Insert a Node after a given Node in Linked List (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 29 Jul, 2024
Given a **linked list, the task is to insert a new node after a given node of the linked list. If the given node is not present in the linked list, print "Node not found".
**Examples:
**Input: LinkedList = 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5, newData = 1, key = 2
**Output: LinkedList = 2 -> **1 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5**Input: LinkedList = 1 -> 3 -> 5 -> 7, newData = 1, key = 2
**Output: Node not found
**Approach: To solve the problem, follow the below idea:
If we want to insert a new node after a given node, we first locate that node. If the node is not found, print "Node not found". If we find it, we set the **new node's next reference to point to the node that follows the given node. Then, we update the given node's next to point to the new node.
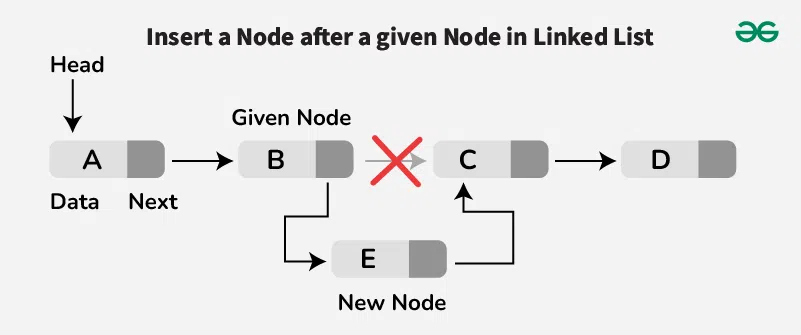
Follow the below steps for inserting a node after a given node:
- Traverse the linked list to find the given node.
- If the given node is not found, print "Node not found".
- Else if the given node is found, create a new node, say **new_node initialized with the given data.
- Make the next pointer of **new_node as next of given node.
- Update the next pointer of given node point to the **new_node.
Below is the implementation of the approach:
C++ `
// C++ Program to insert a node after a given node
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;
// Definition of a linked list node struct Node { int data; Node* next;
// Constructor to initialize the node
Node(int data) {
this->data = data;
this->next = nullptr;
}};
// Function to insert a new node after a given node Node* insertAfter(Node* head, int key, int newData) { Node* curr = head;
// Iterate over Linked List to find the key
while (curr != nullptr) {
if (curr->data == key)
break;
curr = curr->next;
}
// if curr becomes NULL means, given key is not
// found in linked list
if (curr == nullptr) {
cout << "Node not found" << endl;
// Return the head of the original linked list
return head;
}
// Allocate new node and make the element to be inserted
// as a new node
Node* newNode = new Node(newData);
// Set the next pointer of new node to the next pointer of given node
newNode->next = curr->next;
// Change the next pointer of given node to the new node
curr->next = newNode;
// Return the head of the modified linked list
return head;}
// Function to print the linked list void printList(Node* node) { while (node != nullptr) { cout << node->data << " "; node = node->next; } cout << endl; }
// Driver code int main() {
// Create a hard-coded linked list:
// 2 -> 3 -> 5 -> 6
Node* head = new Node(2);
head->next = new Node(3);
head->next->next = new Node(5);
head->next->next->next = new Node(6);
cout << "Original Linked List: ";
printList(head);
// Key: Insert node after key
int key = 3, newData = 4;
// Insert a new node with data 4 after the node having
// data 3
head = insertAfter(head, key, newData);
cout << "Linked List after insertion: ";
printList(head);
return 0;}
C
// C Program to insert a node after a given node
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h>
// Definition of a linked list node struct Node { int data; struct Node* next; };
// Function to create and return a new node struct Node* createNode(int data) { struct Node* newNode = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); newNode->data = data; newNode->next = NULL; return newNode; }
// Function to insert a new node after a given node and // return the head of modified list struct Node* insertAfter(struct Node* head, int key, int newData) {
// Initialize curr Pointer to head
struct Node* curr = head;
// Iterate over Linked List to find the key
while (curr != NULL) {
if (curr->data == key)
break;
curr = curr->next;
}
// if curr becomes NULL means, given key is not found in
// linked list
if (curr == NULL) {
printf("Node not found\n");
// Return the head of the original linked list
return head;
}
// Allocate new node and make the element to be inserted
// as a new node
struct Node* newNode
= (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
newNode->data = newData;
// Set the next pointer of new node to the next pointer
// of given node
newNode->next = curr->next;
// Change the next pointer of given node to the new node
curr->next = newNode;
// Return the head of the modified linked list
return head;}
// Function to print the linked list void printList(struct Node* node) { while (node != NULL) { printf("%d ", node->data); node = node->next; } printf("\n"); }
// Driver code int main() {
// Create the linked list 2 -> 3 -> 5 -> 6
struct Node* head = createNode(2);
head->next = createNode(3);
head->next->next = createNode(5);
head->next->next->next = createNode(6);
printf("Original Linked List: ");
printList(head);
// Key: Insert node after key
int key = 3, newData = 4;
// Insert a new node with data 4 after the node with data 3
head = insertAfter(head, key, newData);
printf("Linked List after insertion: ");
printList(head);
return 0;}
Java
// Java Program to insert a node after a given node
// Definition of a linked list node class Node { int data; Node next;
// Constructor to initialize the node
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}}
// Driver code public class GFG {
// Function to insert a new node after a given node
public static Node insertAfter(Node head, int key, int newData) {
// Initialize curr Pointer to head
Node curr = head;
// Iterate over Linked List to find the key
while (curr != null) {
if (curr.data == key)
break;
curr = curr.next;
}
// If curr becomes null means, given key is not
// found in linked list
if (curr == null) {
System.out.println("Node not found");
// Return the head of the original linked list
return head;
}
// Allocate new node and make the element to be
// inserted as a new node
Node newNode = new Node(newData);
// Set the next pointer of new node to the next
// pointer of given node
newNode.next = curr.next;
// Change the next pointer of given node to the
// new node
curr.next = newNode;
// Return the head of the modified linked list
return head;
}
// Function to print the linked list
public static void printList(Node node) {
while (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create the linked list 2 -> 3 -> 5 -> 6
Node head = new Node(2);
head.next = new Node(3);
head.next.next = new Node(5);
head.next.next.next = new Node(6);
System.out.print("Original Linked List: ");
printList(head);
// Key: Insert node after key
int key = 3, newData = 4;
// Insert a new node with data 4 after the node
// having data 3
head = insertAfter(head, key, newData);
System.out.print("Linked List after insertion: ");
printList(head);
}}
Python
Python Program to insert a node after a given node
Definition of a linked list node
class Node:
# Constructor to initialize the node
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = NoneFunction to insert a new node after a given node
def insert_after(head, key, new_data): curr = head
# Iterate over Linked List to find the key
while curr is not None:
if curr.data == key:
break
curr = curr.next
# if curr becomes None means, given key is not
# found in linked list
if curr is None:
print("Node not found")
# Return the head of the original linked list
return head
# Allocate new node and make the element to be inserted
# as a new node
new_node = Node(new_data)
# Set the next pointer of new node to the next pointer of given node
new_node.next = curr.next
# Change the next pointer of given node to the new node
curr.next = new_node
# Return the head of the modified linked list
return headFunction to print the linked list
def print_list(node): while node is not None: print(node.data, end=" ") node = node.next print()
Driver code
if name == "main":
# Create a hard-coded linked list:
# 2 -> 3 -> 5 -> 6
head = Node(2)
head.next = Node(3)
head.next.next = Node(5)
head.next.next.next = Node(6)
print("Original Linked List: ", end="")
print_list(head)
# Key: Insert node after key
key = 3
new_data = 4
# Insert a new node with data 4 after the node having
# data 3
head = insert_after(head, key, new_data)
print("Linked List after insertion: ", end="")
print_list(head)C#
// C# Program to insert a node after a given node
using System;
// Definition of a linked list node class Node { public int Data; public Node Next;
// Constructor to initialize the node
public Node(int data) {
this.Data = data;
this.Next = null;
}}
class GFG {
// Function to insert a new node after a given node
static Node InsertAfter(Node head, int key, int newData) {
Node curr = head;
// Iterate over Linked List to find the key
while (curr != null) {
if (curr.Data == key)
break;
curr = curr.Next;
}
// if curr becomes null means, given key is not
// found in linked list
if (curr == null) {
Console.WriteLine("Node not found");
// Return the head of the original linked list
return head;
}
// Allocate new node and make the element to be inserted
// as a new node
Node newNode = new Node(newData);
// Set the next pointer of new node to the next pointer of given node
newNode.Next = curr.Next;
// Change the next pointer of given node to the new node
curr.Next = newNode;
// Return the head of the modified linked list
return head;
}
// Function to print the linked list
static void PrintList(Node node) {
while (node != null) {
Console.Write(node.Data + " ");
node = node.Next;
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
// Driver code
static void Main() {
// Create a hard-coded linked list:
// 2 -> 3 -> 5 -> 6
Node head = new Node(2);
head.Next = new Node(3);
head.Next.Next = new Node(5);
head.Next.Next.Next = new Node(6);
Console.Write("Original Linked List: ");
PrintList(head);
// Key: Insert node after key
int key = 3, newData = 4;
// Insert a new node with data 4 after the node having
// data 3
head = InsertAfter(head, key, newData);
Console.Write("Linked List after insertion: ");
PrintList(head);
}}
JavaScript
// Javascript Program to insert a node after a given node
// Definition of a linked list node class Node {
// Constructor to initialize the node
constructor(data)
{
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}}
// Function to insert a new node after a given node function insertAfter(head, key, newData) { let curr = head;
// Iterate over Linked List to find the key
while (curr !== null) {
if (curr.data === key) {
break;
}
curr = curr.next;
}
// if curr becomes null means, given key is not
// found in linked list
if (curr === null) {
console.log("Node not found");
// Return the head of the original linked list
return head;
}
// Allocate new node and make the element to be inserted
// as a new node
let newNode = new Node(newData);
// Set the next pointer of new node to the next pointer
// of given node
newNode.next = curr.next;
// Change the next pointer of given node to the new node
curr.next = newNode;
// Return the head of the modified linked list
return head;}
// Function to print the linked list function printList(node) { while (node !== null) { console.log(node.data + " "); node = node.next; } console.log(); }
// Driver code
// Create a hard-coded linked list: // 2 -> 3 -> 5 -> 6 let head = new Node(2); head.next = new Node(3); head.next.next = new Node(5); head.next.next.next = new Node(6);
console.log("Original Linked List: "); printList(head);
// Key: Insert node after key let key = 3, newData = 4;
// Insert a new node with data 4 after the node having // data 3 head = insertAfter(head, key, newData);
console.log("Linked List after insertion: "); printList(head);
`
Output
Original Linked List: 2 3 5 6 Linked List after insertion: 2 3 4 5 6
**Time Complexity: O(N), where **N is the number of nodes in the linked list.
**Auxiliary Space: O(1)