Flatten a multilevel linked list using level order traversal (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 03 Oct, 2024
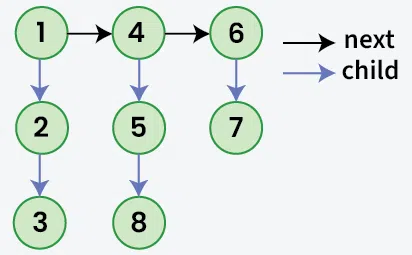
Given a linked list where in addition to the **next pointer, each node has a **child pointer, which may or may not point to a separate list. These child lists may have **one or more children of their own to produce a **multilevel linked list. Given the **head of the **first level of the list. The task is to **flatten the list so that all the nodes appear in a **single-level linked list. Flatten the list in a way that all nodes at the first level should come **first, then nodes of the **second level, and so on.
**Examples:
**Input:
**Output: 1->4->6->2->5->7->3->8
**Explanation: The multilevel linked list is flattened as it has no child pointers.
**Approach:
To **flatten a multilevel linked list, start from the **top level and process each node **sequentially. For each node, if it has a child node, **append this child node to the **end of the **current list. Continue this process for every node, updating the **end of the list accordingly, until all nodes are processed and the list is flattened.
Step by step implementation:
- Initialize **curr and **tail pointer points to **head node initially.
- Start traversing from the first level and set the **tail to the **last node.
- Start traversing from **curr horizontally until curr is not **NULL:
- If curr->child is not equal to NULL, then **append the child list to the end of the resultant list by using tail->next = curr->child. Traverse the child list horizontally , and set **tail to the last node of the child list. Set **curr->child = NULL to remove the link.
- Move the **curr pointer to the **next node in the list.
- Return the **head node.
Following is the implementation of the above algorithm.
C++ `
// C++ Program to flatten list with // next and child pointers #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;
class Node { public: int data; Node *next; Node *child; Node (int x) { data = x; next = nullptr; child = nullptr; } };
// function that flattens // a multilevel linked list void flattenList(Node *head) {
// Base case
if (head == nullptr)
return;
// Find tail node of first level
Node *tail = head;
while (tail->next != nullptr)
tail = tail->next;
// One by one traverse through all nodes of first level
// linked list till we reach the tail node
Node *curr = head;
while (curr != nullptr) {
// If current node has a child
if (curr->child) {
// then append the child at the end of current list
tail->next = curr->child;
// and update the tail to new last node
Node* tmp = curr->child;
while (tmp->next)
tmp = tmp->next;
tail = tmp;
// Remove link between curr and child node
curr->child = nullptr;
}
// Change current node
curr = curr->next;
} }
void printList(Node head) { Node curr = head; while (curr != NULL) { cout << curr->data << " "; curr = curr->next; } cout<<endl; }
int main() {
//Linked List -
// 1 -> 2 -> 3
// | |
// 4 -> 5 6
// |
// 7
Node *head = new Node(1);
head->next = new Node(2);
head->next->next = new Node(3);
head->child = new Node(4);
head->child->next = new Node(5);
head->next->next->child = new Node(6);
head->child->child = new Node(7);
flattenList(head);
printList(head);
return 0; }
C
// C Program to flatten list with // next and child pointers #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h>
struct Node { int data; struct Node* next; struct Node* child; };
// function that flattens // a multilevel linked list void flattenList(struct Node *head) {
// Base case
if (head == NULL)
return;
// Find tail node of first level
struct Node *tail = head;
while (tail->next != NULL)
tail = tail->next;
// One by one traverse through all nodes of first level
// linked list till we reach the tail node
struct Node *curr = head;
while (curr != NULL) {
// If current node has a child
if (curr->child) {
// then append the child at the end of current list
tail->next = curr->child;
// and update the tail to new last node
struct Node *tmp = curr->child;
while (tmp->next)
tmp = tmp->next;
tail = tmp;
// Remove link between curr and child node
curr->child = NULL;
}
// Change current node
curr = curr->next;
}}
void printList(struct Node* head) { struct Node* curr = head; while (curr != NULL) { printf("%d ", curr->data); curr = curr->next; } printf("\n"); }
struct Node* createNode(int new_data) { struct Node* new_node = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); new_node->data = new_data; new_node->next = new_node->child = NULL; return new_node; }
int main() {
//Linked List -
// 1 -> 2 -> 3
// | |
// 4 -> 5 6
// |
// 7
struct Node *head = createNode(1);
head->next = createNode(2);
head->next->next = createNode(3);
head->child = createNode(4);
head->child->next = createNode(5);
head->next->next->child = createNode(6);
head->child->child = createNode(7);
flattenList(head);
printList(head);
return 0;}
Java
// Java Program to flatten list with // next and child pointers
class Node { int data; Node next, child;
Node(int x) {
data = x;
next = null;
child = null;
}}
public class GfG {
// function that flattens
// a multilevel linked list
static void flattenList(Node head) {
// Base case
if (head == null)
return;
// Find tail node of first level
Node tail = head;
while (tail.next != null)
tail = tail.next;
// One by one traverse through all nodes of first level
Node curr = head;
while (curr != null) {
// If current node has a child
if (curr.child != null) {
// then append the child at the end of current list
tail.next = curr.child;
// and update the tail to new last node
Node tmp = curr.child;
while (tmp.next != null)
tmp = tmp.next;
tail = tmp;
// Remove link between curr and child node
curr.child = null;
}
// Change current node
curr = curr.next;
}
}
static void printList(Node head) {
Node curr = head;
while (curr != null) {
System.out.print(curr.data + " ");
curr = curr.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Linked List -
// 1 -> 2 -> 3
// | |
// 4 -> 5 6
// |
// 7
Node head = new Node(1);
head.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next = new Node(3);
head.child = new Node(4);
head.child.next = new Node(5);
head.next.next.child = new Node(6);
head.child.child = new Node(7);
flattenList(head);
printList(head);
}}
Python
Python Program to flatten list with
next and child pointers
class Node: def init(self, new_value): self.data = new_value self.next = None self.child = None
function that flattens
a multilevel linked list
def flatten_list(head):
# Base case
if head is None:
return
# Find tail node of first level
tail = head
while tail.next is not None:
tail = tail.next
# traverse through all nodes of first level
curr = head
while curr != None:
# If current node has a child
if curr.child is not None:
# then append the child at the end of current list
tail.next = curr.child
# and update the tail to new last node
tmp = curr.child
while tmp.next is not None:
tmp = tmp.next
tail = tmp
# Remove link between curr and child node
curr.child = None
# Change current node
curr = curr.nextdef print_list(head): curr = head while curr is not None: print(curr.data, end=" ") curr = curr.next print()
if name == "main":
#Linked List -
# 1 -> 2 -> 3
# | |
# 4 -> 5 6
# |
# 7
head = Node(1)
head.next = Node(2)
head.next.next = Node(3)
head.child = Node(4)
head.child.next = Node(5)
head.next.next.child = Node(6)
head.child.child = Node(7)
flatten_list(head)
print_list(head)C#
// C# Program to flatten list with // next and child pointers using System;
class Node { public int data; public Node next, child;
public Node(int x) {
data = x;
next = null;
child = null;
}}
class GfG {
// function that flattens
// a multilevel linked list
static void FlattenList(Node head) {
// Base case
if (head == null)
return;
// Find tail node of first level
Node tail = head;
while (tail.next != null)
tail = tail.next;
// traverse through all nodes of first level
Node curr = head;
while (curr != null) {
// If current node has a child
if (curr.child != null) {
// then append the child at the end of current list
tail.next = curr.child;
// and update the tail to new last node
Node tmp = curr.child;
while (tmp.next != null)
tmp = tmp.next;
tail = tmp;
// Remove link between curr and child node
curr.child = null;
}
// Change current node
curr = curr.next;
}
}
static void PrintList(Node head) {
Node curr = head;
while (curr != null) {
Console.Write(curr.data + " ");
curr = curr.next;
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
static void Main(string[] args) {
//Linked List -
// 1 -> 2 -> 3
// | |
// 4 -> 5 6
// |
// 7
Node head = new Node(1);
head.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next = new Node(3);
head.child = new Node(4);
head.child.next = new Node(5);
head.next.next.child = new Node(6);
head.child.child = new Node(7);
FlattenList(head);
PrintList(head);
}}
JavaScript
// JavaScript Program to flatten list with // next and child pointers
class Node { constructor(new_value) { this.data = new_value; this.next = null; this.child = null; } }
// function that flattens // a multilevel linked list function flattenList(head) {
// Base case
if (head === null)
return;
// Find tail node of first level
let tail = head;
while (tail.next !== null)
tail = tail.next;
// traverse through all nodes of first level
let curr = head;
while (curr !== null) {
// If current node has a child
if (curr.child !== null) {
// then append the child at the end of current list
tail.next = curr.child;
// and update the tail to new last node
let tmp = curr.child;
while (tmp.next !== null)
tmp = tmp.next;
tail = tmp;
// Remove link between curr and child node
curr.child = null;
}
// Change current node
curr = curr.next;
}}
function printList(head) { let curr = head; while (curr !== null) { console.log(curr.data); curr = curr.next; } }
//Linked List -
// 1 -> 2 -> 3
// | |
// 4 -> 5 6
// |
// 7
let head = new Node(1);
head.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next = new Node(3);
head.child = new Node(4);
head.child.next = new Node(5);
head.next.next.child = new Node(6);
head.child.child = new Node(7);
flattenList(head); printList(head);
`
**Time Complexity: O(n), where **n is the number of nodes in the list.
**Auxiliary Space: O(1)