Generating all possible Subsequences using Recursion including the empty one. (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 26 Nov, 2024
Given an **array arr[]. The task is to find all the **possible subsequences of the given array using recursion.
**Examples:
**Input: arr[] = [1, 2, 3]
**Output : [3], [2], [2, 3], [1], [1, 3], [1, 2], [1, 2, 3], []**Input: arr[] = [1, 2]
**Output : [2], [1], [1, 2], []
**Approach:
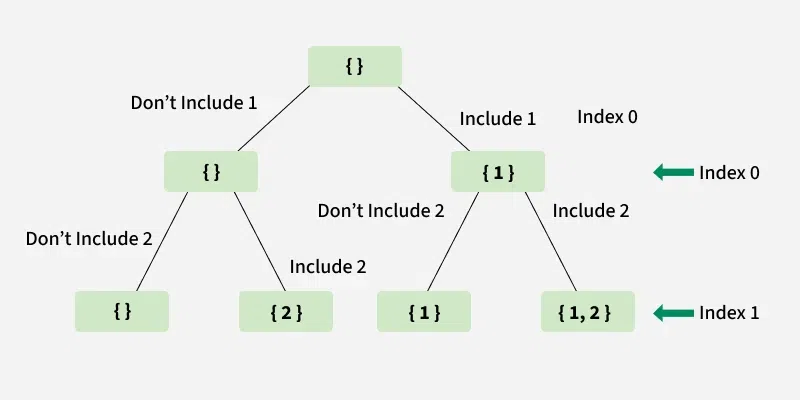
For **every element in the array, there are **two choices, **either to **include it in the **subsequence or **not include it. Apply this for **every element in the array starting from **index 0 until we reach the last index. Print the **subsequence once the last index is reached.
The below diagram shows the **recursion tree for array, arr[] = [1, 2].
C++ `
// C++ code to find all possible // subsequences for given array using // recursion
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;
void findSubsequences(int curr, vector &arr, vector &subarr, vector<vector> &res) {
// Base case: When we reach the end of the array, // add the current subsequence to the result if (curr == arr.size()) { res.push_back(subarr); return; }
// Include the current element in the subsequence
subarr.push_back(arr[curr]);
// Recurse to the next element
findSubsequences(curr + 1, arr, subarr, res);
// Backtrack: Remove the current element and explore// the next possibility subarr.pop_back();
// Do not include the current element
// in the subsequence
findSubsequences(curr + 1, arr, subarr, res);}
int main() { vector arr = {1, 2, 3}; int n = arr.size();
vector<int> subarr;
vector<vector<int>> res;
findSubsequences(0, arr, subarr, res);
for (int i = 0; i < res.size(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < res[i].size(); j++) {
cout << res[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;}
Java
// Java code to find all possible // subsequences for given array using // recursion
import java.util.*;
class GfG {
static void findSubsequences(int curr, int[] arr,
List<Integer> subarr,
List<List<Integer> > res) {
// Base case: When we reach the end of the array,
// add the current subsequence to the result
if (curr == arr.length) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(
subarr));
return;
}
// Include the current element in
// the subsequence
subarr.add(arr[curr]);
// Recurse to the next element
findSubsequences(
curr + 1, arr, subarr,
res);
// Backtrack: Remove the current element and explore
// the next possibility
subarr.remove(subarr.size() - 1);
// Do not include the current
// element in the subsequence
findSubsequences(
curr + 1, arr, subarr,
res);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = { 1, 2, 3 };
List<Integer> subarr = new ArrayList<>();
List<List<Integer> > res = new ArrayList<>();
findSubsequences(0, arr, subarr, res);
for (List<Integer> subsequence : res) {
for (int num : subsequence) {
System.out.print(num + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}}
Python
Python program to find all possible
subsequences for given array using
recursion
def findSubsequences(curr, arr, subArr, res):
# Base case: When we reach the end of the array,
# add the current subsequence to the result
if curr == len(arr):
res.append(subArr.copy())
return
# Include the current element in the subsequence
subArr.append(arr[curr])
# Recurse to the next element
findSubsequences(curr + 1, arr, subArr, res)
# Backtrack: Remove the current element and
# explore the next possibility
subArr.pop()
# Do not include the current element in the subsequence
findSubsequences(curr + 1, arr, subArr, res)if name == "main": arr = [1, 2, 3]
# Temporary list to store the
# current subsequence
subArr = []
# Resultant list to store all subsequences
res = []
# Call the function to find all subsequences
# starting from index 0
findSubsequences(0, arr, subArr, res)
for subsequence in res:
print(" ".join(map(str, subsequence)))C#
// C# code to find all possible // subsequences for given array using // recursion
using System; using System.Collections.Generic;
class GfG {
static void findSubsequences(int curr, int[] arr,
List<int> subArr,
List<List<int> > res) {
// Base case: When we reach the end of the array,
// add the current subsequence to the result
if (curr == arr.Length) {
res.Add(new List<int>(subArr));
return;
}
// Include the current element in
// the subsequence
subArr.Add(arr[curr]);
// Recurse to the next element
findSubsequences(curr + 1, arr, subArr, res);
// Backtrack: Remove the current element and explore
// the next possibility
subArr.RemoveAt(subArr.Count - 1);
// Do not include the current
// element in the subsequence
findSubsequences(curr + 1, arr, subArr, res);
}
static void Main() {
int[] arr = { 1, 2, 3 };
// Temporary list to store the current subsequence
List<int> subArr = new List<int>();
// Resultant list to store all subsequences
List<List<int> > res = new List<List<int> >();
// Call the function to find all subsequences
// starting from index 0
findSubsequences(0, arr, subArr, res);
foreach(var subsequence in res) {
Console.WriteLine(
string.Join(" ", subsequence));
}
}}
JavaScript
// JavaScript code to find all possible // subsequences for given array using // recursion
function findSubsequences(curr, arr, subArr, res) {
// Base case: When we reach the end of the array, add
// the current subsequence to the result
if (curr === arr.length) {
res.push([...subArr ]);
return;
}
// Include the current element in the
// subsequence
subArr.push(arr[curr]);
// Recurse to the next element
findSubsequences(curr + 1, arr, subArr, res);
// Backtrack: Remove the current element and explore the
// next possibility
subArr.pop();
// Do not include the current element in
// the subsequence
findSubsequences(curr + 1, arr, subArr, res);}
const arr = [ 1, 2, 3 ];
let subArr = []; let res = [];
findSubsequences(0, arr, subArr, res);
res.forEach(subsequence => { console.log(subsequence.join( " ")); });
`
Output
1 2 3 1 2 1 3 1 2 3 2 3
**Time complexity: O(2^n)
**Auxiliary Space: O(n)
**Related article: