Find the kth node in vertical order traversal of a Binary Tree (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 17 Oct, 2024
Given a binary tree and an integer **k, the task is to return the **kth node in the **vertical order traversal of a binary tree. If no such node exists then return **-1.
The vertical order traversal of a binary tree means to print it vertically.
**Examples:
**Input: k = 3
**Output: 1
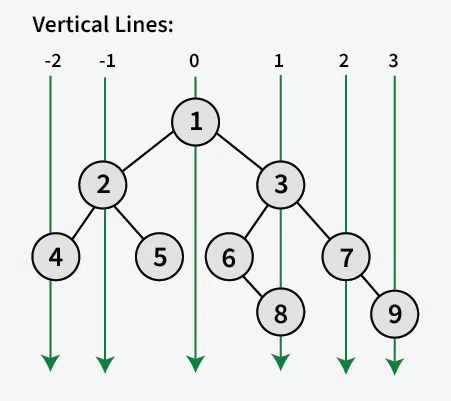
**Explanation: The below image shows the horizontal distances used to print vertical traversal starting from the leftmost level to the rightmost level. The complete vertical order will be 4 2 1 5 6 3 8 7 9.
**Approach:
The idea is to perform vertical order traversal of the binary tree, which involves **visiting nodes column by column from **left to right. Check if the **current node is the **kth node then return its value, if number of nodes in the tree is **less than k then return -1.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++ `
// C++ code of Find the kth node in vertical // order traversal #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;
class Node { public: int data; Node* left; Node* right;
Node(int x) {
data = x;
left = nullptr;
right = nullptr;
}};
// The verticalOrder function to print vertical order // of a binary tree with given root vector verticalOrder(Node* root) {
// Base case
if (!root)
return {};
// Create a map and store vertical order in
// map using function getVerticalOrder()
map<int, vector<int>> mp;
int hd = 0;
// Create queue to do level order traversal.
// Every item of queue contains node and
// horizontal distance.
queue<pair<Node*, int>> q;
q.push(make_pair(root, hd));
while (!q.empty()) {
// pop from queue front
pair<Node*, int> curr = q.front();
q.pop();
hd = curr.second;
Node* node = curr.first;
// insert this node's data in vector of map
mp[hd].push_back(node->data);
if (node->left != nullptr)
q.push(make_pair(node->left, hd - 1));
if (node->right != nullptr)
q.push(make_pair(node->right, hd + 1));
}
vector<int> result;
// Traverse the map and print nodes at
// every horizontal distance (hd)
for (auto& entry : mp) {
for (int key : entry.second)
result.push_back(key);
}
return result;}
int main() {
// Tree structure:
// 1
// / \
// 2 3
// / \ / \
// 4 5 6 7
// \ \
// 8 9
// Create binary tree
Node* root = new Node(1);
root->left = new Node(2);
root->right = new Node(3);
root->left->left = new Node(4);
root->left->right = new Node(5);
root->right->left = new Node(6);
root->right->right = new Node(7);
root->right->left->right = new Node(8);
root->right->right->right = new Node(9);
int k = 5;
vector<int> result = verticalOrder(root);
if(k < result.size()) {
cout << result[k-1];
}
else{
cout << -1;
}
return 0;}
Java
// Java code of Find the kth node in vertical // order traversal
import java.util.*;
class Node { int data; Node left, right;
Node(int x) {
data = x;
left = right = null;
}}
class GfG {
// The verticalOrder function to print vertical order
// of a binary tree with given root
static List<Integer> verticalOrder(Node root) {
// Base case
if (root == null)
return new ArrayList<>();
// Create a map and store vertical order in
// map using function getVerticalOrder()
Map<Integer, List<Integer>> mp = new TreeMap<>();
int hd = 0;
// Create queue to do level order traversal.
// Every item of queue contains node and
// horizontal distance.
Queue<Pair> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(new Pair(root, hd));
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
// pop from queue front
Pair curr = q.poll();
hd = curr.hd;
Node node = curr.node;
// insert this node's data in vector of map
if (!mp.containsKey(hd)) {
mp.put(hd, new ArrayList<>());
}
mp.get(hd).add(node.data);
if (node.left != null)
q.add(new Pair(node.left, hd - 1));
if (node.right != null)
q.add(new Pair(node.right, hd + 1));
}
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
// Traverse the map and print nodes at
// every horizontal distance (hd)
for (Map.Entry<Integer,
List<Integer>> entry : mp.entrySet()) {
result.addAll(entry.getValue());
}
return result;
}
static class Pair {
Node node;
int hd;
Pair(Node node, int hd) {
this.node = node;
this.hd = hd;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Tree structure:
// 1
// / \
// 2 3
// / \ / \
// 4 5 6 7
// \ \
// 8 9
// Create binary tree
Node root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.right.left = new Node(6);
root.right.right = new Node(7);
root.right.left.right = new Node(8);
root.right.right.right = new Node(9);
int k = 5;
List<Integer> result = verticalOrder(root);
if (k < result.size()) {
System.out.println(result.get(k - 1));
}
else{
System.out.println(-1);
}
}}
Python
Python code of Find the kth node in vertical
order traversal
from collections import deque, defaultdict
class Node: def init(self, x): self.data = x self.left = None self.right = None
The verticalOrder function to print vertical order
of a binary tree with given root
def verticalOrder(root):
# Base case
if not root:
return []
# Create a map and store vertical order in
# map using function getVerticalOrder()
m = defaultdict(list)
hd = 0
# Create queue to do level order traversal.
# Every item of queue contains node and
# horizontal distance.
q = deque([(root, hd)])
while q:
# pop from queue front
curr = q.popleft()
node = curr[0]
hd = curr[1]
# insert this node's data in
# vector of map
m[hd].append(node.data)
if node.left is not None:
q.append((node.left, hd - 1))
if node.right is not None:
q.append((node.right, hd + 1))
result = []
# Traverse the map and print nodes at
# every horizontal distance (hd)
for key in sorted(m):
result.extend(m[key])
return resultif name == 'main':
# Tree structure:
# 1
# / \
# 2 3
# / \ / \
# 4 5 6 7
# \ \
# 8 9
# Create binary tree
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(5)
root.right.left = Node(6)
root.right.right = Node(7)
root.right.left.right = Node(8)
root.right.right.right = Node(9)
k = 5
result = verticalOrder(root)
if k < len(result):
print(result[k-1])
else:
print(-1)C#
// C# code of Find the kth node in // vertical order traversal
using System; using System.Collections.Generic;
class Node { public int data; public Node left, right;
public Node(int x) {
data = x;
left = right = null;
}}
class GfG {
// The verticalOrder function to print vertical order
// of a binary tree with given root
static List<int> verticalOrder(Node root) {
// Base case
if (root == null)
return new List<int>();
// Create a map and store vertical order in
// map using function getVerticalOrder()
SortedDictionary<int, List<int>> map =
new SortedDictionary<int, List<int>>();
int hd = 0;
// Create queue to do level order traversal.
// Every item of queue contains node and
// horizontal distance.
Queue<(Node, int)> q = new Queue<(Node, int)>();
q.Enqueue((root, hd));
while (q.Count > 0) {
// pop from queue front
var curr = q.Dequeue();
hd = curr.Item2;
Node node = curr.Item1;
// insert this node's data in
// vector of map
if (!map.ContainsKey(hd)) {
map[hd] = new List<int>();
}
map[hd].Add(node.data);
if (node.left != null)
q.Enqueue((node.left, hd - 1));
if (node.right != null)
q.Enqueue((node.right, hd + 1));
}
List<int> result = new List<int>();
// Traverse the map and print nodes at
// every horizontal distance (hd)
foreach (var entry in map) {
result.AddRange(entry.Value);
}
return result;
}
static void Main() {
// Tree structure:
// 1
// / \
// 2 3
// / \ / \
// 4 5 6 7
// \ \
// 8 9
// Create binary tree
Node root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.right.left = new Node(6);
root.right.right = new Node(7);
root.right.left.right = new Node(8);
root.right.right.right = new Node(9);
int k = 5;
List<int> result = verticalOrder(root);
if (k < result.Count) {
Console.WriteLine(result[k - 1]);
}
else {
Console.WriteLine(-1);
}
}}
JavaScript
// Javascript code of Find the kth node in // vertical order traversal class Node { constructor(x) { this.data = x; this.left = null; this.right = null; } }
// The verticalOrder function to print vertical order // of a binary tree with given root function verticalOrder(root) {
// Base case
if (!root) return [];
// Create a map and store vertical order in
// map using function getVerticalOrder()
let m = new Map();
let hd = 0;
// Create queue to do level order traversal.
// Every item of queue contains node and
// horizontal distance.
let q = [];
let index = 0;
q.push({ node: root, hd: hd });
while (index < q.length) {
// pop from queue front
let curr = q[index++];
let node = curr.node;
hd = curr.hd;
// insert this node's data in
// vector of map
if (!m.has(hd)) {
m.set(hd, []);
}
m.get(hd).push(node.data);
if (node.left !== null) {
q.push({ node: node.left, hd: hd - 1 });
}
if (node.right !== null) {
q.push({ node: node.right, hd: hd + 1 });
}
}
let result = [];
// Traverse the map and print nodes at
// every horizontal distance (hd)
[...m.keys()].sort((a, b) => a - b).forEach(key => {
result.push(...m.get(key));
});
return result;}
// Tree structure:
// 1
// /
// 2 3
// / \ /
// 4 5 6 7
// \
// 8 9
const root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.right.left = new Node(6);
root.right.right = new Node(7);
root.right.left.right = new Node(8);
root.right.right.right = new Node(9);
const k = 5;
const result = verticalOrder(root);
if (k <= result.length) { console.log(result[k - 1]); } else { console.log("-1"); }
`
**Time Complexity: O(n log n), where **n is the number of nodes in a tree.
**Auxiliary Space: O(n)