are pipes that can change the output when input values change over time, even without the change detection running. Unlike pure pipes, impure pipes are evaluated every time change detection runs, which can lead to performance issues if not used carefully.
65. What are pure pipes in angular?
Pure pipes in Angular are pipes that only re-evaluate when their input data changes. This makes them more efficient compared to impure pipes, as they are only executed when the values of the inputs change.
66. What is Pipe transform Interface in Angular?
In Angular, the PipeTransform interface is used to define the structure of a custom pipe. It is part of the Pipe decorator, which helps in creating custom pipes to transform data within templates.
Angular Scenario Based Interview Questions
In this section, we will look at real-world scenarios and how to handle them in Angular.
67. Scenario: Handling Data from Multiple APIs
**Question: We are developing an Angular application that needs to fetch data from multiple APIs and display them together on the same page. How would we handle asynchronous API calls and ensure the data is displayed after all responses are received?
**Answer: I would use the **RxJS forkJoin operator to handle multiple API calls concurrently. This ensures that all API responses are received before processing the data. Here's how I would implement it:
JavaScript `
import { forkJoin } from 'rxjs'; import { HttpClient } from '@angular/common/http';
constructor(private http: HttpClient) { }
getData() { const api1$ = this.http.get('https://api1.example.com'); const api2$ = this.http.get('https://api2.example.com');
forkJoin([api1$, api2$]).subscribe(
([api1Response, api2Response]) => {
// Process data from both APIs
this.processData(api1Response, api2Response);
},
error => {
console.error('Error fetching data', error);
}
);}
`
forkJoin waits until all observables complete and then emits the results in an array. This is perfect for scenarios where you want to fetch data from multiple sources simultaneously.
68. Scenario: Optimizing Angular Performance with Lazy Loading
**Question: Your Angular application is getting slower due to a large number of modules and components. How would you optimize the application’s performance?
**Answer: One way to optimize an Angular application is by **implementing lazy loading to load modules only when needed. This reduces the initial bundle size, improving load times. Here's an example of setting up lazy loading in Angular:
C++ `
// app-routing.module.ts const routes: Routes = [ { path: 'feature', loadChildren: () => import('./feature/feature.module').then(m => m.FeatureModule) } ];
`
- By using the
loadChildrenproperty, Angular will load the **FeatureModule only when the user navigates to the/featureroute. - This improves the app's performance by deferring the loading of non-essential modules.
69. Scenario: Handling Form Validation in Reactive Forms
**Question: We have a form where the user enters their email, and we need to ensure that it is both valid and unique (not already in use). How would we implement this validation using Angular Reactive Forms?
**Answer: I would use **Reactive Forms with custom synchronous and asynchronous validators. Here's how I would implement both email format validation and uniqueness check:
JavaScript `
import { FormBuilder, FormGroup, Validators } from '@angular/forms'; import { of } from 'rxjs'; import { map, delay } from 'rxjs/operators';
constructor(private fb: FormBuilder) { }
emailForm: FormGroup = this.fb.group({ email: ['', [Validators.required, Validators.email], [this.uniqueEmailValidator.bind(this)]] });
uniqueEmailValidator(control: AbstractControl) { const emailsInUse = ['test@example.com', 'user@example.com']; return of(emailsInUse.includes(control.value)).pipe( delay(500), map(isInUse => (isInUse ? { emailInUse: true } : null)) ); }
`
- The
Validators.emailensures the entered email is valid, while theuniqueEmailValidatorchecks asynchronously whether the email is already in use. - If so, it returns an error, otherwise, it passes validation.
70. Scenario: Debugging Change Detection Issues
**Question: We notice that a component is not updating as expected when data changes. How would you debug and resolve the issue related to Angular's change detection mechanism?
**Answer: First, I would check if the component is using **OnPush change detection strategy:
JavaScript `
@Component({ selector: 'app-sample', templateUrl: './sample.component.html', changeDetection: ChangeDetectionStrategy.OnPush })
`
If the OnPush strategy is being used, Angular only checks for changes when an input reference changes. If the data is updated by mutation, Angular will not detect the change. In this case, I would either:
C++ `
constructor(private cd: ChangeDetectorRef) {}
updateData() {
this.data = { ...this.data, newValue: 'updated' };
this.cd.markForCheck();
}
`
- If the object is mutated directly, OnPush doesn't detect the change.
- Ensure the object reference is changed, or
- Manually trigger change detection using
ChangeDetectorRef: - Creating a new object or using
markForCheckensures that Angular runs change detection.
71. Scenario: Implementing Route Guards for Authentication
**Question: How would you protect specific routes in your Angular application so that only authenticated users can access them?
**Answer: I would implement **Route Guards using Angular’s CanActivate interface to protect routes. Here's an example of how to implement an authentication guard
JavaScript `
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core'; import { CanActivate, Router } from '@angular/router'; import { AuthService } from './auth.service';
@Injectable({ providedIn: 'root' }) export class AuthGuard implements CanActivate {
constructor(private authService: AuthService, private router: Router) { }
canActivate(): boolean {
if (this.authService.isAuthenticated()) {
return true;
} else {
this.router.navigate(['/login']);
return false;
}
}}
`
- The
AuthGuardchecks if the user is authenticated before allowing access to the route. - If the user is not authenticated, they are redirected to the login page.
- This ensures that only authorized users can access certain parts of the application.