C# Inheritance (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 15 Jan, 2025
Inheritance is a fundamental concept in object-oriented programming that allows a child class to inherit the properties from the superclass. The new class inherits the properties and methods of the existing class and can also add new properties and methods of its own. Inheritance promotes code reuse, simplifies code maintenance, and improves code organization.
Syntax:
class derived-class : parent-class
{
// methods and fields
}
- **Derived Class: The class that inherits the other class is known as asubclass(or a derived class, extended class, or child class). The subclass can add its fields and methods in addition to the superclass properties.
- **Parent Class: The class whose features are inherited is known as a superclass (or a base class or a parent class).
**Example:
C# `
// Demonstration of Inheritance using System;
// Base class class GFG { // Data members public string name; public string subject;
public void readers(string name, string subject)
{
this.name = name;
this.subject = subject;
Console.WriteLine("Myself: " + name);
Console.WriteLine("My Favorite Subject is: " + subject);
}}
// Inheriting the GFG class class GeeksforGeeks : GFG { // Constructor of derived class public GeeksforGeeks() { Console.WriteLine("GeeksforGeeks"); } }
class Geeks { static void Main(string[] args) { // Child class object GeeksforGeeks g = new GeeksforGeeks();
// Calling the method of base class
// using the derived class object
g.readers("Geek", "C#");
}}
`
Output
GeeksforGeeks Myself: Geek My Favorite Subject is: C#
Types of Inheritance
In C#, there are mainly 4 types of inheritance which are described below:
- **Single Inheritance: A derived class that inherits from only one base class.
- **Multi-level Inheritance: A derived class that inherits from a base class and the derived class itself becomes the base class for another derived class.
- **Hierarchical Inheritance: A base class that serves as a parent class for two or more derived classes.
- **Multiple Inheritance: A derived class that inherits from two or more base classes (Using Interface).
- **Hybrid Inheritance: A Hybrid Inheritance is a mix of two or more inheritances.
1. Single Inheritance
In single inheritance, subclasses inherit the features of one superclass. In the image below, the class A serves as a base class for the derived class B.

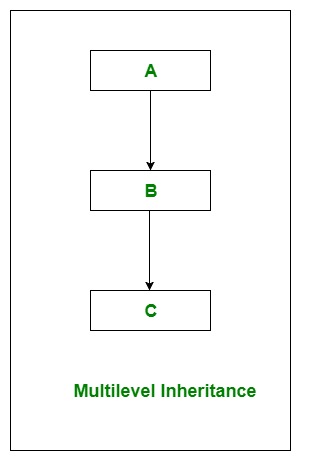
2. Multilevel Inheritance
In Multilevel Inheritance, a derived class will inherit a base class and as well as the derived class also act as the base class for another class. In the below image, class A serves as a base class for the derived class B, which serves as a base class for the derived class C.
3. Hierarchical Inheritance
In Hierarchical Inheritance, one class serves as a superclass (base class) for more than one subclass. In the below image, class A serves as a base class for the derived classes B, C, and D.
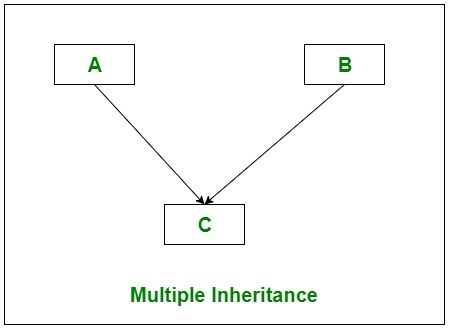
4. Multiple Inheritance
In Multiple inheritance, one class can have more than one superclass and inherit features from all parent classes. Please note that C# does not support multiple inheritance with classes. In C#, we can achieve multiple inheritance only through Interfaces. In the image below, Class C is derived from interfaces A and B.
**5. Hybrid Inheritance (Through Interfaces)
It is a mix of two or more of the above types of inheritance. Since C# doesn’t support multiple inheritance with classes, hybrid inheritance is also not possible with classes. In C#, we can achieve hybrid inheritance only through Interfaces.
**Example:
C# `
// Different types of Inheritance using System;
// Single Inheritance class Animal { public void Eat() { Console.WriteLine("Animal is eating."); } }
class Dog : Animal { public void Bark() { Console.WriteLine("Dog is barking."); } }
// Multi-level Inheritance class Mammal : Animal { public void Run() { Console.WriteLine("Mammal is running."); } }
class Horse : Mammal { public void Gallop() { Console.WriteLine("Horse is galloping."); } }
// Hierarchical Inheritance class Bird : Animal { public void Fly() { Console.WriteLine("Bird is flying."); } }
class Eagle : Bird { public void Hunt() { Console.WriteLine("Eagle is hunting."); } }
class Penguin : Bird { public void Swim() { Console.WriteLine("Penguin is swimming."); } }
// Multiple Inheritance interface I1 { void Method1(); }
interface I2 { void Method2(); }
class MyClass : I1, I2 { public void Method1() { Console.WriteLine("Method1 is called."); }
public void Method2()
{
Console.WriteLine("Method2 is called.");
}}
class Geeks { // Main Method static void Main(string[] args) { // single inheritance Dog dog = new Dog(); dog.Eat();
// multi-level inheritance
Horse horse = new Horse();
horse.Eat();
horse.Run();
// hierarchical inheritance
Eagle eagle = new Eagle();
Penguin penguin = new Penguin();
eagle.Fly();
eagle.Hunt();
penguin.Fly();
penguin.Swim();
// multiple inheritance
MyClass myClass = new MyClass();
myClass.Method1();
myClass.Method2();
Console.ReadLine();
}}
`
Output
Animal is eating. Animal is eating. Mammal is running. Bird is flying. Eagle is hunting. Bird is flying. Penguin is swimming. Method1 is called. Method2 is called.
Important Terms
- **Default Superclass: Except Object class, which has no superclass, every class has one and only one direct superclass(single inheritance). In the absence of any other explicit superclass, every class is implicitly a subclass of Object class.
- **Multiple Inheritance: A superclass can have any number of subclasses. But a subclass can have only one superclass. This is because C# does not support multiple inheritance with classes. Although with interfaces, multiple inheritance is supported by C#.
- **Inheriting Constructors: A subclass inherits all the members (fields, methods) from its superclass. Constructors are not members, so they are not inherited by subclasses, but the constructor of the superclass can be invoked from the subclass.
- **Private member: A subclass does not inherit the private members of its parent class. However, if the superclass has properties(get and set methods) for accessing its private fields, then a subclass can inherit.
Advantages of Inheritance
- **Code Reusability: Inheritance allows us to reuse existing code by inheriting properties and methods from an existing class.
- **Code Maintenance: Inheritance makes code maintenance easier by allowing us to modify the base class and have the changes automatically reflected in the derived classes.
- **Code Organization: Inheritance improves code organization by grouping related classes together in a hierarchical structure.
Disadvantages of Inheritance
- **Tight Coupling: Inheritance creates a tight coupling between the base class and the derived class, which can make the code more difficult to maintain.
- **Complexity: Inheritance can increase the complexity of the code by introducing additional levels of abstraction.
- **Fragility: Inheritance can make the code more fragile by creating dependencies between the base class and the derived class.