Explain the use of req and res objects in Express JS (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 20 Aug, 2024
Express JS is used to build RESTful APIs with Node.js. We have a '**req' (request) object in Express JS which is used to represent the incoming HTTP request that consists of data like parameters, query strings, and also the request body. Along with this, we have '**res' (response) which is used to send the HTTP response to the client which allows the modification of headers and consists of status codes, and resources.
Prerequisites
How are req and res Objects Useful?
Both the objects '**req' and '**res' are responsible for handling the HTTP requests and responses in the web applications. Below are some of the points which describe the benefits of these objects:
1. req (Request) Object:
- **Accessing the Request Data: By using the req object, we can access the various components of the incoming HTTP request which consists of data, headers, parameters, etc.
- **Middleware Interaction: Using the req object in Express.js, middleware functions can change and modify the request object by allowing various tasks of logging and authentication.
- **Routing: By implementing the dynamic routes in the application, the req object can be used as it captures the URL parameters and also allows it to respond dynamically based on the client's input.
2. res (Response) Object:
- **Send Responses: The res object is used to send the HTP responses to the client which includes the resource, data, status codes, and headers.
- **Error Handling: Using the res object we can send the error responses which is important for handling the errors and providing feedback to the client.
- **Content Modification: We can set the custom response headers, status codes, and content through which the response control can be managed by us.
Steps to use req and res objects in Express
**Step 1: In the first step, we will create the new folder as an **http-objects by using the below command in the VScode terminal.
mkdir http-objects
cd http-objects
**Step 2: After creating the folder, initialize the NPM using the below command. Using this the package.json file will be created.
npm init -y
**Step 3: Now, we will install the express dependency for our project using the below command.
npm i express
**Step 4: Now create the below Project Structure of our project which includes the file as **app.js.
Project Structure:

Folder structure
The updated dependencies in **package.json file will look like:
"dependencies": {
"express": "^4.19.2"
}
}
**Example: Write the following code in **app.js file
JavaScript ``
// app.js const express = require('express'); const app = express(); const PORT = 3000;
// GET route app.get('/', (req, res) => { // Log the request URL console.log('Request URL:', req.url);
// Log the request method console.log('Request Method:', req.method);
// Log the request headers console.log('Request Headers:', req.headers);
// Sending a response res.send('Hello World!'); });
// Starting the server
app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log(Server is running on http://localhost:${PORT});
});
``
**Start the server by using the below command:
node app.js
**Output:
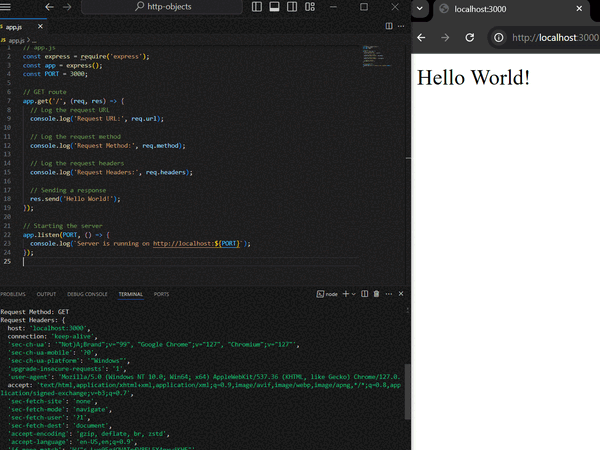
Output
Differences Between req and res objects in Express JS
| Feature | 'req' (Request Object) | 'res' (Response Object) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Represents the HTTP request made by the client | Represents the HTTP response that will be sent to the client |
| Content Type | Contains details about the incoming request (e.g., URL, headers, body) | Used to set the details of the outgoing response (e.g., status code, headers, body) |
| Methods | ****'req.query'**: Access query string parameters ****'req.params'**: Access route parameters ****'req.body'**: Access the body of the request (for POST/PUT) ****'req.headers'**: Access request headers | ****'res.send()'**: Send a response body ****'res.json()'**: Send a JSON response ****'res.status()'**: Set the status code of the response ****'res.sendFile()'**: Send a file as the response |
| Properties | ****'req.method'**: HTTP method (e.g., GET, POST) ****'req.url'**: URL of the request ****'req.cookies'**: Cookies sent by the client ****'req.ip'**: IP address of the client | ****'res.headersSent'**: Boolean indicating if the headers have been sent ****'res.locals'**: Object for passing data to the views ****'res.app'**: Access the Express application object |
| Typical Usage | Access and process incoming data Determine the request path, method, and parameters | Send back a response to the client Set response headers, cookies, and status codes |
| Lifecycle | Begins when the client makes an HTTP request | Ends when a response is sent back to the client |
| Associated with | HTTP Request | HTTP Response |