Array of Linked Lists in C/C++ (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 21 Apr, 2025
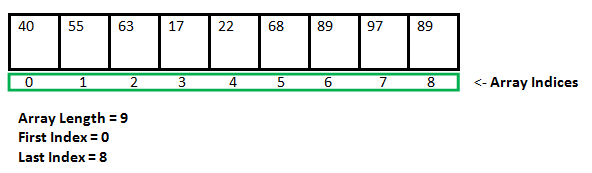
An array in C/C++ or be it in any programming language is a collection of similar data items stored at contiguous memory locations and elements that can be accessed randomly using indices of an array. They can be used to store the collection of primitive data types such as int, float, double, char, etc of any particular type. To add to it, an array in C/C++ can store derived data types such as structures, pointers, etc. Given below is the picture representation of an array.
an array is a container that can hold a fixed number of elements and these elements should be of the same type. Most of the data structures make use of arrays to implement their algorithms.
A linked list is a linear data structure consisting of nodes where each node contains a reference to the next node. To create a link list we need a pointer that points to the first node of the list.
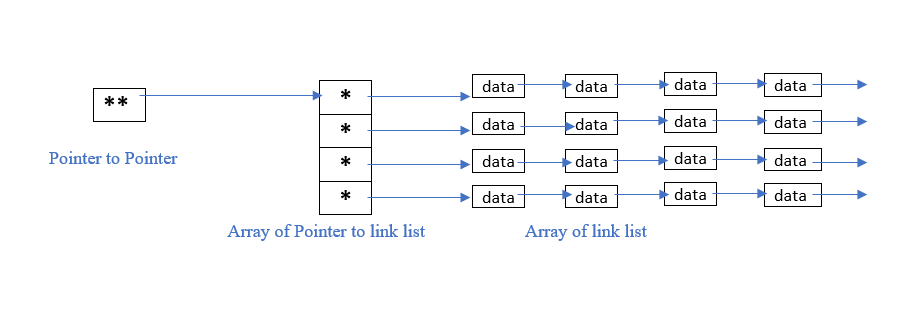
Approach: To create an array of linked lists below are the main requirements:
- An array of pointers.
- For keeping the track of the above-created array of pointers then another pointer is needed that points to the first pointer of the array. This pointer is called pointer to pointer.
Below is the pictorial representation of the array of linked lists:
Below is the C++ program to implement the array of linked lists:
C++ `
// C++ program to illustrate the array // of Linked Lists #include using namespace std;
// Structure of Linked Lists struct info { int data; info* next; };
// Driver Code int main() { int size = 10;
// Pointer To Pointer Array
info** head;
// Array of pointers to info struct
// of size
head = new info*[size];
// Initialize pointer array to NULL
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
*(head + i) = NULL;
}
// Traverse the pointer array
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
// To track last node of the list
info* prev = NULL;
// Randomly taking 4 nodes in each
// linked list
int s = 4;
while (s--) {
// Create a new node
info* n = new info;
// Input the random data
n->data = i * s;
n->next = NULL;
// If the node is first
if (*(head + i) == NULL) {
*(head + i) = n;
}
else {
prev->next = n;
}
prev = n;
}
}
// Print the array of linked list
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
info* temp = *(head + i);
// Linked list number
cout << i << "-->\t";
// Print the Linked List
while (temp != NULL) {
cout << temp->data << " ";
temp = temp->next;
}
cout << '\n';
}
return 0;}
`
Output:
0--> 0 0 0 0 1--> 3 2 1 0 2--> 6 4 2 0 3--> 9 6 3 0 4--> 12 8 4 0 5--> 15 10 5 0 6--> 18 12 6 0 7--> 21 14 7 0 8--> 24 16 8 0 9--> 27 18 9 0
Time Complexity: O(size*4)
Here size is the number of rows of lists
Auxiliary Space: O(size*4)
The extra space is used to store the elements of the lists.