Introduction to Deep Learning (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 16 Dec, 2025
Deep Learning is transforming the way machines understand, learn and interact with complex data. Deep learning mimics neural networks of the human brain, it enables computers to autonomously uncover patterns and make informed decisions from vast amounts of unstructured data.
**How Deep Learning Works?
Neural network consists of layers of interconnected nodes or neurons that collaborate to process input data. In a fully connected deep neural network data flows through multiple layers where each neuron performs nonlinear transformations, allowing the model to learn intricate representations of the data.
In a deep neural network the input layer receives data which passes through hidden layers that transform the data using nonlinear functions. The final output layer generates the model’s prediction.
For more details on neural networks refer to: What is a Neural Network?
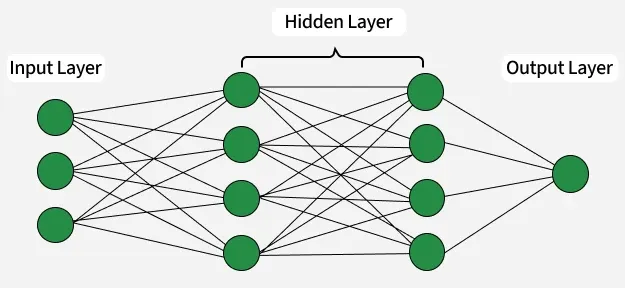
Neural Network
**Difference between Machine Learning and Deep Learning
Machine learning and Deep Learning both are subsets of artificial intelligence but there are many similarities and differences between them.
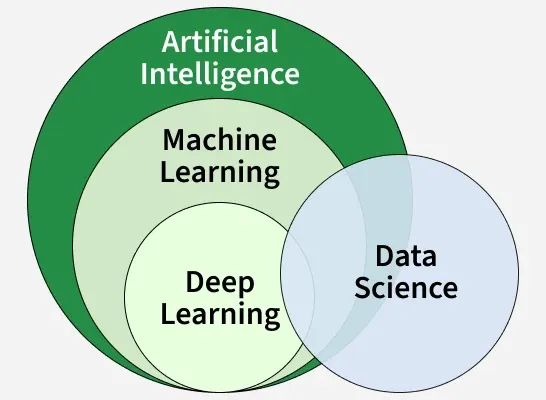
Machine Learning and Deep Learning
| **Aspect | **Machine Learning | **Deep Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Idea | Applies statistical algorithms to learn patterns from data | Uses artificial neural networks to learn patterns from data |
| Data Requirement | Works well with small to medium datasets | Requires a large amount of data |
| Task Complexity | Better for simple and low-label tasks | Better for complex tasks like image and text processing |
| Training Time | Takes less time to train | Takes more time to train |
| Feature Extraction | Features are manually selected and extracted | Features are automatically extracted |
| Learning Process | Not end-to-end | End-to-end learning |
| Model Complexity | Less complex | Highly complex |
| Interpretability | Easy to understand and explain | Hard to interpret (black box) |
| Hardware Requirement | Can run on CPU, needs less computing power | Needs GPU and high-performance systems |
| Use Cases | Spam detection, recommendation systems | Image recognition, NLP, speech recognition |
**Evolution of Neural Architectures
**Perceptron (1950s)
- First simple neural network with a single layer
- Could only solve linearly separable problems
- Failed on complex tasks like the XOR problem
**Multi-Layer Perceptrons (MLPs)
- Introduced hidden layers and non-linear activation functions
- Enabled modeling of non-linear relationships
- Trained effectively using backpropagation
- Marked a major leap in neural network capabilities
Types of neural networks
- **Feedforward neural networks (FNNs): They are the simplest type of ANN, where data flows in one direction from input to output. It is used for basic tasks like classification.
- **Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs): They are specialized for processing grid-like data, such as images. CNNs use convolutional layers to detect spatial hierarchies, making them ideal for computer vision tasks.
- **Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs)****:** Theyare able to process sequential data, such as time series and natural language. RNNs have loops to retain information over time, enabling applications like language modeling and speech recognition. Variants like LSTMs and GRUs address vanishing gradient issues.
- **Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): This consist of two networks—a generator and a discriminator—that compete to create realistic data. GANs are widely used for image generation, style transfer and data augmentation.
- **Autoencoders: They are unsupervised networks that learn efficient data encodings. They compress input data into a latent representation and reconstruct it, useful for dimensionality reduction and anomaly detection.
- **Transformer Networks: It has revolutionized NLP with self-attention mechanisms. Transformers excel at tasks like translation, text generation and sentiment analysis, powering models like GPT and BERT.
**Applications
1. Computer vision
In computer vision, deep learning models enable machines to identify and understand visual data. Some of the main applications of deep learning in computer vision include:
- **Object detection and recognition: Deep learning models are used to identify and locate objects within images and videos, making it possible for machines to perform tasks such as self-driving cars, surveillance and robotics.
- **Image classification: Deep learning models can be used to classify images into categories such as animals, plants and buildings. This is used in applications such as medical imaging, quality control and image retrieval.
- **Image segmentation: Deep learning models can be used for image segmentation into different regions, making it possible to identify specific features within images.
2. Natural language processing (NLP)
In NLP, deep learning model enable machines to understand and generate human language. Some of the main applications of deep learning in NLP include:
- **Automatic Text Generation: Deep learning model can learn the corpus of text and new text like summaries, essays can be automatically generated using these trained models.
- **Language translation: Deep learning models can translate text from one language to another, making it possible to communicate with people from different linguistic backgrounds.
- **Sentiment analysis: Deep learning models can analyze the sentiment of a piece of text, making it possible to determine whether the text is positive, negative or neutral.
- **Speech recognition: Deep learning models can recognize and transcribe spoken words, making it possible to perform tasks such as speech-to-text conversion, voice search and voice-controlled devices.
3. Reinforcement learning
In reinforcement learning, deep learning works as training agents to take action in an environment to maximize a reward. Some of the main applications of deep learning in reinforcement learning include:
- **Game playing: Deep reinforcement learning models have been able to beat human experts at games such as Go, Chess and Atari.
- **Robotics: Deep reinforcement learning models can be used to train robots to perform complex tasks such as grasping objects, navigation and manipulation.
- **Control systems: Deep reinforcement learning models can be used to control complex systems such as power grids, traffic management and supply chain optimization.
Advantages
- **High accuracy: Deep Learning algorithms can achieve state-of-the-art performance in various tasks such as image recognition and natural language processing.
- **Automated feature engineering: Deep Learning algorithms can automatically discover and learn relevant features from data without the need for manual feature engineering.
- **Scalability: Deep Learning models can scale to handle large and complex datasets and can learn from massive amounts of data.
- **Flexibility: Deep Learning models can be applied to a wide range of tasks and can handle various types of data such as images, text and speech.
Disadvantages
Here are some of the main challenges in deep learning:
- **Data availability: It requires large amounts of data to learn from. For using deep learning it's a big concern to gather as much data for training.
- **Computational Resources: For training the deep learning model, it is computationally expensive because it requires specialized hardware like GPUs and TPUs.
- **Interpretability: Deep learning models are complex, it works like a black box. It is very difficult to interpret the result.
- **Overfitting: when the model is trained again and again it becomes too specialized for the training data leading to overfitting and poor performance on new data.
What is Deep Learning? Difference between ML and Deep learning.
