Explain the Working of HTTPS (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 26 Apr, 2025
HTTPS stands for HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure. It is the most common protocol for sending data between a web browser and a website. HTTPS is the secure variant of HTTP and is used to communicate between the user's browser and the website, ensuring that data transfer is encrypted for added security.
Any website, especially those requiring login details, should use HTTPS. You can see a padlock icon in the URL bar, which means the page is secure. Browsers, like Google Chrome, treat HTTPS seriously and mark non-HTTPS websites as "Not Secure."
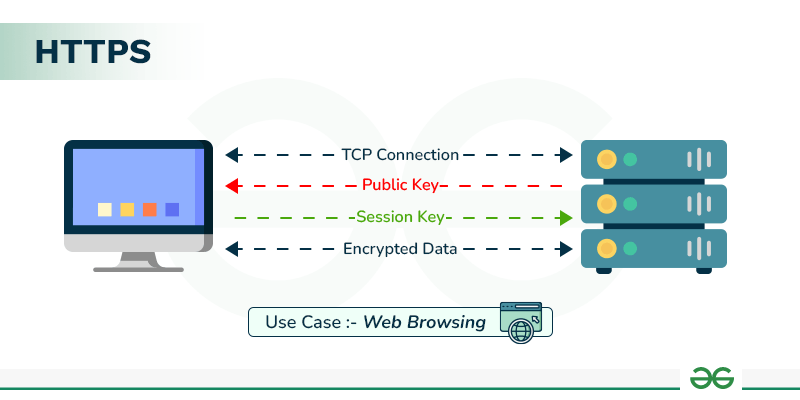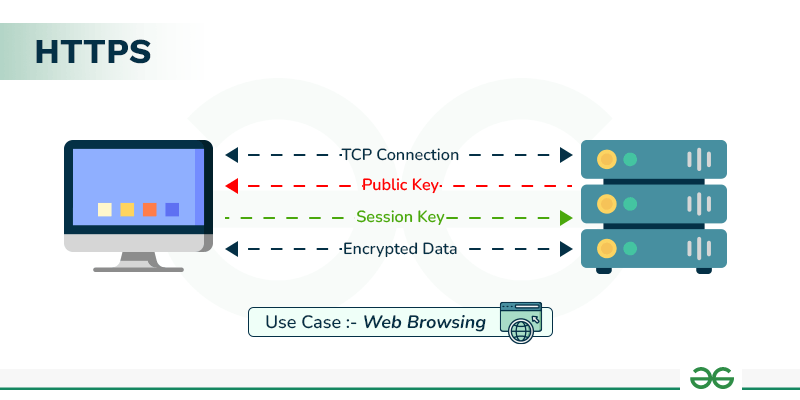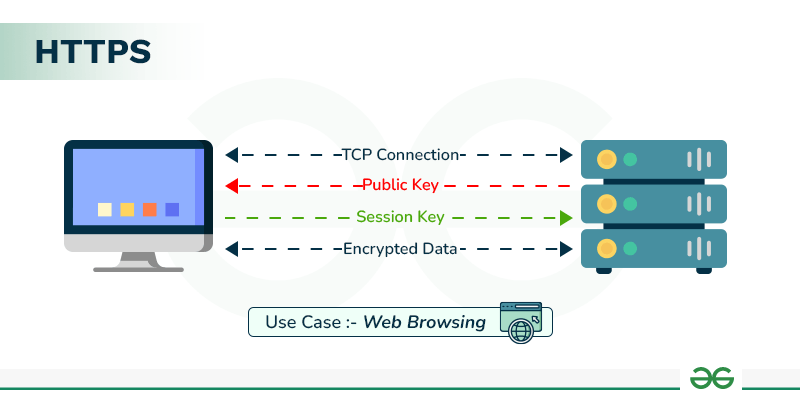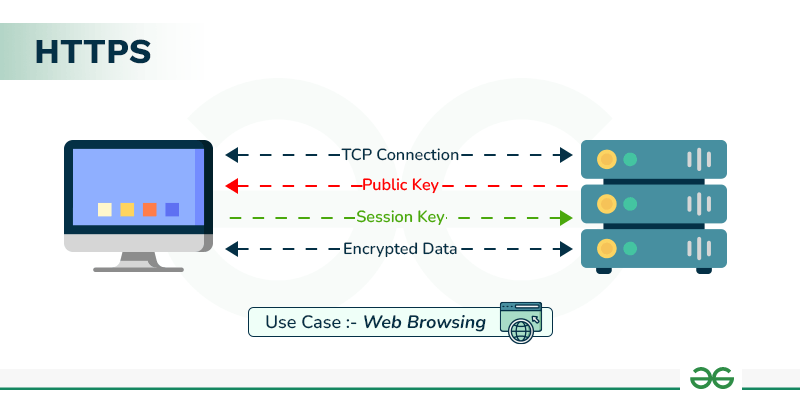
How Does HTTPS Work?
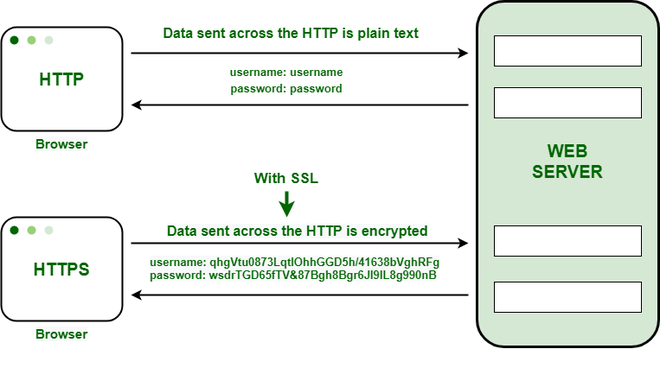
HTTPS establishes the communication between the browser and the web server. It uses the **Secure Socket Layer (SSL) and **Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol for establishing communication. The new version of SSL is **TLS(Transport Layer Security).
HTTPS uses the conventional HTTP protocol and adds a layer of SSL/TLS over it. The workflow of HTTP and HTTPS remains the same, the browsers and servers still communicate with each other using the HTTP protocol. However, this is done over a secure SSL connection. The SSL connection is responsible for the encryption and decryption of the data that is being exchanged to ensure data safety.
Why HTTPS Matters and What Happens Without It?
HTTPS is important because it keeps the information on websites safe from being easily viewed or stolen by anyone who might be spying on the network. When a website uses regular HTTP, data is sent in small chunks called packets that can easily be intercepted using free software. This makes communication, especially over public Wi-Fi, very vulnerable to attacks.
On the other hand, HTTPS encrypts the data, so even if someone manages to intercept the packets, they will appear as random, unreadable characters. For example:
- **Before encryption:
"This is a string of text that is completely readable"
- **After encryption:
"ITM0IRyiEhVpa6VnKyExMiEgNveroyWBPlgGyfkflYjDaaFf/Kn3bo3OfghBPDWo6AfSHlNtL8N7ITEwIXc1gU5X73xMsJormzzXlwOyrCs+9XCPk63Y+z0="
Secure Socket Layer (SSL)
The main responsibility of SSL is to ensure that the data transfer between the communicating systems is **secure and reliable. It is the standard security technology that is used for encryption and decryption of data during the transmission of requests.
As discussed earlier, HTTPS is basically the same old HTTP but with SSL. For establishing a secure communication link between the communicating devices, SSL uses a digital certificate called **SSL certificate.
There are two major roles of the SSL layer
- Ensuring that the browser communicates with the required server directly.
- Ensuring that only the communicating systems have access to the messages they exchange.
Encryption in HTTPS
HTTP transfers data in a hypertext format between the browser and the web server, whereas HTTPS transfers data in an encrypted format. As a result, HTTPS protects websites from having their information broadcast in a way that anyone eavesdropping on the network can easily see. During the transit between the browser and the web server, HTTPS protects the data from being accessed and altered by hackers. Even if the transmission is intercepted, hackers will be unable to use it because the me ssage is encrypted.
It uses an asymmetric public key infrastructure for securing a communication link. There are two different kinds of keys used for encryption -
- **Private Key: It is used for the decryption of the data that has been encrypted by the public key. It resides on the server-side and is controlled by the owner of the website. It is private in nature.
- **Public Key: It is public in nature and is accessible to all the users who communicate with the server. The private key is used for the decryption of the data that has been encrypted by the public key.
Advantage of HTTPS
- **Secure Communication: HTTPS establishes a secure communication link between the communicating system by providing encryption during transmission.
- **Data Integrity: By encrypting the data, HTTPS ensures data integrity. This implies that even if the data is compromised at any point, the hackers won't be able to read or modify the data being exchanged.
- **Privacy and Security: HTTPS prevents attackers from accessing the data being exchanged passively, thereby protecting the privacy and security of the users.
- **Faster Performance: TTPS encrypts the data and reduces its size. Smaller size accounts for faster data transmission in the case of HTTPS.
HTTP vs HTTPS
Below are the basic differences between HTTP and HTTPS.
| HTTP | HTTPS |
|---|---|
| HTTP stands for HyperText Transfer Protocol. | HTTPS stands for HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure. |
| URL begins with “http://”. | URL starts with “https://”. |
| HTTP Works at the Application Layer. | HTTPS works at Transport Layer. |
| HTTP speed is faster than HTTPS. | HTTPS speed is slower than HTTP. |
For more differences between these two, refer to the article Difference between http:// and https://.