How to Randomly Select rows from Pandas DataFrame (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 15 Apr, 2025
In Pandas, it is possible to select rows randomly from a DataFrame with different methods. Randomly selecting rows can be useful for tasks like sampling, testing or data exploration.
Creating Sample Pandas DataFrame
First, we will create a sample Pandas DataFrame that we will use further in our article.
Python `
import pandas as pd
d = {'Name':['Jai', 'Princi', 'Gaurav', 'Anuj', 'Geeku'], 'Age':[27, 24, 22, 32, 15], 'Address':['Delhi', 'Kanpur', 'Allahabad', 'Kannauj', 'Noida'], 'Qualification':['Msc', 'MA', 'MCA', 'Phd', '10th']}
df = pd.DataFrame(d)
df
`
**Output
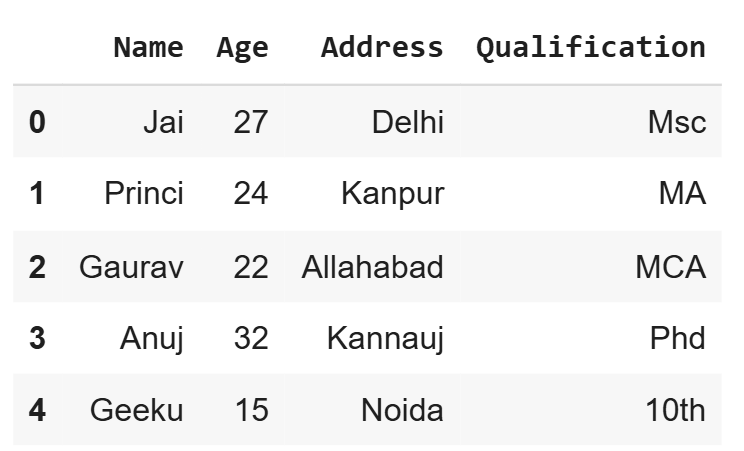
Sample Dataframe
Let’s discuss how to randomly select rows from Pandas DataFrame. A random selection of rows from a DataFrame can be achieved in different ways. Below are the ways by which we can randomly select rows from Pandas DataFrame:
- Using sample() Method
- Using parameter n
- Using frac parameter
- Using replace = false
- Using weights
- Using axis
- Using random_state
- Using NumPy
**1. Using sample() method
In this example, we are using **sample() method to randomly select rows from Pandas DataFram. Sample method returns a random sample of items from an axis of object and this object of same type as our caller.
Python `
Select one random row
dfs = dfs.sample() print(dfs)
`
**Output
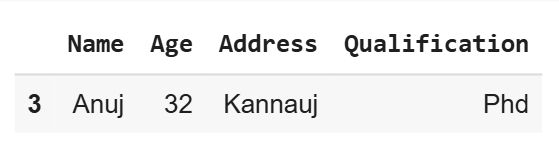
df using sample()
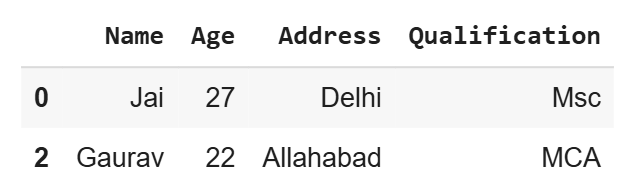
2. Using parameter n
We can specify the number of rows to select using the n parameter. Every time we run this, we’ll get different rows.
Python `
Select 3 random rows
df.sample(n=3)
`
**Output

df using random
3. Using frac Parameter
One can do fraction of axis items and get rows. **For example, if **frac= .5 then sample method return 50% of rows.
Python `
df.sample(frac=0.5) # here you get .50 % of the rows
`
**Output
using frac 50% df
4. Selecting Rows with Replacement (replace=False)
By default, the sample() method doesn’t allow selecting the same row more than once. However, we can allow this by setting replace=True .
Python `
df.sample(n=5, replace=True)
`
**Output
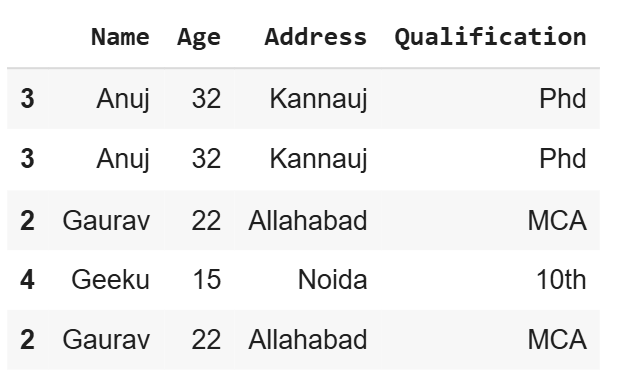
df using replace
5. Using Weights to Select Rows
We can assign weights to rows so that some rows are more likely to be selected than others. The weights parameter controls the probability of selecting each row.
Python `
test_weights = [0.2, 0.4, 0.2, 0.2, 0.4]
df.sample(n=3, weights=test_weights)
`
**Output
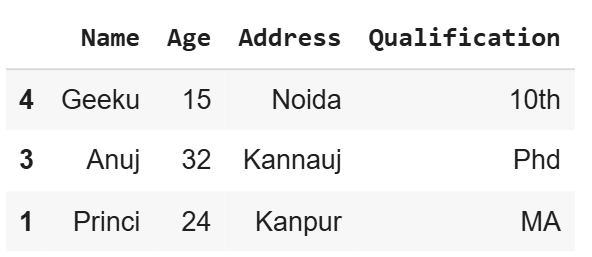
df using weight
6. Using axis Parameter for Column Sampling
The axis accepts number or name. sample() method also allows users to sample columns instead of rows using the axis argument.
Python `
Sample columns instead of rows
df1.sample(axis=0)
`
**Output
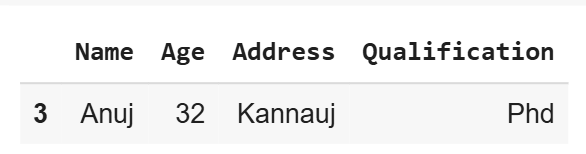
df using column sampling
7. Using random_state for Reproducibility
With a given DataFrame, the sample will always fetch same rows. If random_state is None or np.random, then a randomly-initialized RandomState object is returned.
Python `
df.sample(n=2, random_state=2)
`
**Output
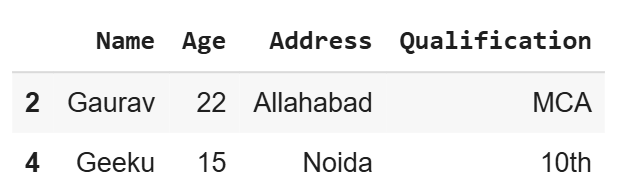
df using random state
**8. Using NumPy for Random Selection
We can also use **NumPy to randomly select rows based on their index. This approach allows us to control the number of rows to select and whether or not to allow replacement.
Python `
import numpy as np
indices = np.random.choice(df.index, size=4, replace=False) df.loc[indices]
`
**Output
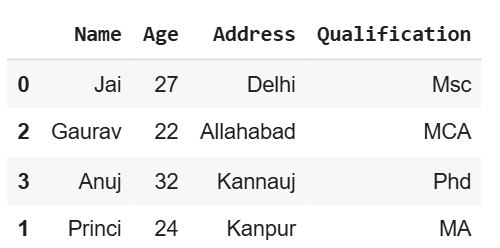
df using numpy
**Related Article: