Difference Between '+' and 'append' in Python (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 04 Jan, 2025
+ Operator creates a new sequence by concatenating two existing sequences and .append() method (available for lists) modifies the existing list in place by adding one item at the end. In this article we are going to compare '+' operator and append in Python.
+ Operator in Python
+ operator is typically used for concatenation of sequences (strings, lists or tuples). When we use + between two sequences, Python creates a new sequence that contains the elements of both. For lists, using + does not modify the original lists. Instead, it returns a new list that is the result of the concatenation.
**Example:
Python `
s1 = "Hello" s2 = "World" res = s1 + " " + s2 print(res)
`
**Output:
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
- '+' operator refers to the accessor method and does not modify the original sequence.
- Strings in Python are immutable, so every time we use + on strings, a new string is created.
Time Complexity of using + operator
- Concatenation with + can be costly in terms of performance if done repeatedly inside a loop, especially for strings, because it creates new objects every time.
- In the case of lists, list1 + list2 has a time complexity of O(n + m), where n and m are the lengths of the lists.
- For efficiency, especially inside loops, consider other methods like list.extend() or using str.join() for strings.
**append method in python
append() method is specific to lists (and some other data structures like deque in the collections module, but most commonly used with lists). append() adds a single element to the end of the existing list. append() modifies the original list in place. It does not create a new list.
**Example:
Python `
n = [1, 2, 3] n.append([4, 5]) print(n)
`
**Output:
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
- Here, .append() has added the list [4, 5] as a single element at the end.
Time Complexity of using append method
- .append() runs in amortized O(1) time, meaning that it’s generally very efficient to add items to the end of a list one by one.
- Since .append() modifies the list in place, if we need to retain the original list for some reason, we'd need to make a copy beforehand.
Graphical comparison between '+' and 'append'
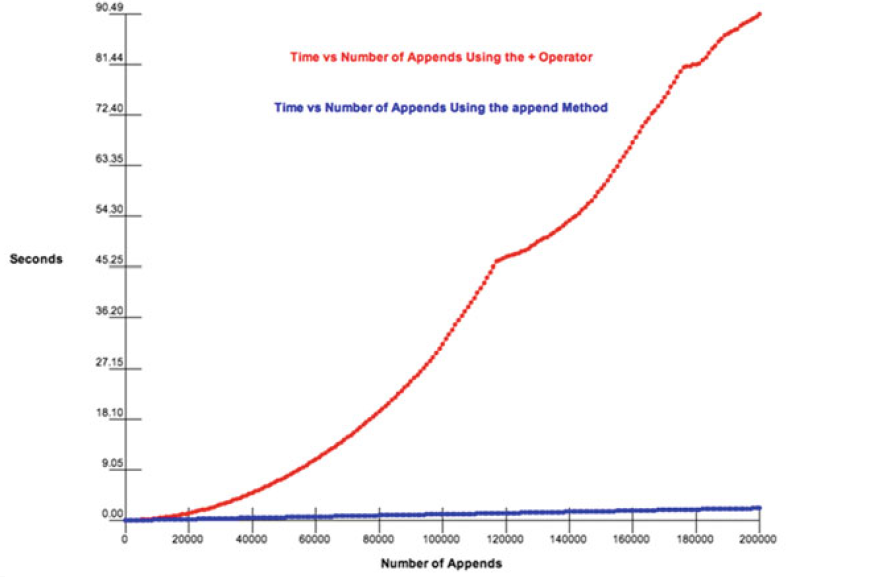
Comparison Between + operator and append method
| Criteria | + Operator | .append() Method |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Concatenates two sequences and returns a new sequence. | Adds a single element to the end of an existing list in place. |
| Data Types | Works with sequences such as strings, lists, and tuples. | Works only with lists (and similar data structures like deque). |
| Mutability | Does not modify the original objects. Creates a new one. | Modifies the original list in place. |
| Example | list1 + list2 creates a new list. | list.append(item) changes the existing list. |
| Resulting Object | New object returned, original sequences remain unchanged. | No new list is created, the original list is modified. |
| Time Complexity | O(n + m) (copies elements from both lists). | Amortized O(1) per append. |
| Typical Use Case | Concatenate two sequences to produce a new one. | Add a single element at a time to an existing list. |