Insertion in Circular Singly Linked List (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 24 Feb, 2025
In this article, we will learn how to insert a node into a circular linked list. Insertion is a fundamental operation in linked lists that involves adding a new node to the list. In a circular linked list, the last node connects back to the first node, creating a loop.
**There are four main ways to add items:
- Insertion in an empty list
- Insertion at the beginning of the list
- Insertion at the end of the list
- Insertion at a specific position in the list
Advantages of using a tail pointer instead of a head pointer
We need to traverse the whole list to insert a node at the beginning. Also, for insertion at the end, the whole list has to be traversed. If instead of the **start pointer, we take a pointer to the last node, then in both cases there won't be any need to traverse the whole list. So insertion at the beginning or the end takes constant time, irrespective of the length of the list.
1. Insertion in an empty List in the circular linked list
To insert a node in empty circular linked list, creates a new node with the given data, sets its next pointer to point to itself, and updates the **last pointer to reference this **new node.
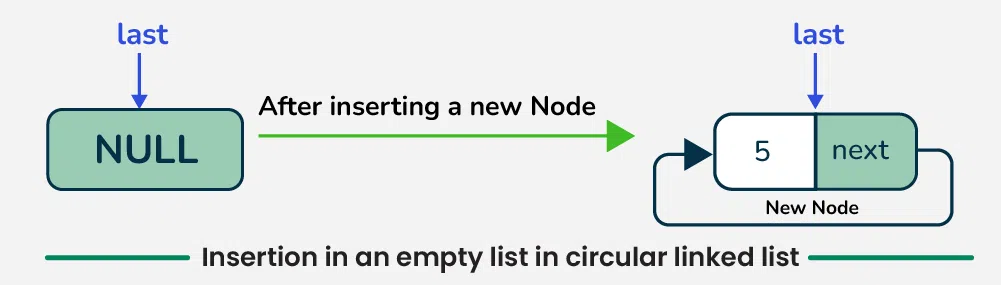
Insertion in an empty List
**Step-by-step approach:
- Check if **last is not **nullptr. If **true, return **last (the list is not empty).
- Otherwise, Create a **new node with the provided data.
- Set the **new node’s next pointer to point to itself (circular link).
- Update **last to point to the **new node and return it.
To read more about insertion in an empty list Refer: Insertion in an empty List in the circular linked list
2. Insertion at the beginning in circular linked list
To insert a new node at the beginning of a circular linked list,
- We first create the **new node and allocate memory for it.
- If the list is empty (indicated by the last pointer being **NULL), we make the **new node point to itself.
- If the list already contains nodes then we set the **new node’s next pointer to point to the **current head of the list (which is **last->next),
- Then update the last node’s next pointer to point to the **new node. This maintains the circular structure of the list.
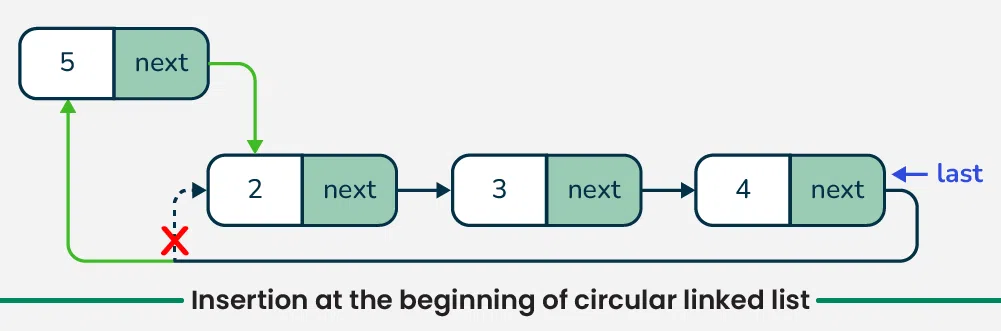
Insertion at the beginning in circular linked list
To read more about Insertion in the beginning Refer: Insertion at the beginning in circular linked list
3. Insertion at the end in circular linked list
To insert a new node at the end of a circular linked list, we first create the new node and allocate memory for it.
- If the list is empty (mean, **last or **tail pointer being NULL), we initialize the list with the **new node and making it point to itself to form a circular structure.
- If the list already contains nodes then we set the **new node’s next pointer to point to the **current head (which is **tail->next)
- Then update the **current tail's next pointer to point to the **new node.
- Finally, we update the **tail pointer to the **new node.
- This will ensure that the **new node is now the **last node in the list while maintaining the circular linkage.
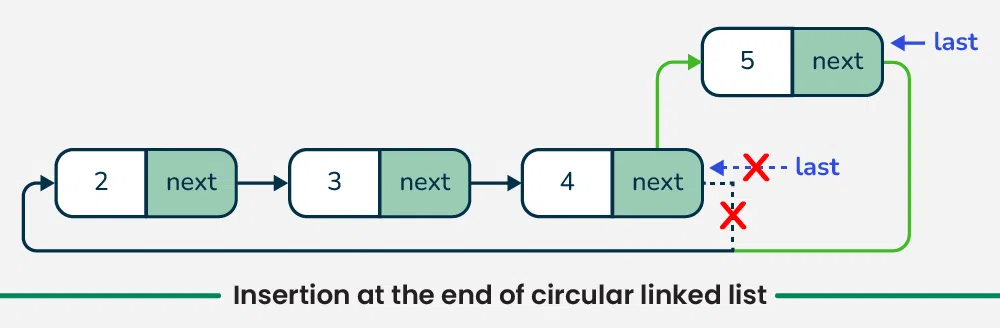
Insertion at the end in circular linked list
To read more about Insertion at the end Refer: Insertion at the end in circular linked list
4. Insertion at specific position in circular linked list
To insert a new node at a specific position in a circular linked list, we first check if the list is empty.
- If it is and the **position is not **1 then we print an error message because the position doesn't exist in the list. I
- f the **position is **1 then we create the **new node and make it point to itself.
- If the list is not empty, we create the **new node and traverse the list to find the correct insertion point.
- If the **position is **1, we insert the **new node at the beginning by adjusting the pointers accordingly.
- For other positions, we traverse through the list until we reach the desired position and inserting the **new node by updating the pointers.
- If the new node is inserted at the end, we also update the **last pointer to reference the new node, maintaining the circular structure of the list.
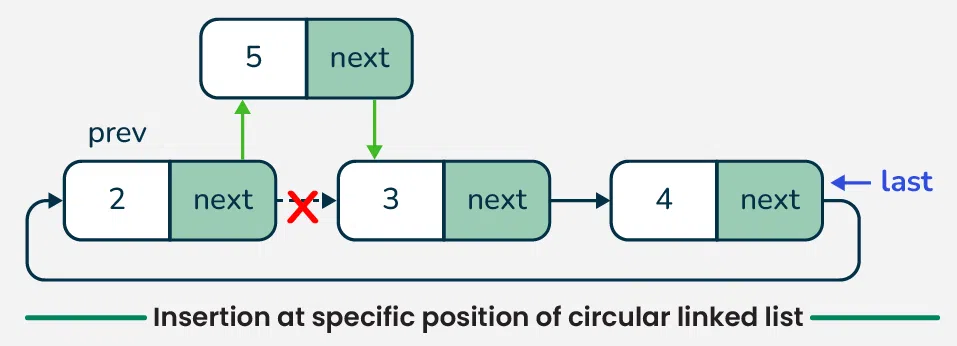
Insertion at specific position in circular linked list
**Step-by-step approach:
- If **last is **nullptr and **pos is not **1, print "**Invalid position!".
- Otherwise, Create a new Node with given data.
- Insert at Beginning: If pos is 1, update pointers and return last.
- **Traverse List: Loop to find the insertion point; print "Invalid position!" if out of bounds.
- **Insert Node: Update pointers to insert the new node.
- **Update Last: If inserted at the end, update **last. C++ `
#include using namespace std;
struct Node{ int data; Node *next; Node(int value){ data = value; next = nullptr; } };
// Function to insert a node at a specific position in a circular linked list Node *insertAtPosition(Node *last, int data, int pos){ if (last == nullptr){ // If the list is empty if (pos != 1){ cout << "Invalid position!" << endl; return last; } // Create a new node and make it point to itself Node *newNode = new Node(data); last = newNode; last->next = last; return last; }
// Create a new node with the given data
Node *newNode = new Node(data);
// curr will point to head initially
Node *curr = last->next;
if (pos == 1){
// Insert at the beginning
newNode->next = curr;
last->next = newNode;
return last;
}
// Traverse the list to find the insertion point
for (int i = 1; i < pos - 1; ++i) {
curr = curr->next;
// If position is out of bounds
if (curr == last->next){
cout << "Invalid position!" << endl;
return last;
}
}
// Insert the new node at the desired position
newNode->next = curr->next;
curr->next = newNode;
// Update last if the new node is inserted at the end
if (curr == last) last = newNode;
return last;}
void printList(Node *last){ if (last == NULL) return;
Node *head = last->next;
while (true){
cout << head->data << " ";
head = head->next;
if (head == last->next) break;
}
cout << endl;}
int main(){ // Create circular linked list: 2, 3, 4 Node *first = new Node(2); first->next = new Node(3); first->next->next = new Node(4);
Node *last = first->next->next;
last->next = first;
cout << "Original list: ";
printList(last);
// Insert elements at specific positions
int data = 5, pos = 2;
last = insertAtPosition(last, data, pos);
cout << "List after insertions: ";
printList(last);
return 0;}
C
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h>
// Define the Node structure struct Node { int data; struct Node *next; };
struct Node* createNode(int value);
// Function to insert a node at a specific position in a circular linked list struct Node* insertAtPosition(struct Node *last, int data, int pos) { if (last == NULL) { // If the list is empty if (pos != 1) { printf("Invalid position!\n"); return last; } // Create a new node and make it point to itself struct Node *newNode = createNode(data); last = newNode; last->next = last; return last; }
// Create a new node with the given data
struct Node *newNode = createNode(data);
// curr will point to head initially
struct Node *curr = last->next;
if (pos == 1) {
// Insert at the beginning
newNode->next = curr;
last->next = newNode;
return last;
}
// Traverse the list to find the insertion point
for (int i = 1; i < pos - 1; ++i) {
curr = curr->next;
// If position is out of bounds
if (curr == last->next) {
printf("Invalid position!\n");
return last;
}
}
// Insert the new node at the desired position
newNode->next = curr->next;
curr->next = newNode;
// Update last if the new node is inserted at the end
if (curr == last) last = newNode;
return last;}
// Function to print the circular linked list void printList(struct Node *last) { if (last == NULL) return;
struct Node *head = last->next;
while (1) {
printf("%d ", head->data);
head = head->next;
if (head == last->next) break;
}
printf("\n");}
// Function to create a new node struct Node* createNode(int value) { struct Node* newNode = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); newNode->data = value; newNode->next = NULL; return newNode; }
int main() { // Create circular linked list: 2, 3, 4 struct Node *first = createNode(2); first->next = createNode(3); first->next->next = createNode(4);
struct Node *last = first->next->next;
last->next = first;
printf("Original list: ");
printList(last);
// Insert elements at specific positions
int data = 5, pos = 2;
last = insertAtPosition(last, data, pos);
printf("List after insertions: ");
printList(last);
return 0;}
Java
class Node { int data; Node next;
Node(int value){
data = value;
next = null;
}}
public class GFG {
// Function to insert a node at a specific position in a
// circular linked list
static Node insertAtPosition(Node last, int data,
int pos){
if (last == null) {
// If the list is empty
if (pos != 1) {
System.out.println("Invalid position!");
return last;
}
// Create a new node and make it point to itself
Node newNode = new Node(data);
last = newNode;
last.next = last;
return last;
}
// Create a new node with the given data
Node newNode = new Node(data);
// curr will point to head initially
Node curr = last.next;
if (pos == 1) {
// Insert at the beginning
newNode.next = curr;
last.next = newNode;
return last;
}
// Traverse the list to find the insertion point
for (int i = 1; i < pos - 1; ++i) {
curr = curr.next;
// If position is out of bounds
if (curr == last.next) {
System.out.println("Invalid position!");
return last;
}
}
// Insert the new node at the desired position
newNode.next = curr.next;
curr.next = newNode;
// Update last if the new node is inserted at the
// end
if (curr == last)
last = newNode;
return last;
}
static void printList(Node last){
if (last == null)
return;
Node head = last.next;
while (true) {
System.out.print(head.data + " ");
head = head.next;
if (head == last.next)
break;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Create circular linked list: 2, 3, 4
Node first = new Node(2);
first.next = new Node(3);
first.next.next = new Node(4);
Node last = first.next.next;
last.next = first;
System.out.print("Original list: ");
printList(last);
// Insert elements at specific positions
int data = 5, pos = 2;
last = insertAtPosition(last, data, pos);
System.out.print("List after insertions: ");
printList(last);
}}
Python
class Node: def init(self, value): self.data = value self.next = None
Function to insert a node at a specific position in a circular linked list
def insertAtPosition(last, data, pos): if last is None: # If the list is empty if pos != 1: print("Invalid position!") return last # Create a new node and make it point to itself new_node = Node(data) last = new_node last.next = last return last
# Create a new node with the given data
new_node = Node(data)
# curr will point to head initially
curr = last.next
if pos == 1:
# Insert at the beginning
new_node.next = curr
last.next = new_node
return last
# Traverse the list to find the insertion point
for i in range(1, pos - 1):
curr = curr.next
# If position is out of bounds
if curr == last.next:
print("Invalid position!")
return last
# Insert the new node at the desired position
new_node.next = curr.next
curr.next = new_node
# Update last if the new node is inserted at the end
if curr == last:
last = new_node
return lastFunction to print the circular linked list
def print_list(last): if last is None: return
head = last.next
while True:
print(head.data, end=" ")
head = head.next
if head == last.next:
break
print()if name == "main": # Create circular linked list: 2, 3, 4 first = Node(2) first.next = Node(3) first.next.next = Node(4)
last = first.next.next
last.next = first
print("Original list: ", end="")
print_list(last)
# Insert elements at specific positions
data = 5
pos = 2
last = insertAtPosition(last, data, pos)
print("List after insertions: ", end="")
print_list(last)JavaScript
class Node { constructor(value){ this.data = value; this.next = null; } }
// Function to insert a node at a specific position in a // circular linked list function insertAtPosition(last, data, pos) { if (last === null) { // If the list is empty if (pos !== 1) { console.log("Invalid position!"); return last; } // Create a new node and make it point to itself let newNode = new Node(data); last = newNode; last.next = last; return last; }
// Create a new node with the given data
let newNode = new Node(data);
// curr will point to head initially
let curr = last.next;
if (pos === 1) {
// Insert at the beginning
newNode.next = curr;
last.next = newNode;
return last;
}
// Traverse the list to find the insertion point
for (let i = 1; i < pos - 1; ++i) {
curr = curr.next;
// If position is out of bounds
if (curr === last.next) {
console.log("Invalid position!");
return last;
}
}
// Insert the new node at the desired position
newNode.next = curr.next;
curr.next = newNode;
// Update last if the new node is inserted at the end
if (curr === last)
last = newNode;
return last;}
// Function to print the circular linked list function printList(last){ if (last === null) return;
let head = last.next;
while (true) {
console.log(head.data + " ");
head = head.next;
if (head === last.next)
break;
}
console.log();}
// Create circular linked list: 2, 3, 4 let first = new Node(2); first.next = new Node(3); first.next.next = new Node(4);
let last = first.next.next; last.next = first;
console.log("Original list: "); printList(last);
// Insert elements at specific positions let data = 5; let pos = 2; last = insertAtPosition(last, data, pos); console.log("List after insertions: "); printList(last);
`
Output
Original list: 2 3 4 List after insertions: 2 5 3 4
**Time Complexity: O(n), we have to traverse the list to find the specific position.
**Auxiliary Space: O(1)