Differences between an API Gateway and a Load Balancer (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 01 Aug, 2024
An **API Gateway and a **Load Balancer are both critical components in managing backend services, but they serve distinct purposes. An API Gateway acts as a single entry point for client requests, handling routing, request transformation, and cross-cutting concerns like authentication and logging. In contrast, a Load Balancer distributes incoming network traffic across multiple servers to ensure high availability and reliability. Understanding these differences is key to designing efficient, scalable systems that leverage each component’s strengths effectively.
Differences between an API Gateway and a Load Balancer
Important Topics for API Gateway vs. Load Balancer
- What is API Gateway?
- What is a Load Balancer?
- API Gateway vs. Load Balancer
- Use Cases of API Gateway
- Use Cases of a Load Balancer
What is API Gateway?
API Gateway, a serverless management tool, functions as an intermediary between microservices and users. By establishing APIs in your client application, you can make them accessible to outside programmers as well. Supporting HTTP, WebSocket, and REST APIs, API Gateway serves as an exclusive server that can personalize every client.
Here are some of the advantages of using API Gateway:
- **Improved performance: By enabling the system to handle a greater quantity of requests and respond faster to clients, the API gateway can assist in enhancing general performance. This is due to its capacity to handle responsibilities like routing and load balancing.
- **Simplified system design: The clients have an easier time accessing the microservices, and the overall system design is simplified thanks to the API gateway’s provision of a solitary entry point.
- **Enhanced security: Using the API gateway allows for intensified security measures, as it can enforce access control and authentication policies to deter unwanted access and safeguard the system.
- **Improved scalability: The API gateway can distribute incoming requests among multiple instances of a microservice, enabling the system to scale more easily and handle a larger number of requests.
What is a Load Balancer?
To make sure that performance stays top-notch and to avoid server crashes, a load balancer plays a key role in the layout of any system. It distributes incoming requests among multiple servers so that no single server gets swamped with traffic. It’s a vital component.
Here are some of the advantages of using API Gateway:
- **Big Data: Businesses can make informed decisions based on the examination of worldwide user-provided big data, which offers actionable insights.
- **Improve Efficiency: In order to provide clients with a better experience, servers need to run smoothly and provide swift responses. Load balancers are the key to achieving this by reducing the pressure on servers.
- **Predictive Analysis: Load balancer software can use predictive analysis to anticipate traffic bottlenecks before they materialize in reality.
- **Scalability: Services don’t need to be impacted if you modify the server infrastructure due to the ability of Load Balancers to provide scalability.
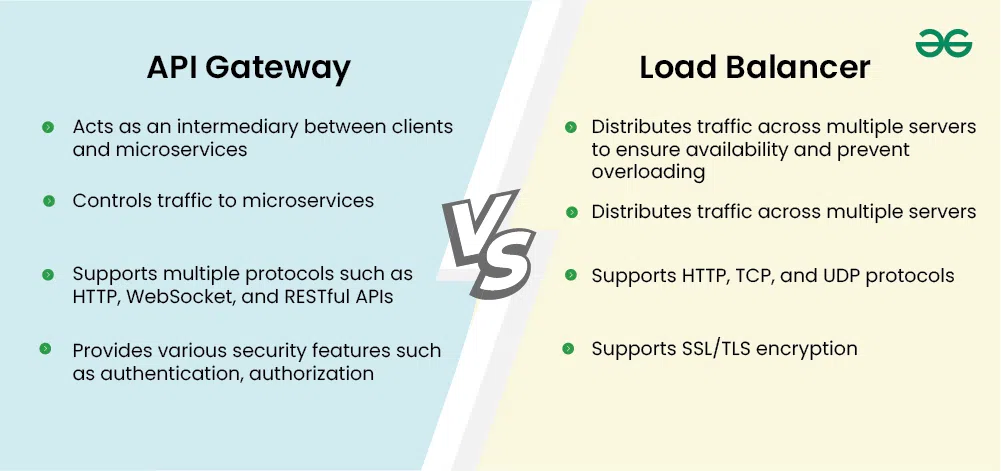
API Gateway vs. Load Balancer
Below are the differences between the API Gateway vs. Load Balancer:
| **Feature | API Gateway | **Load Balancer |
|---|---|---|
| **Function | Acts as an intermediary between clients and microservices, enabling developers to create, manage, and secure APIs | Distributes traffic across multiple servers to ensure availability and prevent overloading |
| **Traffic Management | Controls traffic to microservices | Distributes traffic across multiple servers |
| **Protocol Support | Supports multiple protocols such as HTTP, WebSocket, and RESTful APIs | Supports HTTP, TCP, and UDP protocols |
| **Security | Provides various security features such as authentication, authorization, and encryption | Supports SSL/TLS encryption |
| **Monitoring | Provides in-depth insights into API usage, latency, and error rates | Provides basic monitoring of server health |
| **Scalability | Can horizontally scale to handle increasing traffic | Can horizontally scale to handle increasing traffic |
| **Deployment | Deployed as a separate service or hosted solution | Deployed on-premise or as a cloud service cost typically |
| **Cost | Typically more expensive than a load balancer | Typically less expensive than an API gateway |
Use Cases of API Gateway
An **API Gateway serves as a critical component in modern architecture, managing and orchestrating API requests. Here are some key use cases for an API Gateway:
- **Request Routing: Directs client requests to appropriate backend services based on URL paths or request parameters.
- **Authentication and Authorization: Handles authentication and authorization by verifying user credentials and ensuring access control before forwarding requests.
- **Rate Limiting and Throttling: Enforces rate limits to control the number of requests a client can make within a given time period, preventing abuse and ensuring fair usage.
- **Request Transformation and Aggregation: Transforms and aggregates requests and responses between clients and services, such as modifying request formats or merging responses from multiple services.
- **Caching: Caches responses from backend services to reduce latency and load on services, improving performance for frequently requested data.
Use Cases of a Load Balancer
A **Load Balancer plays a crucial role in distributing network or application traffic across multiple servers to ensure high availability, reliability, and scalability. Here are some key use cases for a Load Balancer:
- **Traffic Distribution: Distributes incoming traffic across multiple servers to prevent any single server from becoming overwhelmed, ensuring balanced load and optimal performance.
- **High Availability: Ensures continuous availability of applications by redirecting traffic to healthy servers and avoiding servers that are down or experiencing issues.
- **Scalability: Facilitates scaling of applications by distributing traffic to a dynamically changing number of servers, accommodating varying load levels.
- **Health Monitoring: Continuously monitors the health and performance of servers and routes traffic only to servers that pass health checks.
- **Session Persistence (Sticky Sessions): Maintains user session information by directing subsequent requests from the same user to the same server, ensuring consistency in user experience.