Control Structures in Programming Languages (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 16 Jan, 2020
Control Structures are just a way to specify flow of control in programs. Any algorithm or program can be more clear and understood if they use self-contained modules called as logic or control structures. It basically analyzes and chooses in which direction a program flows based on certain parameters or conditions. There are three basic types of logic, or flow of control, known as:
- Sequence logic, or sequential flow
- Selection logic, or conditional flow
- Iteration logic, or repetitive flow
Let us see them in detail:
- **Sequential Logic (Sequential Flow)**Sequential logic as the name suggests follows a serial or sequential flow in which the flow depends on the series of instructions given to the computer. Unless new instructions are given, the modules are executed in the obvious sequence. The sequences may be given, by means of numbered steps explicitly. Also, implicitly follows the order in which modules are written. Most of the processing, even some complex problems, will generally follow this elementary flow pattern.
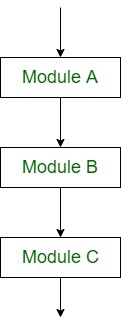
Sequential Control flow - **Selection Logic (Conditional Flow)**Selection Logic simply involves a number of conditions or parameters which decides one out of several written modules. The structures which use these type of logic are known as Conditional Structures. These structures can be of three types:
- Single AlternativeThis structure has the form:
If (condition) then:
[Module A]
[End of If structure]
Implementation:
* C/C++ if statement with Examples
* Java if statement with Examples - Double AlternativeThis structure has the form:
If (Condition), then:
[Module A]
Else:
[Module B]
[End if structure]
Implementation:
* C/C++ if-else statement with Examples
* Java if-else statement with Examples - Multiple AlternativesThis structure has the form:
If (condition A), then:
[Module A]
Else if (condition B), then:
[Module B]
..
..
Else if (condition N), then:
[Module N]
[End If structure]
Implementation:
* C/C++ if-else if statement with Examples
* Java if-else if statement with Examples - Single AlternativeThis structure has the form:
In this way, the flow of the program depends on the set of conditions that are written. This can be more understood by the following flow charts: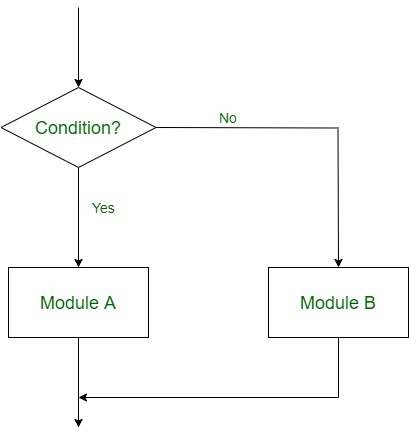
Double Alternative Control Flow
3. **Iteration Logic (Repetitive Flow)**The Iteration logic employs a loop which involves a repeat statement followed by a module known as the body of a loop. The two types of these structures are: In this, there requires a statement that initializes the condition controlling the loop, and there must also be a statement inside the module that will change this condition leading to the end of the loop.