Binary Tree in C (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 06 Jun, 2024
A **binary tree is a non-linear hierarchical data structure in which each node has at most two children known as the left child and the right child. It can be visualized as a hierarchical structure where the topmost node is called the root node and the nodes at the bottom are called leaf nodes or leaves.
In this article, we will learn the basics of binary trees, types of binary trees, basic operations that can be performed on binary trees as well as applications, advantages, and disadvantages of binary trees in C.
Representation of Binary Tree
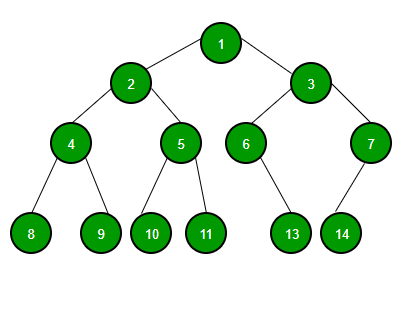
Binary Tree Representation
Each node of a binary tree has the following 3 parts:
- Data
- Pointer to left child node
- Pointer to right child node
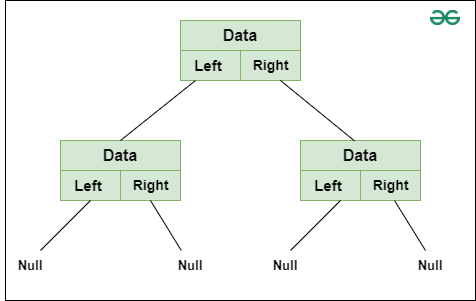
Binary Tree- Node Representation
To create a binary tree, we have to first create a node having a data, pointer to left child and pointer to right child using the below structure format:
struct node
{
int data;
struct node *left;
struct node *right;
};
To learn more about binary tree refer: Introduction to Binary Tree – Data Structure and Algorithm Tutorials
**Basic Operations on Binary Tree in C
The following are the basics operations that can performed on a binary tree:
- Insertion
- Deletion
- Search
- Traversing (Pre-order, Post-order and In-order)
Here, we will learn about three basic operations that can be performed on a binary: insertion, deletion, and searching.
| Operation | Description | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Insertion | This function is used to insert values in a binary tree. | O(N) | O(N) |
| Deletion | This function is used to delete the specified node from a binary tree | O(N) | O(N) |
| Search | This function is used to search a given key in a binary tree | O(N) | O(N) |
**1. Insertion in Binary Tree
In a binary tree a new node can be inserted anywhere as a right child or left child of a node. To insert a node in a binary tree, follow the below approach:
**Approach:
- Start iterating using level order traversal in a binary tree.
- If a node whose left child is missing is found then insert the given new node as the left child of that node.
- Else if a node whose right child is missing is found then insert the given node as the right child of that node.
- Else a node whose both right child and left child are missing is found then insert the new node as the left or right child (any position) of that node.
2. Deletion in Binary Tree
In a binary tree we can delete a node from anywhere and then again rearrange it to maintain the property of binary tree and the leaf nodes can be deleted without performing any replacement and shifting of nodes. To delete a node from a binary tree, follow the below approach:
**Approach:
- Start traversing from the root node of the tree.
- Find the node that you want to delete and the node at the deepest right.
- Replace the target node (node to be deleted ) with the deepest rightmost node.
- Finally, delete the deepest rightmost node (as it contains the node to be deleted now).
3. Searching in Binary Tree
In a binary tree we can search a node by traversing and comparing each node with target node (node to be searched). To search for a given node in a binary tree follow the below approach:
**Approach:
- Start traversing from the root node of the tree.
- Compare the target node (node to be searched) with each node's value.
- If the current node's value is equal to target node, then target node is found.
- else if, the current node's value is not equal to target node, again start searching the left and right child by traversing.
- else, you reach the end of the tree and do no find any node's value equal to target value, then the target node is not present in the tree.
C Program to Implement Binary Tree
The below program demonstrates all the basic operations on a binary search tree: creation, searching, traversal, insertion and deletion in C.
C `
// C program to to implement binary tree
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h>
// Define a structure for tree nodes typedef struct Node { int data; struct Node* left; struct Node* right; } Node;
// Function to create a new node Node* createNode(int data) { Node* newNode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node)); newNode->data = data; newNode->left = NULL; newNode->right = NULL; return newNode; }
// Function for inserting a node in a binary tree void insert(Node** root, int data) { Node* newNode = createNode(data); if (*root == NULL) { *root = newNode; return; }
// Level order traversal to find the appropriate place
// for insertion
Node* temp;
Node* queue[100];
int front = -1, rear = -1;
queue[++rear] = *root;
while (front != rear) {
temp = queue[++front];
// Insert new node as the left child
if (temp->left == NULL) {
temp->left = newNode;
return;
}
// if left child is not missing push it to the queue
else {
queue[++rear] = temp->left;
}
// Insert new node as the right child
if (temp->right == NULL) {
temp->right = newNode;
return;
}
// if right child is not missing push it to the
// queue
else {
queue[++rear] = temp->right;
}
}}
// Function to perform level order traversal to find the // deepest rightmost node Node* getDeepestRightmostNode(Node* root) { Node* temp; Node* queue[100]; int front = -1, rear = -1; queue[++rear] = root;
while (front != rear) {
temp = queue[++front];
if (temp->left != NULL) {
queue[++rear] = temp->left;
}
if (temp->right != NULL) {
queue[++rear] = temp->right;
}
}
return temp;}
// Function for deleting deepest rightmost node in a binary // tree void deleteDeepestRightmostNode(Node* root, Node* dNode) { Node* temp; Node* queue[100]; int front = -1, rear = -1; queue[++rear] = root;
while (front != rear) {
temp = queue[++front];
if (temp == dNode) {
temp = NULL;
free(dNode);
return;
}
if (temp->right != NULL) {
if (temp->right == dNode) {
temp->right = NULL;
free(dNode);
return;
}
else {
queue[++rear] = temp->right;
}
}
if (temp->left != NULL) {
if (temp->left == dNode) {
temp->left = NULL;
free(dNode);
return;
}
else {
queue[++rear] = temp->left;
}
}
}}
// Function to delete a node in the binary tree void delete (Node** root, int data) { if (*root == NULL) { printf("Tree is empty.\n"); return; }
if ((*root)->left == NULL && (*root)->right == NULL) {
if ((*root)->data == data) {
free(*root);
*root = NULL;
return;
}
else {
printf("Node not found.\n");
return;
}
}
Node* temp;
Node* queue[100];
int front = -1, rear = -1;
queue[++rear] = *root;
Node* keyNode = NULL;
while (front != rear) {
temp = queue[++front];
if (temp->data == data) {
keyNode = temp;
}
if (temp->left != NULL) {
queue[++rear] = temp->left;
}
if (temp->right != NULL) {
queue[++rear] = temp->right;
}
}
if (keyNode != NULL) {
Node* deepestNode = getDeepestRightmostNode(*root);
keyNode->data = deepestNode->data;
deleteDeepestRightmostNode(*root, deepestNode);
}
else {
printf("Node not found.\n");
}}
// Function to search for a node in the binary tree Node* search(Node* root, int data) { if (root == NULL) { return NULL; }
Node* temp;
Node* queue[100];
int front = -1, rear = -1;
queue[++rear] = root;
while (front != rear) {
temp = queue[++front];
if (temp->data == data) {
return temp;
}
if (temp->left != NULL) {
queue[++rear] = temp->left;
}
if (temp->right != NULL) {
queue[++rear] = temp->right;
}
}
return NULL;}
// function to perform inorder traversal in a binary tree void inorderTraversal(Node* root) { if (root == NULL) { return; }
inorderTraversal(root->left);
printf("%d ", root->data);
inorderTraversal(root->right);}
int main() { Node* root = NULL;
// Inserting nodes
insert(&root, 20);
insert(&root, 30);
insert(&root, 40);
insert(&root, 50);
insert(&root, 60);
insert(&root, 70);
insert(&root, 80);
// Inorder traversal
printf("Inorder traversal of the given Binary Search "
"Tree is: ");
inorderTraversal(root);
printf("\n");
// Deleting a node
int deleteValue = 20;
delete (&root, deleteValue);
printf("After deletion of %d: ", deleteValue);
inorderTraversal(root);
printf("\n");
// Inserting a new node
int insertValue = 25;
insert(&root, insertValue);
printf("After insertion of %d: ", insertValue);
inorderTraversal(root);
printf("\n");
// Searching for a node
int target = 25;
Node* searchResult = search(root, target);
if (searchResult != NULL) {
printf("Node %d found in the BST.\n", target);
}
else {
printf("Node %d not found in the BST.\n", target);
}
return 0;}
`
Output
Inorder traversal of the given Binary Search Tree is: 50 30 60 20 70 40 80 After deletion of 20: 50 30 60 80 70 40 After insertion of 25: 50 30 60 80 70 40 25 Node 25 found in the BST.
**Time Complexity: O(N), here N is the number of nodes in a binary tree.
**Auxilliary Space: O(N)
Types of Binary Trees in C
Binary trees can be of many types depending on the parameter we took for the classification of the trees. The following are the types of binary trees:
According to Number of Children
- **Full Binary Tree: A binary tree in which every node other than the leaves has two children.
- **Degenerate Binary Tree: A tree where each parent node has only one child.
- **Skewed Binary Trees: A binary tree in which all the nodes are skewed to the left or right.
According to Completion of Levels
- **Complete Binary Tree: A binary tree in which all levels are completely filled except possibly the last level, and the last level has all keys as left as possible.
- **Perfect Binary Tree: A binary tree in which all the internal nodes have two children and all leaves are at the same level.
- **Balanced Binary Tree: A binary tree in which the height of the left and right subtrees of any node differ by not more than one.
According to Node Values
- **Binary Search Tree (BST): A binary tree in which all the left descendants of a node are less than the node and all the right descendants are greater than the node.
- **AVL Tree: A self-balancing binary search tree where the difference in heights between left and right subtrees is at most one.
- **Red-Black Tree: A binary search tree with an extra bit of storage per node: its color, which can be either red or black. It ensures the tree remains balanced.
- **B Tree: A self-balancing search tree in which nodes can have multiple children and is optimized for systems that read and write large blocks of data.
- **B+ Tree: An extension of the B tree which maintains the data in a sorted order and allows sequential access.
- **Segment Tree: A binary tree used for storing the intervals or segments. It allows querying which of the stored segments contain a given point.
- **Fenwick Tree (Binary Indexed Tree): A data structure that provides efficient methods for calculation and manipulation of the prefix sums of a table of values.
Applications of Binary Trees
Binary tree are the versatile data structure widely used in the various applications due to the hierarchical nature and efficient performance in the certain operations. Following are some applications of the binary tree:
- **Full Binary Tree: It is used in the binary heap implementations and it is optimal merge patterns.
- **Complete Binary Tree: It is used in the binary heaps which are useful in the priority queues and it is used in the efficient storage management such as heap sort.
- **Perfect Binary Tree: It is used in the complete binary tree implementation for the efficiency and it is perfect for the implementing full binary trees in the array representations.
- **Balanced Binary Tree: It is used in the AVL and Red-Black trees for the efficient searching operation, insertion operation and deletion operation.
- **Binary Search Tree (BST): It is used in the database indexing and also it is used in the dictionary and phonebook applications. It is also efficient for the search operation, insert operation and delete operation when it was balanced.
- **AVL Tree: It is used in the situations where the search time needs to be minimized. It is database applications where the frequent insertions and deletions are expected.
- **Red-Black Tree: It is used in C++ STL map and multimap implementations.
- **Segment Tree: It is used in the computational geometry for the problems such as finding intersections, range, queries, etc.,
- **Fenwick Tree (Binary Indexed Tree): It is used in the scenarios requiring the dynamic cumulative frequency tables. It is efficient for the frequency queries and updates.