Convert String to int in C++ (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 19 May, 2025
Converting a string to int is one of the most frequently encountered tasks in C++. As both string and int are not in the same object hierarchy, we cannot perform implicit or explicit type casting as we can do in case of double to int or float to int conversion. Conversion is mostly done so that we can convert numbers that are stored as strings.
**Example:
**Input: "191"
**Output: 191
There are 6 significant methods to convert strings to numbers in C++ as follows:
Table of Content
- Using stoi() Function
- Using atoi()
- Using stringstream Class
- Using sscanf()
- Using For Loop
- Using strtol()
1. String to int Conversion Using stoi() Function
The **stoi() function in C++ takes a string as an argument and returns its value in integer form. This approach is popular in current versions of C++, as it was first introduced in C++11.
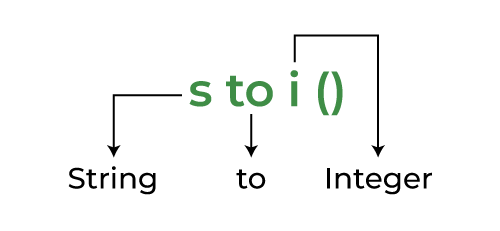
Breakdown of stoi() in simple terms
**Syntax:
C++ `
stoi(str, position, base);
`
**Parameters:
- **str: string to be converted. (compulsory)
- **position: starting position. (optional with default value = 0)
- **base: base of the number system. (optional with default value = 10)
For more on handling data types and conversions, check out our Complete C++ Course, where you’ll learn how to work with strings, numbers, and various conversions in C++.
**Example:
C++ `
#include #include using namespace std;
int main() { string str1 = "45"; string str2 = "3.14159"; char str3[] = "31337 geek";
// Store the integer value which // by stoi() int myint1 = stoi(str1); int myint2 = stoi(str2); int myint3 = stoi(str3);
cout << "stoi("" << str1 << "") is " << myint1 << '\n'; cout << "stoi("" << str2 << "") is " << myint2 << '\n'; cout << "stoi("" << str3 << "") is " << myint3; return 0; }
`
Output
stoi("45") is 45 stoi("3.14159") is 3 stoi("31337 geek") is 31337
2. String to int Conversion Using atoi()
The **atoi() function in C++ takes a character array or string literal as an argument and returns its value in an **integer. It is defined in the ****<stdlib.h>** header file. This function is inherited by C++ from C language, so it only works on C style strings i.e. array of characters.
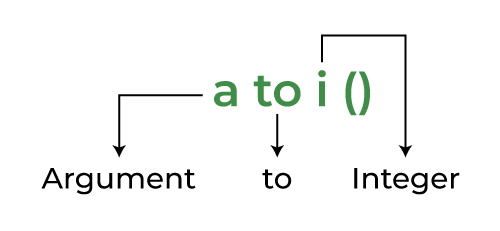
Breakdown of atoi() in simple terms
**Syntax:
C++ `
atoi(str);
`
**Example:
C++ `
#include #include <stdlib.h> using namespace std;
int main() { char str1[] = "141"; char str2[] = "3.14";
// Convert string into integer
// using atoi()
int res1 = atoi(str1);
int res2 = atoi(str2);
cout << "atoi(" << str1 << ") is " << res1 << "\n";
cout << "atoi(" << str2 << ") is " << res2;
return 0;}
`
Output
atoi(141) is 141 atoi(3.14) is 3
**stoi() vs atoi()
The differences between stoi() and atoi() are shown below:
| stoi() | atoi() |
|---|---|
| stoi() is added in C++ 11. | atoi() is a legacy C-style function. |
| stoi() works for both C++ strings and C-style strings (character array and string literal). | atoi() works only for C-style strings (character array and string literal). |
| stoi() can take up to three parameters, the second parameter is for starting index and the third parameter is for the base of the input number. | atoi()takes only one parameter and returns an integer value. |
3. String to int Conversion Using stringstream Class
The stringstream class in C++ allows us to associate a string to be read as if it were a stream. We can use it to easily convert strings of digits into ints, floats, or doubles. The **stringstream class is defined inside the <****sstream**> header file.
It works similar to other input and output streams in C++. We first create a **stringstream object as shown below:
C++ `
stringstream ss;
`
Then insert a numeric string into it using the ( ****<<** ) insertion operator:
C++ `
ss << myString; ss << myCstring;
`
At last, we extract the numeric value from the stream using the ( >> ) **extraction operator:
C++ `
ss >> myChar; ss >> myCstring;
`
The below C++ program demonstrates how to convert a string to int using a stringstream object:
C++ `
#include #include using namespace std;
int main() { string s = "12345";
// object from the class stringstream
stringstream geek;
// inserting string s in geek stream
geek << s;
// The object has the value 12345
// and stream it to the integer x
int x = 0;
geek >> x;
// Now the variable x holds the
// value 12345
cout << "Value of x + 1 : " << x + 1;
return 0;}
`
Output
Value of x + 1 : 12346
To summarize, stringstream is a convenient way to manipulate strings. This method also works for both C style strings or C++ style strings.
4. Converting String to int Using sscanf()
'**sscanf()****'** is a C-style function similar to scanf(). It reads input from a string rather than standard input.
**Syntax:
C++ `
sscanf(source, formatted_string, ...);
`
**Parameters:
- **source: source string.
- **formatted_string: a string that contains the format specifiers.
- ****... :** variable arguments list that contains the address of the variables in which we want to store input data.
There should be at least as many of these arguments as the number of values stored by the format specifiers.
**Return Value:
- On success, the function returns the number of variables filled.
- In the case of an input failure, before any data could be successfully read, the end of the function (EOF) is returned.
**Example:
C++ `
#include using namespace std;
int main() { const char* str = "12345"; int x; sscanf(str, "%d", &x); cout << "The value of x: " << x; return 0; }
`
Output
The value of x: 12345
5. Using For Loop Convert Strings into int
It is the naive method of string to int conversion where we compare each character to its ASCII values and then get the value of that numeric character.
**Example:
C++ `
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;
int main() { string number = "13"; int i = 0;
// Traversing string
for (char c : number) {
// Checking if the element is number
if (c >= '0' && c <= '9') {
i = i * 10 + (c - '0');
}
// Otherwise print bad output
else {
cout << "Bad Input";
return 1;
}
}
cout << i;}
`
Above program converts a string into an integer by iterating through each character, checking if it's a digit, and then calculating the integer value by updating the variable **i as **i **= i * 10 + (c - '0') for each valid digit. Non-digit characters result in a "Bad Input" message and terminate the program.
**6. String to int Conversion Using strtol()
The strtol function is used to converts a string to a long integer value, respectively.
**Syntax:
C++ `
strtol(str, endptr, base);
`
**Parameters:
- **st: Pointer to the null-terminated string to be converted
- **endptr: Reference to a pointer to character. The function stores the address of the first invalid character in *endptr. If endptr is a null pointer, the function does not store this information.
- **base: The number base to interpret the string. Must be between 2 and 36, inclusive, or 0. If base is 0, the function determines the base from the string itself. If the base is 16, the string may begin with the prefix "0x" or "0X", in which case the number is parsed as a hexadecimal value.
**Return Value:
- If the string is empty or does not contain any digits, 0 is returned.
- If the conversion is successful, the function returns the converted long integer value.
- If the conversion fails, the function returns 0 and sets *endptr to point to the beginning of the string.
**Example:
C++ `
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h>
int main() { char str[] = "12345"; char* endptr; long int value = strtol(str, &endptr, 10); if (endptr == str) { printf("No digits were found\n"); } else if (*endptr != '\0') { printf("Invalid input: %s\n", str); } else { printf("The value is %ld\n", value); } return 0; }
`