Level of a Node in Binary Tree (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 29 Sep, 2024
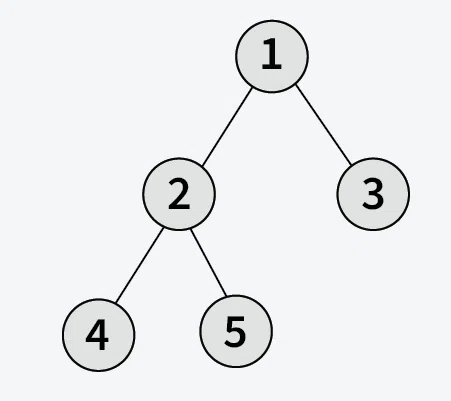
Given a **Binary Tree and a **key, the task is to find the **level of key in the Binary Tree.
**Examples:
**Input : key = 4
**Output: 3
**Explanation: The level of the key in above binary tree is 3.**Input : key = 10
**Output: -1
**Explanation: Key is not present in the above Binary tree.
Table of Content
- [Expected Approach - 1] Using Recursion - O(n) Time and O(h) Space
- [Expected Approach - 2] Using Level Order Traversal- O(n) Time and O(n) Space
**[Expected Approach - 1] Using Recursion - O(n) Time and O(h) Space
The idea is to start from the **root and level as 1. If the target matches with root's data, return **level. Else **recursively call for left and right subtrees with level as **level + 1.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++ `
// C++ code to find level of a Node in Binary Tree
#include using namespace std;
class Node { public: int data; Node* left; Node* right;
Node(int val) {
data = val;
left = right = nullptr;
}};
// Recursive function to find the level of the target key int getLevel(Node* root, int target, int level) { if (root == nullptr) { return -1; }
// If the target key matches the current node's
// data, return the level
if (root->data == target) {
return level;
}
// Recursively call for left and right subtrees
int leftLevel = getLevel(root->left, target, level + 1);
if (leftLevel != -1) {
return leftLevel;
}
return getLevel(root->right, target, level + 1);}
int main() {
// Creating a sample binary tree:
// 1
// / \
// 2 3
// / \ / \
// 4 5 6 7
Node* root = new Node(1);
root->left = new Node(2);
root->right = new Node(3);
root->left->left = new Node(4);
root->left->right = new Node(5);
root->right->left = new Node(6);
root->right->right = new Node(7);
int target = 5;
cout << getLevel(root, target, 1) << endl;
return 0;}
C
// C code to find level of a Node in Binary Tree
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h>
struct Node { int data; struct Node* left; struct Node* right; };
int getLevel(struct Node* root, int target, int level) { if (root == NULL) { return -1; }
// If the target key matches the current node's data, return the level
if (root->data == target) {
return level;
}
// Recursively call for left and right subtrees
int leftLevel = getLevel(root->left, target, level + 1);
if (leftLevel != -1) {
return leftLevel;
}
return getLevel(root->right, target, level + 1);}
struct Node* createNode(int val) { struct Node* newNode = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); newNode->data = val; newNode->left = newNode->right = NULL; return newNode; }
int main() {
// Creating a sample binary tree:
// 1
// / \
// 2 3
// / \ / \
// 4 5 6 7
struct Node* root = createNode(1);
root->left = createNode(2);
root->right = createNode(3);
root->left->left = createNode(4);
root->left->right = createNode(5);
root->right->left = createNode(6);
root->right->right = createNode(7);
int target = 5;
printf("%d\n", getLevel(root, target, 1));
return 0;}
Java
// Java code to find level of a Node in Binary Tree
class Node { int data; Node left, right;
Node(int val) {
data = val;
left = right = null;
}}
class GfG {
// Recursive function to find the level of the target key
static int getLevel(Node root, int target, int level) {
if (root == null) {
return -1;
}
// If the target key matches the current node's
// data, return the level
if (root.data == target) {
return level;
}
// Recursively call for left and right subtrees
int leftLevel = getLevel(root.left, target, level + 1);
if (leftLevel != -1) {
return leftLevel;
}
return getLevel(root.right, target, level + 1);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating a sample binary tree:
// 1
// / \
// 2 3
// / \ / \
// 4 5 6 7
Node root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.right.left = new Node(6);
root.right.right = new Node(7);
int target = 5;
System.out.println(getLevel(root, target, 1));
}}
Python
Python code to find level of a Node in Binary Tree
class Node: def init(self, val): self.data = val self.left = None self.right = None
Recursive function to find the level of the target key
def getLevel(root, target, level): if root is None: return -1
# If the target key matches the current node's
# data, return the level
if root.data == target:
return level
# Recursively call for left and right subtrees
leftLevel = getLevel(root.left, target, level + 1)
if leftLevel != -1:
return leftLevel
return getLevel(root.right, target, level + 1)if name == "main":
# Creating a sample binary tree:
# 1
# / \
# 2 3
# / \ / \
# 4 5 6 7
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(5)
root.right.left = Node(6)
root.right.right = Node(7)
target = 5
print(getLevel(root, target, 1))C#
// C# code to find level of a Node in Binary Tree
using System;
class Node { public int Data; public Node Left; public Node Right;
public Node(int val) {
Data = val;
Left = Right = null;
}}
class GfG {
// Recursive function to find the level of the target key
static int GetLevel(Node root, int target, int level) {
if (root == null) {
return -1;
}
// If the target key matches the current
// node's data, return the level
if (root.Data == target) {
return level;
}
// Recursively call for left and right subtrees
int leftLevel = GetLevel(root.Left, target, level + 1);
if (leftLevel != -1) {
return leftLevel;
}
return GetLevel(root.Right, target, level + 1);
}
static void Main() {
// Creating a sample binary tree:
// 1
// / \
// 2 3
// / \ / \
// 4 5 6 7
Node root = new Node(1);
root.Left = new Node(2);
root.Right = new Node(3);
root.Left.Left = new Node(4);
root.Left.Right = new Node(5);
root.Right.Left = new Node(6);
root.Right.Right = new Node(7);
int target = 5;
Console.WriteLine(GetLevel(root, target, 1));
}}
JavaScript
// Javascript code to find level of a Node // in Binary Tree
class Node { constructor(val) { this.data = val; this.left = null; this.right = null; } }
// Recursive function to find the level of the target key function getLevel(root, target, level) { if (root === null) { return -1; }
// If the target key matches the current node's
// data, return the level
if (root.data === target) {
return level;
}
// Recursively call for left and right subtrees
let leftLevel = getLevel(root.left, target, level + 1);
if (leftLevel !== -1) {
return leftLevel;
}
return getLevel(root.right, target, level + 1);}
// Creating a sample binary tree:
// 1
// /
// 2 3
// / \ /
// 4 5 6 7
const root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.right.left = new Node(6);
root.right.right = new Node(7);
const target = 5; console.log(getLevel(root, target, 1));
`
**Time Complexity: O(n), where **n is the number of nodes in the binary tree.
**Auxiliary Space: O(h), where **h is height of binary tree.
**[Expected Approach - 2] Using Level Order Traversal- O(n) Time and O(n) Space
The idea is to perform a level-order traversal and keep track of the **current level as we traverse the tree. If the **key matches with root's data, return level.
C++ `
// C++ code to find level of a Node in Binary Tree
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;
class Node { public: int data; Node* left; Node* right;
Node(int val) {
data = val;
left = right = nullptr;
}};
// Function to find the level of the target key int getLevel(Node* root, int target) { if (root == nullptr) { return -1; }
// Create a queue for level-order // traversal queue<Node*> q; q.push(root); int level = 1;
while (!q.empty()) {
int size = q.size();
// Process all nodes at the current level
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Node* curr = q.front();
q.pop();
// Check if the current node matches the target
if (curr->data == target) {
return level;
}
// Push the left and right children to the queue
if (curr->left != nullptr) {
q.push(curr->left);
}
if (curr->right != nullptr) {
q.push(curr->right);
}
}
level++;
}
return -1;}
int main() {
// Creating a sample binary tree:
// 1
// / \
// 2 3
// / \ / \
// 4 5 6 7
Node* root = new Node(1);
root->left = new Node(2);
root->right = new Node(3);
root->left->left = new Node(4);
root->left->right = new Node(5);
root->right->left = new Node(6);
root->right->right = new Node(7);
int target = 5;
cout << getLevel(root, target);
return 0;}
Java
// Java code to find level of a Node // in Binary Tree
import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue;
class Node { int data; Node left, right;
Node(int val) {
data = val;
left = right = null;
}}
// Function to find the level of // the target key class GfG {
static int getLevel(Node root, int target) {
if (root == null) {
return -1;
}
// Create a queue for level-order traversal
Queue<Node> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(root);
int level = 1;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int size = q.size();
// Process all nodes at the current level
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Node curr = q.poll();
// Check if the current node matches the target
if (curr.data == target) {
return level;
}
// Push the left and right children to the queue
if (curr.left != null) {
q.add(curr.left);
}
if (curr.right != null) {
q.add(curr.right);
}
}
level++;
}
return -1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating a sample binary tree:
// 1
// / \
// 2 3
// / \ / \
// 4 5 6 7
Node root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.right.left = new Node(6);
root.right.right = new Node(7);
int target = 5;
System.out.println(getLevel(root, target));
}}
Python
Python code to find level of a Node in Binary Tree
class Node: def init(self, val): self.data = val self.left = None self.right = None
Function to find the level of the target key
def getLevel(root, target): if root is None: return -1
# Create a queue for level-order traversal
q = []
q.append(root)
level = 1
while len(q) > 0:
size = len(q)
# Process all nodes at the current level
for i in range(size):
curr = q.pop(0)
# Check if the current node matches the target
if curr.data == target:
return level
# Push the left and right children to the queue
if curr.left is not None:
q.append(curr.left)
if curr.right is not None:
q.append(curr.right)
level += 1
return -1if name == "main":
# Creating a sample binary tree:
# 1
# / \
# 2 3
# / \ / \
# 4 5 6 7
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(5)
root.right.left = Node(6)
root.right.right = Node(7)
target = 5
print(getLevel(root, target))C#
// C# code to find level of a Node in Binary Tree
using System; using System.Collections.Generic;
class Node { public int data; public Node left, right;
public Node(int val) {
data = val;
left = right = null;
}}
class GfG {
// Function to find the level of the target key
static int GetLevel(Node root, int target) {
if (root == null) {
return -1;
}
// Create a queue for level-order traversal
Queue<Node> q = new Queue<Node>();
q.Enqueue(root);
int level = 1;
while (q.Count > 0) {
int size = q.Count;
// Process all nodes at the current level
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Node curr = q.Dequeue();
// Check if the current node matches the target
if (curr.data == target) {
return level;
}
// Push the left and right children to the queue
if (curr.left != null) {
q.Enqueue(curr.left);
}
if (curr.right != null) {
q.Enqueue(curr.right);
}
}
level++;
}
return -1;
}
static void Main(string[] args) {
// Creating a sample binary tree:
// 1
// / \
// 2 3
// / \ / \
// 4 5 6 7
Node root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.right.left = new Node(6);
root.right.right = new Node(7);
int target = 5;
Console.WriteLine(GetLevel(root, target));
}}
JavaScript
// Javascript code to find level of // a Node in Binary Tree
class Node { constructor(val) { this.data = val; this.left = this.right = null; } }
// Function to find the level of the target key function getLevel(root, target) { if (root === null) { return -1; }
// Create a queue for level-order traversal
let q = [];
q.push(root);
let level = 1;
while (q.length > 0) {
let size = q.length;
// Process all nodes at the current level
for (let i = 0; i < size; i++) {
let curr = q.shift();
// Check if the current node matches the target
if (curr.data === target) {
return level;
}
// Push the left and right children to the queue
if (curr.left !== null) {
q.push(curr.left);
}
if (curr.right !== null) {
q.push(curr.right);
}
}
level++;
}
return -1;}
// Creating the binary tree
// 1
// /
// 2 3
// / \ /
// 4 5 6 7
let root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.right.left = new Node(6);
root.right.right = new Node(7);
let target = 5; console.log(getLevel(root, target));
`
**Time Complexity: O(n), where n is the number of nodes in the binary tree.
**Auxiliary Space: O(n)