Array Introduction (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 10 Sep, 2025
An arrayis a collection of items of the same variable type that are stored at contiguous memory locations. It is one of the most popular and simple data structures used in programming.
Basic terminologies of Array
- **Array Element: Elements are items stored in an array.
- **Array Index: Elements are accessed by their indexes. Indexes in most of the programming languages start from 0.
Memory representation of Array
In an array, all the elements or their references are stored in contiguous memory locations. This allows for efficient access and manipulation of elements.
Declaration of Array
Arrays can be declared in various ways in different languages. For better illustration, below are some language-specific array declarations:
C++ `
// This array will store integer type element int arr[5];
// This array will store char type element char arr[10];
// This array will store float type element float arr[20];
C
// This array will store integer type element int arr[5];
// This array will store char type element char arr[10];
// This array will store float type element float arr[20];
Java
// This array will store integer type element int arr[];
// This array will store char type element char arr[];
// This array will store float type element float arr[];
Python
In Python, all types of lists are created same way
arr = []
C#
// This array will store integer type element int[] arr;
// This array will store char type element char[] arr2;
// This array will store float type element float[] arr3;
Javascript
// JS code let arr = []
`
Initialization of Array
Arrays can be initialized in different ways in different languages. Below are some language-specific array initialization:
C++ `
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 }; char arr[5] = { 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e' }; float arr[10] = { 1.4, 2.0, 24, 5.0, 0.0 };
C
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 }; char arr[5] = { 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e' }; float arr[10] = { 1.4, 2.0, 24, 5.0, 0.0 };
Java
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 }; char arr[] = { 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e' }; float arr[] = { 1.4f, 2.0f, 24f, 5.0f, 0.0f };
Python
This list will store integer type elements
arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
This list will store character type elements (strings in Python)
arr = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e']
This list will store float type elements
arr = [1.4, 2.0, 24.0, 5.0, 0.0] # All float values
C#
int[] arr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 }; char[] arr = { 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e' }; float[] arr = { 1.4f, 2.0f, 24f, 5.0f, 0.0f };
JavaScript
let arr = [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ]; let arr = [ 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e' ]; let arr = [ 1.4, 2.0, 24, 5.0, 0.0 ];
`
Why do we Need Arrays?
Assume there is a class of five students and if we have to keep records of their marks in examination then, we can do this by declaring five variables individual and keeping track of records but what if the number of students becomes very large, it would be challenging to manipulate and maintain the data. So we use an array of students.

Types of Arrays
Arrays can be classified in two ways:
- On the basis of Size
- On the basis of Dimensions
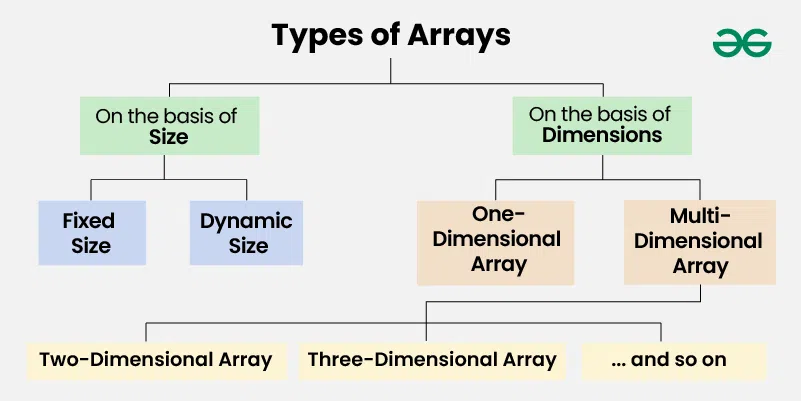
Types of Arrays on the basis of Size
**1. Fixed Sized Arrays
- We cannot alter or update the size of this array. Here only a fixed size (i,e. the size that is mentioned in square brackets **[]) of memory will be allocated for storage.
- In case, we don't know the size of the array then if we declare a larger size and store a lesser number of elements, it will result in a wastage of memory. And if we declare a lesser size than the number of elements then we won't get enough memory to store all the elements. C++ `
// Method 1 to create a fixed sized array. // Here the memory is allocated at compile time. int arr[5];
// Another way (creation and initialization both) int arr2[5] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
// Method 2 to create a fixed sized array // Here memory is allocated at run time (Also // known as dynamically allocated arrays) int *arr = new int[5];
C
// Method 1 to create a fixed sized array. // Here the memory is allocated at compile time. int arr1[5];
// Another way (creation and initialization both) int arr2[5] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
// Method 2 to create a fixed sized array // Here memory is allocated at run time (Also // known as dynamically allocated arrays) int arr = (int)malloc(n * sizeof(int));
Java
// Fixed sized array examples int[] arr1 = new int [5];
// Another way (Array creation and // initialization both) int[] arr2 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
Python
Create a fixed-size list of length 5,
initialized with zeros
arr = [0] * 5
Output the fixed-size list
print(arr)
C#
// Fixed sized array examples int[] arr1 = new int [5];
// Another way (Array creation and // initialization both) int[] arr2 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
`
**2. Dynamic Sized Arrays
The size of the array changes as per user requirements during execution of code so the coders do not have to worry about sizes. They can add and removed the elements as per the need. The memory is mostly dynamically allocated and de-allocated in these arrays.
C++ `
#include
// Dynamic Integer Array vector v;
C
// C does not seem to support // dynamic sized arrays as of now
Java
// Dynamic Integer Array ArrayList arr = new ArrayList<>();
Python
Dynamic Array
arr = []
C#
// Similar to Java ArrayList myList = new ArrayList();
JavaScript
// Dynamic Sized Array let arr = new Array();
`
Types of Arrays on the basis of Dimensions
**1. One-dimensional Array(1-D Array): You can imagine a 1d array as a row, where elements are stored one after another.
.webp)
**2. Multi-dimensional Array: A multi-dimensional array is an array with more than one dimension. We can use multidimensional array to store complex data in the form of tables, etc. We can have 2-D arrays, 3-D arrays, 4-D arrays and so on.
- **Two-Dimensional Array(2-D Array or Matrix): 2-D Multidimensional arrays can be considered as an array of arrays or as a matrix consisting of rows and columns.
To read more about Matrix Refer, Matrix Data Structure
.webp)
- **Three-Dimensional Array(3-D Array): A 3-D Multidimensional array contains three dimensions, so it can be considered an array of two-dimensional arrays.
.webp)
Operations on Array
- Traversal in Array
- **Insertions : At Beginning, At given position and At the end.
- **Deletion : From Beginning, Given Position, First Occurrence, All occurrences and From End
- **Searching : Linear Search and Binary Search