Applying Lambda functions to Pandas Dataframe (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 09 Aug, 2024
In Python Pandas, we have the freedom to add different functions whenever needed like lambda function, sort function, etc. We can apply a lambda function to both the columns and rows of the Pandas data frame.
**Syntax: lambda arguments: expression
An anonymous function which we can pass in instantly without defining a name or any thing like a full traditional function.
Applying Lambda Functions to Pandas
Below are some methods and ways by which we can apply lambda functions to Pandas:
- Dataframe.assign() on a Single Column
- Dataframe.assign() on Multiple Columns
- Dataframe.apply() on a Single Row
- Dataframe.apply() on Multiple Rows
- Lambda Function on Multiple Rows and Columns Simultaneously
Dataframe.assign() on a Single Column
In this example, we will apply the lambda function Dataframe.assign() to a single column. The function is applied to the 'Total_Marks' column, and a new column 'Percentage' is formed with its help.
Python `
importing pandas library
import pandas as pd
creating and initializing a list
values= [['Rohan',455],['Elvish',250],['Deepak',495], ['Soni',400],['Radhika',350],['Vansh',450]]
creating a pandas dataframe
df = pd.DataFrame(values,columns=['Name','Total_Marks'])
Applying lambda function to find
percentage of 'Total_Marks' column
using df.assign()
df = df.assign(Percentage = lambda x: (x['Total_Marks'] /500 * 100))
displaying the data frame
df
`
**Output:
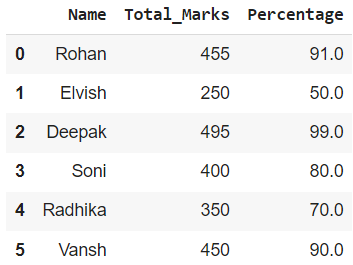
Dataframe.assign() on a Single Column
**Dataframe.assign() on Multiple Columns
In this example, we will apply the lambda function Dataframe.assign() to multiple columns. The lambda function is applied to 3 columns i.e., 'Field_1', 'Field_2', and 'Field_3'.
Python `
importing pandas library
import pandas as pd
creating and initializing a nested list
values_list = [[15, 2.5, 100], [20, 4.5, 50], [25, 5.2, 80], [45, 5.8, 48], [40, 6.3, 70], [41, 6.4, 90], [51, 2.3, 111]]
creating a pandas dataframe
df = pd.DataFrame(values_list, columns=['Field_1', 'Field_2', 'Field_3'])
Applying lambda function to find
the product of 3 columns using
df.assign()
df = df.assign(Product=lambda x: (x['Field_1'] * x['Field_2'] * x['Field_3']))
printing dataframe
df
`
**Output:
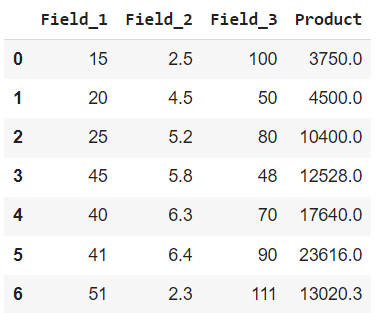
Dataframe.assign() on Multiple Columns
**Dataframe.apply() on a Single Row
In this example, we will apply the lambda function Dataframe.apply() to single row. The lambda function is applied to a row starting with 'd' and hence square all values corresponding to it.
Python `
importing pandas and numpy libraries
import pandas as pd import numpy as np
creating and initializing a nested list
values_list = [[15, 2.5, 100], [20, 4.5, 50], [25, 5.2, 80], [45, 5.8, 48], [40, 6.3, 70], [41, 6.4, 90], [51, 2.3, 111]]
creating a pandas dataframe
df = pd.DataFrame(values_list, columns=['Field_1', 'Field_2', 'Field_3'], index=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g'])
Apply function numpy.square() to square
the values of one row only i.e. row
with index name 'd'
df = df.apply(lambda x: np.square(x) if x.name == 'd' else x, axis=1)
printing dataframe
df
`
**Output:
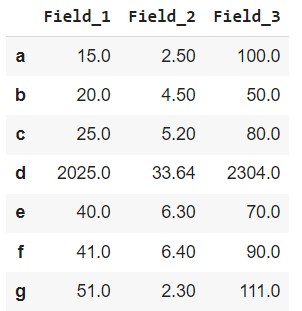
Dataframe.apply() on a Single Row
**Dataframe.apply() on Multiple Rows
In this example, we will apply the lambda function to multiple rows using Dataframe.apply(). The lambda function is applied to 3 rows starting with 'a', 'e', and 'g'.
Python `
importing pandas and numpylibraries
import pandas as pd import numpy as np
creating and initializing a nested list
values_list = [[15, 2.5, 100], [20, 4.5, 50], [25, 5.2, 80], [45, 5.8, 48], [40, 6.3, 70], [41, 6.4, 90], [51, 2.3, 111]]
creating a pandas dataframe
df = pd.DataFrame(values_list, columns=['Field_1', 'Field_2', 'Field_3'], index=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g'])
Apply function numpy.square() to square
the values of 3 rows only i.e. with row
index name 'a', 'e' and 'g' only
df = df.apply(lambda x: np.square(x) if x.name in [ 'a', 'e', 'g'] else x, axis=1)
printing dataframe
df
`
**Output:
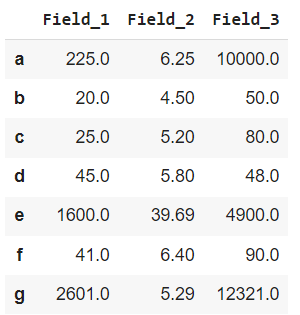
Dataframe.apply() on Multiple Rows
Lambda Function on Multiple Rows and Columns Simultaneously
In this example, we will apply the lambda function simultaneously to multiple columns and rows using dataframe.assign() and dataframe.apply().
Python `
importing pandas and numpylibraries
import pandas as pd import numpy as np
creating and initializing a nested list
values_list = [[1.5, 2.5, 10.0], [2.0, 4.5, 5.0], [2.5, 5.2, 8.0], [4.5, 5.8, 4.8], [4.0, 6.3, 70], [4.1, 6.4, 9.0], [5.1, 2.3, 11.1]]
creating a pandas dataframe
df = pd.DataFrame(values_list, columns=['Field_1', 'Field_2', 'Field_3'], index=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g'])
Apply function numpy.square() to square
the values of 2 rows only i.e. with row
index name 'b' and 'f' only
df = df.apply(lambda x: np.square(x) if x.name in ['b', 'f'] else x, axis=1)
Applying lambda function to find product of 3 columns
i.e 'Field_1', 'Field_2' and 'Field_3'
df = df.assign(Product=lambda x: (x['Field_1'] * x['Field_2'] * x['Field_3']))
printing dataframe
df
`
**Output
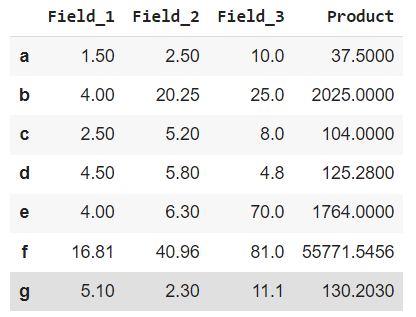
Lambda Function on Multiple Rows and Columns Simultaneously