VBA Multiple (Nested) If Statements in Excel (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 06 Dec, 2023
VBA in Excel stands for **Visual Basic for Applications, which is Microsoft's programming language. To optimize the performance and reduce the time in Excel we need **Macros and VBA is the tool used in the backend.
What decision-making reasoning do you often use in your Excel worksheets? In most circumstances, you would test your condition using an IF formula and return one value if the condition is met and another value if it is not. You can nest multiple IFs inside of one another to assess more than one condition and return different values based on the outcomes.
**Where to Put the VBA Code in Excel?
In the Microsoft Excel tabs, select the **Developer Tab. Initially, the Developer Tab may not be available.
The Developer Tab can be enabled easily by a two-step process :
- Right-click on any of the existing tabs at the top of the Excel window.
- Now select **Customize the Ribbon from the pop-down menu.

- In the **Excel Options Box, check the box Developer to enable it and click on OK.

- Now, the Developer Tab is visible.

- Now click on the **Visual Basic option in the Developer tab and make a new module to write the program using the Select Case statement.
**Developer -> Visual Basic -> Tools -> Macros
- Create a Macro and give any suitable name.
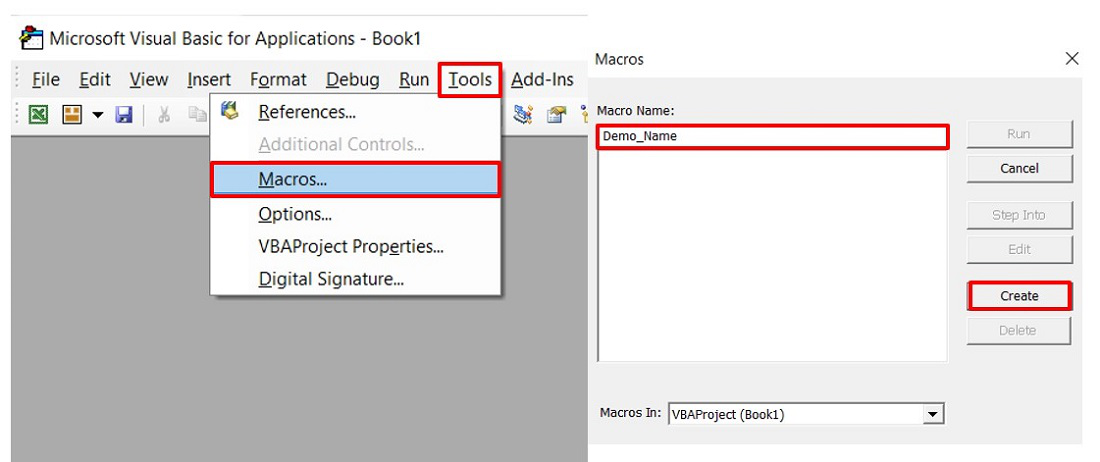
- This will open the Editor window where we can write the code.

The **syntax for the If statement in Excel is:
If condition/expression Then
Code Block for True
Else
Code Block for False
End If
A Single IF Statement
The structure of a Single If statement in Excel is :
If condition/expression Then
Code Block 1
Else
Code Block 2
End If
Excel Nested IFs Statement
The structure of the Nested If statement in Excel is :
If condition/expression Then
Code Block 1
Else If condition/expression Then
Code Block 2
Else If condition/expression Then
Code Block 3
Else
Code Block 4
Else
Code Block 5
End If
Some important **keywords used in Excel are as follows :
- InputBox,: To take input from the user
- **MsgBox: To display output to the user
Nested If Practical Example
Consider a grading system where grading is based on the marks obtained in the exam. For example, If a student obtained 95 marks, the grade obtained by the student is S grade, and so on.
**Code
Sub Nested_If_Grade()
'Declaring the variable marks
Dim marks As Integer
'Asking marks from the user
marks = InputBox("Enter Your Marks:")
If marks >= 90 Then
MsgBox "You got S grade"
Else
If marks >= 80 Then
MsgBox "You got A grade"
Else
If marks >= 70 Then
MsgBox "You got B grade"
Else
If marks >= 60 Then
MsgBox "You got C grade"
Else
If marks >= 50 Then
MsgBox "You got D grade"
Else
If marks >= 40 Then
MsgBox "You got E grade"
Else
MsgBox "You have failed in the exam"
End If
End If
End If
End If
End If
End If
End Sub
**Result :


Using ElseIf
ElseIf allows us to streamline the code because it only moves to the second if statement if the first one returns a false.
**Code
Sub Demo()
'Declaring the variable marks
Dim marks As Integer
'Asking marks from the user
marks = InputBox("Enter Your Marks:")
If marks >= 90 Then
MsgBox "You got S grade"
ElseIf marks >= 80 Then
MsgBox "You got A grade"
ElseIf marks >= 70 Then
MsgBox "You got B grade"
ElseIf marks >= 60 Then
MsgBox "You got C grade"
ElseIf marks >= 50 Then
MsgBox "You got D grade"
ElseIf marks >= 40 Then
MsgBox "You got E grade"
Else
MsgBox "You have failed in the exam"
End If
End Sub
**Result:

Result

Result
