Callbacks and Events in NodeJS (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 19 Feb, 2025
Callbacks and events are fundamental building blocks for asynchronous programming in NodeJS. They're essential for handling operations that might take some time, ensuring your application handles asynchronous operations smoothly.
**Callback in NodeJS
In NodeJS, Callbacks are functions passed as arguments to other functions and executed when the task completes. This is how NodeJS handles tasks that take time, like getting data from the internet, without making your program wait.
When an asynchronous function is executed, Node.js does not wait for it to complete. Instead, it moves on to the next task and invokes the callback function once the asynchronous operation finishes.
JavaScript `
function fetchData(callback) { setTimeout(() => { const data = 'Sample Data'; callback(null, data); }, 1000); }
fetchData((error, data) => { if (error) { console.error('Error:', error); } else { console.log('Data:', data); } });
`
**In this example
- fetchData simulates an asynchronous operation using setTimeout.
- It accepts a callback function to handle the result.
- After 1 second, it calls the callback with null (indicating no error) and the data.
- The callback checks for errors and logs the data if successful.
**Output:
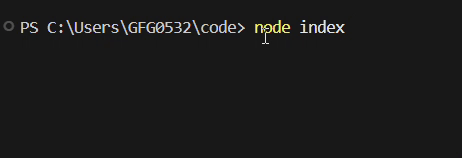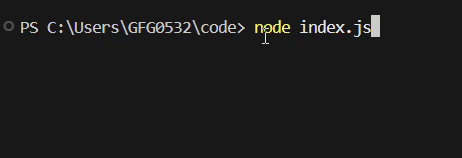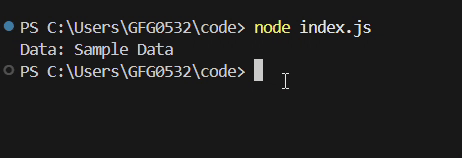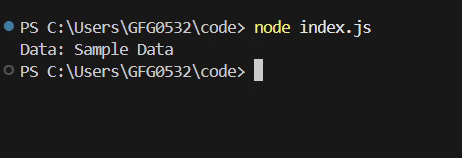
Callback in NodeJS
Types of Callbacks
- **Synchronous Callback: A callback that is executed immediately within the same function execution.
- **Asynchronous Callback: A callback that is executed after an asynchronous operation completes.
To learn more about callbacks, you can refer to the Article - Callback in NodeJS
**Events in NodeJS
In NodeJS, events are actions or occurrences that the application can detect and respond to, such as 'data' or 'error'. The EventEmitter class enables objects to emit events and allows listeners to handle them asynchronously, handling non-blocking operations.
JavaScript `
const EventEmitter = require('events');
// Create a new instance of EventEmitter const eventEmitter = new EventEmitter();
// Register an event listener for the 'greet' event eventEmitter.on('greet', () => { console.log('Hello, welcome to Node.js!'); });
// Emit the 'greet' event eventEmitter.emit('greet');
`
**In this example
- We use EventEmitter to create something that can send and listen for events.
- eventEmitter.on is how we say "Hey, when the 'greet' event happens, run this code."
- eventEmitter.emit is how we actually make the 'greet' event happen. This triggers the code we set up to run.
**Output:
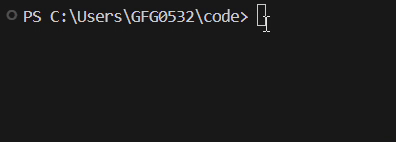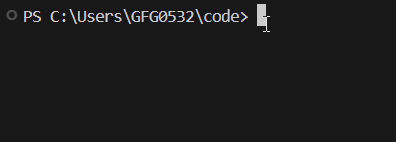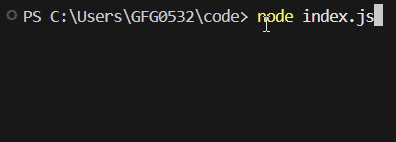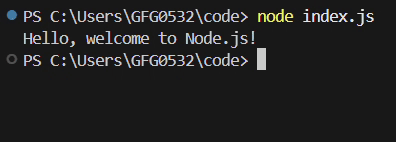
Events in NodeJS
To learn more about events in NodeJS, check out the article - Events in NodeJS
Callbacks vs Events
| Feature | Callbacks | Events |
|---|---|---|
| Execution Flow | Executes once per operation | Can be triggered multiple times |
| Code Structure | Nested and can lead to callback hell | More organized and manageable |
| Use Case | Used for single asynchronous operations | Used for handling multiple occurrences of an event |