Basic Operations for Queue in Data Structure (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 28 Mar, 2025
**Queue is a linear data structure that follows FIFO (First In First Out) Principle, so the first element inserted is the first to be popped out.
**Basic Operations on Queue
Some of the basic operations for Queue in Data Structure are:
- **enqueue() - Insertion of elements to the queue.
- **dequeue() - Removal of elements from the queue.
- **getFront()- Acquires the data element available at the front node of the queue without deleting it.
- **getRear() - This operation returns the element at the rear end without removing it.
- **isFull() - Validates if the queue is full.
- **isEmpty() - Checks if the queue is empty.
- **size() - This operation returns the size of the queue i.e. the total number of elements it contains.

Queue Data Structure
**Operation 1: enqueue()
Inserts an element at the end of the queue i.e. at the rear end.
The following steps should be taken to enqueue (insert) data into a queue:
- Check if the queue is full.
- If the queue is full, return overflow error and exit.
- If the queue is not full, increment the rear pointer to point to the next empty space.
- Add the data element to the queue location, where the rear is pointing.
- return success.
**Operation 2: dequeue()
This operation removes and returns an element that is at the front end of the queue.
The following steps are taken to perform the dequeue operation:
- Check if the queue is empty.
- If the queue is empty, return the underflow error and exit.
- If the queue is not empty, access the data where the front is pointing.
- Increment the front pointer to point to the next available data element.
- The Return success.
**Operation 3: getFront()
This operation returns the element at the front end of the queue without removing it.
The following steps are taken to perform the getFront() operation:
- If the queue is empty, return the most minimum value (e.g.,
-1). - Otherwise, return the front value of the queue.

getFront
Operation 4: getRear()
This operation returns the element at the rear end without removing it.
The following steps are taken to perform the rear operation:
- If the queue is empty return the most minimum value.
- otherwise, return the rear value.

getRear
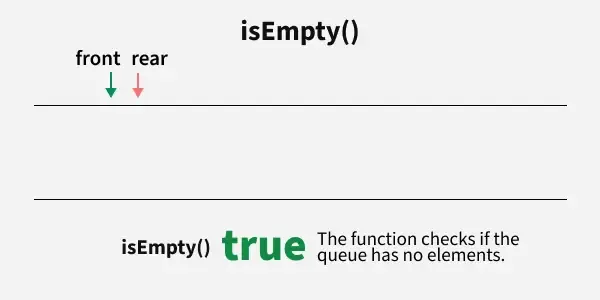
**Operation 5: isEmpty()
This operation returns a boolean value that indicates whether the queue is empty or not.
The following steps are taken to perform the Empty operation:
- check if front value is equal to -1 or not, if yes then return true means queue is empty.
- Otherwise return false, means queue is not empty.
isEmpty
Operation 6: size()
This operation returns the size of the queue i.e. the total number of elements it contains.

size()
Code Implementation of all the operations:
C++ `
#include #include using namespace std;
queue q;
bool isEmpty() { return q.empty(); }
void qEnqueue(int data) { q.push(data); }
void qDequeue() { if (isEmpty()) { return; } q.pop(); }
int getFront() { if (isEmpty()) return -1; return q.front(); }
int getRear() { if (isEmpty()) return -1; return q.back(); }
int main() { qEnqueue(1); qEnqueue(8); qEnqueue(3); qEnqueue(6); qEnqueue(2);
if (!isEmpty()) {
cout << "Queue after enqueue operation: ";
queue<int> tempQueue = q;
while (!tempQueue.empty()) {
cout << tempQueue.front() << " ";
tempQueue.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << "Front: " << getFront() << endl;
cout << "Rear: " << getRear() << endl;
cout << "Queue size: " << q.size() << endl;
qDequeue();
cout << "Is queue empty? " << (isEmpty() ? "Yes" : "No") << endl;
return 0;}
Java
import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue;
public class GfG { static Queue q = new LinkedList<>();
static boolean isEmpty() {
return q.isEmpty();
}
static void qEnqueue(int data) {
q.add(data);
}
static void qDequeue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return;
}
q.poll();
}
static int getFront() {
if (isEmpty()) return -1;
return q.peek();
}
static int getRear() {
if (isEmpty()) return -1;
return ((LinkedList<Integer>) q).getLast();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
qEnqueue(1);
qEnqueue(8);
qEnqueue(3);
qEnqueue(6);
qEnqueue(2);
if (!isEmpty()) {
System.out.print("Queue after enqueue operation: ");
for (int num : q) {
System.out.print(num + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("Front: " + getFront());
System.out.println("Rear: " + getRear());
System.out.println("Queue size: " + q.size());
qDequeue();
System.out.println("Is queue empty? " + (isEmpty() ? "Yes" : "No"));
}}
Python
Importing necessary modules
from collections import deque
q = deque()
def isEmpty(): return len(q) == 0
def qEnqueue(data): q.append(data)
def qDequeue(): if isEmpty(): return q.popleft()
def getFront(): if isEmpty(): return -1 return q[0]
def getRear(): if isEmpty(): return -1 return q[-1]
if name == 'main': qEnqueue(1) qEnqueue(8) qEnqueue(3) qEnqueue(6) qEnqueue(2)
if not isEmpty():
print("Queue after enqueue operation: ", list(q))
print("Front: ", getFront())
print("Rear: ", getRear())
print("Queue size: ", len(q))
qDequeue()
print("Is queue empty? ", "Yes" if isEmpty() else "No")C#
// Importing necessary namespaces using System; using System.Collections.Generic;
class GfG { static Queue q = new Queue();
static bool IsEmpty() {
return q.Count == 0;
}
static void QEnqueue(int data) {
q.Enqueue(data);
}
static void QDequeue() {
if (IsEmpty()) {
return;
}
q.Dequeue();
}
static int GetFront() {
if (IsEmpty()) return -1;
return q.Peek();
}
static int GetRear() {
if (IsEmpty()) return -1;
return q.ToArray()[q.Count - 1];
}
static void Main() {
QEnqueue(1);
QEnqueue(8);
QEnqueue(3);
QEnqueue(6);
QEnqueue(2);
if (!IsEmpty()) {
Console.WriteLine("Queue after enqueue operation: " + string.Join(" ", q));
}
Console.WriteLine("Front: " + GetFront());
Console.WriteLine("Rear: " + GetRear());
Console.WriteLine("Queue size: " + q.Count);
QDequeue();
Console.WriteLine("Is queue empty? " + (IsEmpty() ? "Yes" : "No"));
}}
JavaScript
// Using a class to implement a queue class Queue { constructor() { this.items = []; }
isEmpty() {
return this.items.length === 0;
}
enqueue(data) {
this.items.push(data);
}
dequeue() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
this.items.shift();
}
getFront() {
if (this.isEmpty()) return -1;
return this.items[0];
}
getRear() {
if (this.isEmpty()) return -1;
return this.items[this.items.length - 1];
}
size() {
return this.items.length;
}}
const q = new Queue();
q.enqueue(1); q.enqueue(8); q.enqueue(3); q.enqueue(6); q.enqueue(2);
if (!q.isEmpty()) { console.log('Queue after enqueue operation: ', q.items); }
console.log('Front: ', q.getFront()); console.log('Rear: ', q.getRear()); console.log('Queue size: ', q.size());
q.dequeue();
console.log('Is queue empty? ', q.isEmpty() ? 'Yes' : 'No');
`
Output
Queue after enqueue operation: 1 8 3 6 2 Front: 1 Rear: 2 Queue size: 5 Is queue empty? No