Basic Operations in Stack Data Structure with Implementations (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 03 Nov, 2024
In order to make manipulations in a stack, there are certain operations provided to us for Stack, which include:
- **push() to insert an element into the stack
- **pop() to remove an element from the stack
- **top() Returns the top element of the stack.
- **isEmpty() returns true if the stack is empty else false.
- **size() returns the size of the stack.
In this post, we will see how to perform these operations on Stack.
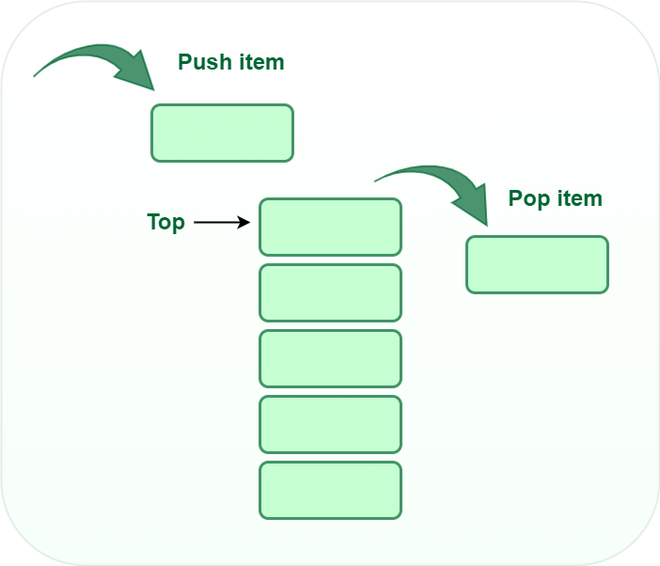
**Push Operation in Stack:
Push operation **adds an item to the stack.
If the stack is full, then it is said to be an Overflow condition.
Below is a sample program to show Push operation in Stack.
C++ `
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;
int main() {
stack<int> s; // creating a stack of integers
s.push(1); // This pushes 1 to the stack top
s.push(2); // This pushes 2 to the stack top
s.push(3); // This pushes 3 to the stack top
s.push(4); // This pushes 4 to the stack top
s.push(5); // This pushes 5 to the stack top
// printing the stack
while (!s.empty()) {
cout << s.top() << " ";
s.pop();
}
// The above loop prints "5 4 3 2 1" }
Java
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
public class StackExample { public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayDeque s = new ArrayDeque<>();
s.push(1); // Pushing 1 to the top
s.push(2); // Pushing 2 to the top
s.push(3); // Pushing 3 to the top
s.push(4); // Pushing 4 to the top
s.push(5); // Pushing 5 to the top
// Printing in reverse order
while (!s.isEmpty()) {
System.out.print(s.pop() + " ");
}
// The output will be "5 4 3 2 1"
}}
Python
Python Code:
stack = []
stack.append(1) # This pushes 1 to the stack top
stack.append(2) # This pushes 2 to the stack top
stack.append(3) # This pushes 3 to the stack top
stack.append(4) # This pushes 4 to the stack top
stack.append(5) # This pushes 5 to the stack top
printing the stack
while stack: print(stack[-1], end=" ") stack.pop()
The above loop prints "5 4 3 2 1"
This code is contributed by Sakshi
C#
using System; using System.Collections.Generic;
class Program { static void Main() { Stack s = new Stack(); // Creating a stack // of integers
s.Push(1); // Pushing 1 to the stack top
s.Push(2); // Pushing 2 to the stack top
s.Push(3); // Pushing 3 to the stack top
s.Push(4); // Pushing 4 to the stack top
s.Push(5); // Pushing 5 to the stack top
// Printing the stack
while (s.Count > 0) {
Console.Write(
s.Peek()
+ " "); // Peek() gets the top element
// without removing it
s.Pop(); // Pop() removes the top element
}
// The above loop prints "5 4 3 2 1"
}}
JavaScript
class Stack { constructor() { this.stack = []; }
push(value) {
this.stack.push(value); // Pushes the value to the stack top
}
top() {
return this.stack[this.stack.length - 1]; // Returns the element at the top of the stack
}
pop() {
return this.stack.pop(); // Removes and returns the top element of the stack
}
isEmpty() {
return this.stack.length === 0; // Checks if the stack is empty
}}
function main() { const s = new Stack(); // Creating a stack
s.push(1); // Pushing 1 to the stack top
s.push(2); // Pushing 2 to the stack top
s.push(3); // Pushing 3 to the stack top
s.push(4); // Pushing 4 to the stack top
s.push(5); // Pushing 5 to the stack top
// Printing the stack
while (!s.isEmpty()) {
console.log(s.top() + " "); // Outputting the top element
s.pop(); // Removing the top element
}
// The above loop prints "5 4 3 2 1"}
main(); // Calling the main function
`
**Pop Operation in Stack:
Pop operation is used to **remove an item from the stack.
The items are popped in the reversed order in which they are pushed. If the stack is empty, then it is said to be an **Underflow **condition.
Below is a sample program to show Pop operation in Stack.
C++ `
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;
int main() { stack s; // creating a stack of integers
s.push(1); // This pushes 1 to the stack top
s.push(2); // This pushes 2 to the stack top
s.push(3); // This pushes 3 to the stack top
s.push(4); // This pushes 4 to the stack top
s.push(5); // This pushes 5 to the stack top
// Now, let us remove elements from the stack using pop function
while (!s.empty()) {
cout << s.top() << " ";
s.pop(); // removes the top element from the stack
}}
Java
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayDeque s = new ArrayDeque<>(); /
s.push(1); // Pushing 1 to the stack top
s.push(2);
s.push(3);
s.push(4);
s.push(5);
// Removing elements from the stack using pop function
while (!s.isEmpty()) {
System.out.print(s.peek() + " "); /
s.pop();
}
}}
Python
stack = []
stack.append(1) # This pushes 1 to the stack top stack.append(2) # This pushes 2 to the stack top stack.append(3) # This pushes 3 to the stack top stack.append(4) # This pushes 4 to the stack top stack.append(5) # This pushes 5 to the stack top
Now, let us remove elements from the stack using pop function
while stack: print(stack[-1], end=" ") stack.pop() # removes the top element from the stack
C#
using System; using System.Collections.Generic;
class Program { static void Main() { // Creating a stack of integers Stack s = new Stack();
// Pushing elements onto the stack
s.Push(1); // This pushes 1 to the stack top
s.Push(2); // This pushes 2 to the stack top
s.Push(3); // This pushes 3 to the stack top
s.Push(4); // This pushes 4 to the stack top
s.Push(5); // This pushes 5 to the stack top
// Removing elements from the stack using Pop function
while (s.Count > 0) {
Console.Write(s.Peek() + " "); // Displaying the top element without removing it
s.Pop(); // Removes the top element from the stack
}
}}
JavaScript
// Creating a stack let stack = [];
// Pushing elements to the stack stack.push(1); // This pushes 1 to the stack top stack.push(2); // This pushes 2 to the stack top stack.push(3); // This pushes 3 to the stack top stack.push(4); // This pushes 4 to the stack top stack.push(5); // This pushes 5 to the stack top
// Removing elements from the stack using pop function while (stack.length > 0) { console.log(stack[stack.length - 1]); // Print the top element stack.pop(); // Removes the top element from the stack }
`
**Top Operation in Stack:
Top operation is used to **return the top element of the stack.
Below is a sample program to show Pop operation in Stack.
C++ `
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;
int topElement(stack& s) { return s.top(); }
int main() {
stack<int> s; // creating a stack of integers
s.push(1); // This pushes 1 to the stack top
cout << topElement(s)
<< endl; // Prints 1 since 1 is present at the
// stack top
s.push(2); // This pushes 2 to the stack top
cout << topElement(s)
<< endl; // Prints 2 since 2 is present at the
// stack top
s.push(3); // This pushes 3 to the stack top
cout << topElement(s)
<< endl; // Prints 3 since 3 is present at the
// stack top }
Java
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
public class StackExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayDeque<Integer> s = new ArrayDeque<>();
// Pushing 1 to the stack top
s.push(1);
System.out.println(s.peek()); // Prints 1
// Pushing 2 to the stack top
s.push(2);
System.out.println(s.peek()); // Prints 2
// Pushing 3 to the stack top
s.push(3);
System.out.println(s.peek()); // Prints 3
}}
Python
Python code:
def topElement(s): return s[-1]
s = [] # creating a stack of integers
s.append(1) # This pushes 1 to the stack top print(topElement(s)) # Prints 1 since 1 is present at the stack top
s.append(2) # This pushes 2 to the stack top print(topElement(s)) # Prints 2 since 2 is present at the stack top
s.append(3) # This pushes 3 to the stack top print(topElement(s)) # Prints 3 since 3 is present at the stack top
This code is contributed by Sakshi
C#
using System; using System.Collections.Generic;
class Program { static int TopElement(Stack s) { return s.Peek(); }
static void Main()
{
Stack<int> s = new Stack<int>(); // creating a stack of integers
s.Push(1); // This pushes 1 to the stack top
Console.WriteLine(TopElement(s)); // Prints 1 since 1 is present at the stack top
s.Push(2); // This pushes 2 to the stack top
Console.WriteLine(TopElement(s)); // Prints 2 since 2 is present at the stack top
s.Push(3); // This pushes 3 to the stack top
Console.WriteLine(TopElement(s)); // Prints 3 since 3 is present at the stack top
}}
JavaScript
function topElement(s) { return s[s.length - 1]; }
// Main function function main() { let s = []; // Creating an array to act as a stack
s.push(1); // Pushing 1 to the stack
console.log(topElement(s)); // Prints 1 since 1 is at the top of the stack
s.push(2); // Pushing 2 to the stack
console.log(topElement(s)); // Prints 2 since 2 is at the top of the stack
s.push(3); // Pushing 3 to the stack
console.log(topElement(s)); // Prints 3 since 3 is at the top of the stack}
// Calling the main function main(); //THis code is contributed by Utkarsh
`
**isEmpty Operation in Stack:
isEmpty operation is a boolean operation that is used to **determine if the stack is empty or not.
This operation will return true if the stack is empty, else false.
Below is a sample program to show Pop operation in Stack.
C++ `
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;
bool isEmpty(stack& s) {
bool isStackEmpty
= s.empty(); // checking whether stack is empty or
// not and storing it into isStackEmpty
// variable
return isStackEmpty; // returning bool value stored in
// isStackEmpty }
int main() {
stack<int> s;
// The if - else conditional statements below prints
// "Stack is empty."
if (isEmpty(s)) {
cout << "Stack is empty." << endl;
}
else {
cout << "Stack is not empty." << endl;
}
s.push(1); // Inserting value 1 to the stack top
// The if - else conditional statements below prints
// "Stack is not empty."
if (isEmpty(s)) {
cout << "Stack is empty." << endl;
}
else {
cout << "Stack is not empty." << endl;
} }
Java
import java.util.Stack;
public class Main { public static boolean isEmpty(Stack s) { return s.empty(); }
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<Integer> s = new Stack<>();
if (isEmpty(s)) {
System.out.println("Stack is empty.");
} else {
System.out.println("Stack is not empty.");
}
s.push(1);
if (isEmpty(s)) {
System.out.println("Stack is empty.");
} else {
System.out.println("Stack is not empty.");
}
}}
Python
Python Code:
def isEmpty(s): isStackEmpty = len(s) == 0 # checking whether stack is empty or # not and storing it into isStackEmpty variable return isStackEmpty # returning bool value stored in isStackEmpty
s = []
The if - else conditional statements below prints "Stack is empty."
if isEmpty(s): print("Stack is empty.") else: print("Stack is not empty.")
s.append(1) # Inserting value 1 to the stack top
The if - else conditional statements below prints "Stack is not empty."
if isEmpty(s): print("Stack is empty.") else: print("Stack is not empty.")
This code is contributed by Sakshi
C#
using System; using System.Collections.Generic;
class Program { // Function to check if a stack is empty static bool IsEmpty(Stack s) { return s.Count == 0; }
static void Main()
{
Stack<int> s = new Stack<int>();
// Check if the stack is empty
if (IsEmpty(s))
{
Console.WriteLine("Stack is empty.");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Stack is not empty.");
}
// Push a value (1) onto the stack
s.Push(1);
// Check if the stack is empty after pushing a value
if (IsEmpty(s))
{
Console.WriteLine("Stack is empty.");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Stack is not empty.");
}
}}
JavaScript
function isEmpty(stack) { // checking whether stack is empty or not return stack.length === 0; }
function main() { const s = [];
// The if - else conditional statements below prints "Stack is empty."
if (isEmpty(s)) {
console.log("Stack is empty.");
} else {
console.log("Stack is not empty.");
}
s.push(1); // Inserting value 1 to the stack top
// The if - else conditional statements below prints "Stack is not empty."
if (isEmpty(s)) {
console.log("Stack is empty.");
} else {
console.log("Stack is not empty.");
}}
// Run the main function main(); //This code is contributed by Monu.
`
Output
Stack is empty. Stack is not empty.
**size() Operation in Stack:
Size operation in Stack is used to return the **count of elements that are present inside the stack.
Below is a sample program to show Pop operation in Stack.
C++ `
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;
int main() {
stack<int> s; // creating a stack of integers
cout << s.size()
<< endl; // Prints 0 since the stack is empty
s.push(1); // This pushes 1 to the stack top
s.push(2); // This pushes 2 to the stack top
cout << s.size() << endl; // Prints 2 since the stack
// contains two elements
s.push(3); // This pushes 3 to the stack top
cout << s.size() << endl; // Prints 3 since the stack
// contains three elements }
Java
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayDeque s = new ArrayDeque<>();
System.out.println(s.size()); // Prints 0 since the stack is empty
s.push(1); // Pushing 1 to the stack top
s.push(2); // Pushing 2 to the stack top
System.out.println(s.size()); // Prints 2 since the stack contains two elements
s.push(3); // Pushing 3 to the stack top
System.out.println(s.size()); // Prints 3 since the stack contains three elements
}}
Python
PYthon Code:
stack = [] # creating an empty list as a stack
print(len(stack)) # Prints 0 since the stack is empty
stack.append(1) # This appends 1 to the stack stack.append(2) # This appends 2 to the stack print(len(stack)) # Prints 2 since the stack contains two elements
stack.append(3) # This appends 3 to the stack print(len(stack)) # Prints 3 since the stack contains three element
This code is contributed by Sakshi
C#
using System; using System.Collections.Generic;
public class Program { public static void Main(string[] args) { Stack s = new Stack(); // creating a stack of integers
Console.WriteLine(s.Count); // Prints 0 since the stack is empty
s.Push(1); // This pushes 1 to the stack top
s.Push(2); // This pushes 2 to the stack top
Console.WriteLine(s.Count); // Prints 2 since the stack contains two elements
s.Push(3); // This pushes 3 to the stack top
Console.WriteLine(s.Count); // Prints 3 since the stack contains three elements
}} //This code is contribiuted by Kishan.
JavaScript
let stack = []; // Creating an array to simulate a stack
console.log(stack.length); // Prints 0 since the stack is empty
stack.push(1); // This pushes 1 to the stack top stack.push(2); // This pushes 2 to the stack top console.log(stack.length); // Prints 2 since the stack contains two elements
stack.push(3); // This pushes 3 to the stack top console.log(stack.length); // Prints 3 since the stack contains three elements //This code is contributed by Aman.
`