How to Save a Plot to a File Using Matplotlib? (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 11 Apr, 2025
Matplotlib is a popular Python library to create plots, charts, and graphs of different types. **show() is used to plot a plot, but it doesn’t save the plot to a file. In this article, we will see various methods through which a Matplotlib plot can be saved as an image file.
**Methods to Save a Plot in Matplotlib
There are several ways to save plots in **Matplotlib:
- Using**
savefig()** - Using
matplotlib.pyplot.imsave() - Using the Pillow Library
1. Using savefig() Method
savefig() method is the most popular way of saving plots of Matplotlib. This function enables you to save a plot in the form of a file on your local system in different formats like PNG, JPEG, SVG, etc.
In this example, we are creating our own data list, and using Matplotlib we are plotting a bar graph and saving it to the same directory. To save generated graphs in a file on a storage disk, savefig() method is used.
Python `
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
year = ['2010', '2002', '2004', '2006', '2008'] production = [25, 15, 35, 30, 10]
Plotting bar chart
plt.bar(year, production)
Saving the plot as a JPEG file
plt.savefig("output.jpg")
Saving the plot with additional parameters (this is optional)
plt.savefig("output1.jpg", facecolor='yellow', bbox_inches="tight", pad_inches=0.3, transparent=True)
`
**Output
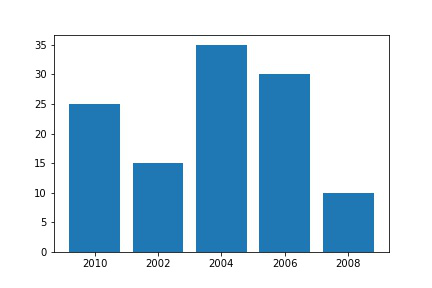
plot
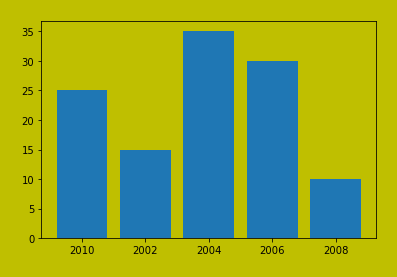
plot
**2. Using matplotlib.pyplot.imsave()
imsave() function is another method to save a plot as an image file. It’s commonly used to save 2D arrays as image files, making it especially useful for working with image data.
Python `
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np
Generate random image data
img = np.random.rand(100, 100)
Save image
plt.imsave('sample_image.png', img, cmap='gray')
`
**Output

**3. Using the Pillow Library (PIL)
In certain instances, it could be helpful to transform a Matplotlib plot into a Pillow (PIL) Image object and save it. This is specifically useful when one is dealing with image processing operations that need Pillow.
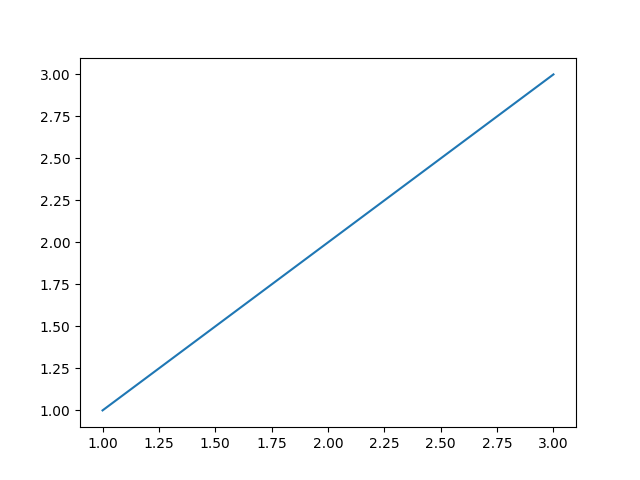
BytesIO: We use aBytesIObuffer to store the plot image in memory, which can then be processed by PIL.fig.savefig(): Instead of converting the canvas directly to a string, we save the plot to the buffer in PNG format.Image.open(): We load the image from the buffer into a PIL image object. Python `
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from PIL import Image import io
fig, ax = plt.subplots() ax.plot([1, 2, 3], [1, 2, 3])
Save the plot to a BytesIO object
buf = io.BytesIO() fig.savefig(buf, format='png')
Convert the BytesIO object to a PIL Image
buf.seek(0) img = Image.open(buf)
Save the image
img.save('pil_image_save.png')
`
**Output
saving plot