How to Convert Floats to Strings in Pandas DataFrame? (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 20 Aug, 2020
In this post, we’ll see different ways to Convert Floats to Strings in Pandas Dataframe? Pandas Dataframe provides the freedom to change the data type of column values. We can change them from Integers to Float type, Integer to String, String to Integer, Float to String, etc.
There are three methods to convert Float to String:
Method 1: Using DataFrame.astype().
Syntax :
DataFrame.astype(dtype, copy=True, errors=’raise’, **kwargs)
This is used to cast a pandas object to a specified dtype. This function also provides the capability to convert any suitable existing column to categorical type.
Example 1: Converting one column from float to string.
Python3
import pandas as pd
data = [[ 'Harvey' , 10 , 45.25 ], [ 'Carson' , 15 , 54.85 ],
`` [ 'juli' , 14 , 87.21 ], [ 'Ricky' , 20 , 45.23 ],
`` [ 'Gregory' , 21 , 77.25 ], [ 'Jessie' , 16 , 95.21 ]]
df = pd.DataFrame(data, columns = [ 'Name' , 'Age' , 'Marks' ],
`` index = [ 'a' , 'b' , 'c' , 'd' , 'e' , 'f' ])
print (df.dtypes)
Output:

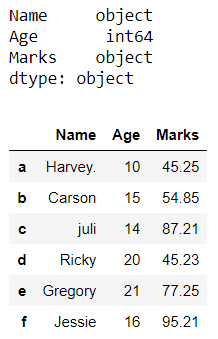
Now, we change the data type of column ‘Marks’ from ‘float64’ to ‘object’.
Python3
df[ 'Marks' ] = df[ 'Marks' ].astype( str )
print ()
print (df.dtypes)
df
Output:
Example 2: Converting more than one column from float to string.
Python3
import pandas as pd
data = [[ 'Harvey.' , 10.5 , 45.25 , 95.2 ], [ 'Carson' , 15.2 , 54.85 , 50.8 ],
`` [ 'juli' , 14.9 , 87.21 , 60.4 ], [ 'Ricky' , 20.3 , 45.23 , 99.5 ],
`` [ 'Gregory' , 21.1 , 77.25 , 90.9 ], [ 'Jessie' , 16.4 , 95.21 , 10.85 ]]
df = pd.DataFrame(data, columns = [ 'Name' , 'Age' , 'Marks' , 'Accuracy' ],
`` index = [ 'a' , 'b' , 'c' , 'd' , 'e' , 'f' ])
print (df.dtypes)
Output:

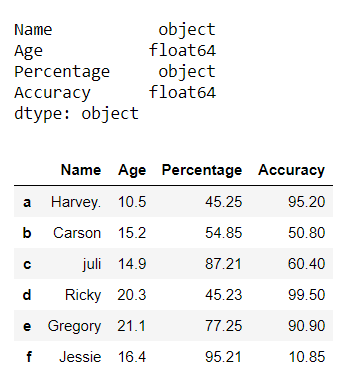
Now, we change the data type of columns ‘Accuracy‘ and ‘Age‘ from ‘float64’ to ‘object’.
Python3
df = df.astype({ "Age" : 'str' , "Accuracy" : 'str' })
print ()
print (df.dtypes)
df
Output:

Method 2: Using Series.apply().
Syntax :
DataFrame.apply(func, axis=0, raw=False, result_type=None, args=(), **kwds)
This method allows the users to pass a function and apply it on every single value of the Pandas series.
Example: Converting column of a Dataframe from float to string.
Python3
import pandas as pd
data = [[ 'Harvey.' , 10.5 , 45.25 , 95.2 ], [ 'Carson' , 15.2 , 54.85 , 50.8 ],
`` [ 'juli' , 14.9 , 87.21 , 60.4 ], [ 'Ricky' , 20.3 , 45.23 , 99.5 ],
`` [ 'Gregory' , 21.1 , 77.25 , 90.9 ], [ 'Jessie' , 16.4 , 95.21 , 10.85 ]]
df = pd.DataFrame(data, columns = [ 'Name' , 'Age' , 'Percentage' , 'Accuracy' ],
`` index = [ 'a' , 'b' , 'c' , 'd' , 'e' , 'f' ])
print (df.dtypes)
Output:

Now, we change the data type of column ‘Percentage‘ from ‘float64′ to ”object’.
Python3
df[ 'Percentage' ] = df[ 'Percentage' ]. apply ( str )
print ()
print (df.dtypes)
df
Output:
Method 3: Using Series.map().
Syntax:
Series.map(arg, na_action=None)
This method is used to map values from two series having one column same.
Example: Converting column of a dataframe from float to string.
Python3
import pandas as pd
data = [[ 'Harvey.' , 10.5 , 45.25 , 95.2 ], [ 'Carson' , 15.2 , 54.85 , 50.8 ],
`` [ 'juli' , 14.9 , 87.21 , 60.4 ], [ 'Ricky' , 20.3 , 45.23 , 99.5 ],
`` [ 'Gregory' , 21.1 , 77.25 , 90.9 ], [ 'Jessie' , 16.4 , 95.21 , 10.85 ]]
df = pd.DataFrame(data, columns = [ 'Name' , 'Age' , 'Percentage' , 'Accuracy' ],
`` index = [ 'a' , 'b' , 'c' , 'd' , 'e' , 'f' ])
print (df.dtypes)
Output:

Now, we change the data type of column ‘Age‘ from ‘float64′ to ”object’.
Python3
df[ 'Age' ] = df[ 'Age' ]. map ( str )
print ()
print (df.dtypes)
df
Output:
