Detect cycle in an undirected graph using BFS (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 04 Apr, 2025
Given an undirected graph, the task is to determine if **cycle is present in it or not.
**Examples:
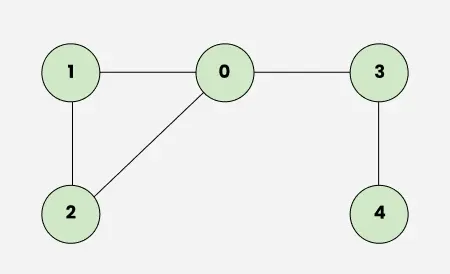
**Input: V = 5, edges[][] = [[0, 1], [0, 2], [0, 3], [1, 2], [3, 4]]
Undirected Graph with 5 Node
**Output: true
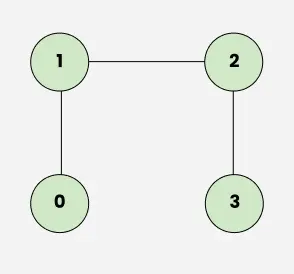
**Explanation: _The diagram clearly shows a cycle 0 → 2 → 1 → 0.**Input: V = 4, edges[][] = [[0, 1], [1, 2], [2, 3]]
Undirected graph with 4 Node
**Output: false
**Approach:
The idea is to use BFS to detect a cycle in an undirected graph. We start BFS for all components of the graph and check if a node has been visited earlier, ensuring that we **do not consider the parent node of the current node while making this check. If we encounter a visited node that is not the parent, a **cycle exists in the graph. Otherwise, we continue BFS by marking the node as visited and inserting it into the queue.
Step by step approach:
- **Initialize a visited array of size
n(number of nodes) tofalse. - **Iterate through all nodes from
0ton-1. If a node is not visited, start BFS. - **Push the node into the queue with its parent set to
-1. - **Perform BFS:
- Pop a node from the queue.
- Traverse all its adjacent nodes.
- If an adjacent node is visited and **is not the parent, return
true(cycle detected). - Otherwise, if the adjacent node is not visited, mark it as visited and push it into the queue with the current node as its parent.
- If no cycle is found after checking all components, return
false.
**Implementation:
C++ `
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;
// Function to perform BFS from node start bool bfs(int start, vector<vector>& adj, vector& visited) { queue<pair<int, int>> q; q.push({start, -1}); visited[start] = true;
while (!q.empty()) {
int node = q.front().first;
int parent = q.front().second;
q.pop();
for (int neighbor : adj[node]) {
if (!visited[neighbor]) {
visited[neighbor] = true;
q.push({neighbor, node});
}
else if (neighbor != parent) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;}
vector<vector> constructadj(int V, vector<vector> &edges){
vector<vector<int>> adj(V);
for (auto it : edges)
{
adj[it[0]].push_back(it[1]);
adj[it[1]].push_back(it[0]);
}
return adj;}
bool isCycle(int V, vector<vector>& edges) {
vector<vector<int>> adj = constructadj(V, edges);
vector<bool> visited(V, false);
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
if (!visited[i]) {
if (bfs(i, adj, visited)) {
return true;
}
}
}
// If no cycle is found
return false;}
int main() { vector<vector> edges = {{0, 1}, {0, 2}, {0, 3}, {1, 2}, {3, 4}}; int V = 5;
isCycle(V,edges) ? cout<<"true": cout<<"false";
return 0;}
Java
import java.util.*;
public class CycleDetection {
// Function to perform BFS from a start node
static boolean bfs(int start, List<Integer>[] adj,
boolean[] visited)
{
Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(new int[] { start, -1 });
visited[start] = true;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int[] front = q.poll();
int node = front[0];
int parent = front[1];
for (int neighbor : adj[node]) {
if (!visited[neighbor]) {
visited[neighbor] = true;
q.offer(new int[] { neighbor, node });
}
// If visited and not the parent, cycle
// exists
else if (neighbor != parent) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
static List<Integer>[] constructadj(int V,
int[][] edges)
{
List<Integer>[] adj = new ArrayList[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
adj[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
for (int[] edge : edges) {
int u = edge[0], v = edge[1];
adj[u].add(v);
adj[v].add(u);
}
return adj;
}
static boolean isCycle(int V, int[][] edges)
{
// Create adjacency list
List<Integer>[] adj = constructadj(V, edges);
boolean[] visited = new boolean[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
if (!visited[i]) {
if (bfs(i, adj, visited)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[][] edges = {
{0, 1}, {0, 2}, {0, 3}, {1, 2}, {3, 4}
};
int V = 5;
System.out.println(isCycle(V, edges) ? "true"
: "false");
}}
Python
from collections import deque
def bfs(start, adj, visited): queue = deque([(start, -1)]) visited[start] = True
while queue:
node, parent = queue.popleft()
for neighbor in adj[node]:
if not visited[neighbor]:
visited[neighbor] = True
queue.append((neighbor, node))
elif neighbor != parent:
return True
return Falsedef constructadj(V, edges): adj = [[] for _ in range(V)] # Initialize adjacency list
for edge in edges:
u, v = edge
adj[u].append(v)
adj[v].append(u)
return adjdef iscycle(V, edges): adj = constructadj(V,edges)
visited = [False] * V
for i in range(V):
if not visited[i]:
if bfs(i, adj, visited):
return True
return FalseTest the function
edges = [[0, 1], [0, 2], [0, 3], [1, 2], [3, 4]] V = 5 print("true" if iscycle(V, edges) else "false")
C#
using System; using System.Collections.Generic;
class CycleDetection { // Function to perform BFS from a start node static bool Bfs(int start, List[] adj, bool[] visited) { Queue<(int, int)> q = new Queue<(int, int)>(); q.Enqueue((start, -1)); visited[start] = true;
while (q.Count > 0)
{
var (node, parent) = q.Dequeue();
foreach (int neighbor in adj[node])
{
if (!visited[neighbor])
{
visited[neighbor] = true;
q.Enqueue((neighbor, node));
}
// If visited and not the parent, cycle exists
else if (neighbor != parent)
{
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
// Function to construct the adjacency list
static List<int>[] constructadj(int V, int[][] edges)
{
List<int>[] adj = new List<int>[V];
// Initialize each list in the adjacency list
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
adj[i] = new List<int>();
}
foreach (var edge in edges)
{
adj[edge[0]].Add(edge[1]);
adj[edge[1]].Add(edge[0]);
}
return adj;
}
static bool IsCycle(int V, int[][] edges)
{
// Create adjacency list
List<int>[] adj = constructadj(V, edges);
bool[] visited = new bool[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
if (!visited[i])
{
if (Bfs(i, adj, visited))
{
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
static void Main()
{
int[][] edges = new int[][]
{
new int[] {0, 1}, new int[] {0, 2}, new int[] {0, 3},
new int[] {1, 2}, new int[] {3, 4}
};
int V = 5;
Console.WriteLine(IsCycle(V, edges) ? "true" : "false");
}}
JavaScript
function bfs(start, adj, visited) { let queue = [[start, -1]]; visited[start] = true;
while (queue.length > 0) {
let [node, parent] = queue.shift();
for (let neighbor of adj[node]) {
if (!visited[neighbor]) {
visited[neighbor] = true;
queue.push([neighbor, node]);
} else if (neighbor !== parent) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;}
function constructadj(V, edges){ let adj = Array.from({length : V}, () => []);
// Build the adjacency list
for (let edge of edges) {
let [u, v] = edge;
adj[u].push(v);
adj[v].push(u);
}
return adj;}
function isCycle(V, edges) { let adj = constructadj(V,edges);
let visited = Array(V).fill(false);
for (let i = 0; i < V; i++) {
if (!visited[i]) {
if (bfs(i, adj, visited)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;}
// Test the function let edges = [[0, 1], [0, 2], [0, 3], [1, 2], [3, 4]]; let V = 5; console.log(isCycle(V, edges) ? "true" : "false");
`
**Time Complexity: **O(V+E), It visits each node once and processes each edge once using an adjacency list.
**Space Complexity: O(V), O(V) for the queue and visited array.
We do not count the adjacency list in auxiliary space as it is necessary for representing the input graph.
**Related Articles: