Insert a Node at Front/Beginning of a Linked List (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 26 Jul, 2024
Given a linked list, the task is to insert a new node at the beginning/start/front of the linked list.
**Example:
**Input: LinkedList = 2->3->4->5, NewNode = 1
**Output: 1 2 3 4 5**Input: LinkedList = 2->10, NewNode = 1
**Output: 1 2 10
**Approach:
To insert a new node at the front, we create a **new node and point its **next reference to the **current head of the linked list. Then, we update the **head to be this new node. This operation is efficient because it only requires adjusting a few pointers.
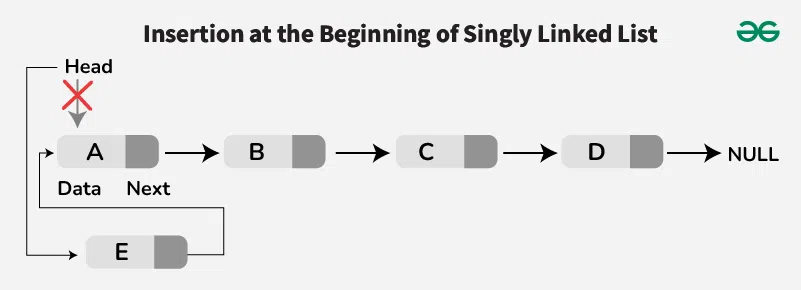
Insertion at Front/Beginning of Linked List
**Algorithm:
- Make the first node of Linked List linked to the new node
- Remove the head from the original first node of Linked List
- Make the new node as the Head of the Linked List.
Below is the implementation of the approach:
C++ `
// C++ Program to insert the node at the beginning of // Linked List
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;
// Define a node in the linked list struct Node { int data; // Data stored in the node Node* next; // Pointer to the next node in the list
// Constructor to initialize the node
Node(int new_data)
{
data = new_data;
next = nullptr; // Set next to null
}};
// Function to insert a new node at the beginning of the // list Node* insertAtFront(Node* head, int new_data) { // Create a new node with the given data Node* new_node = new Node(new_data);
// Make the next of the new node point to the current
// head
new_node->next = head;
// Return the new node as the new head of the list
return new_node;}
// Function to print the contents of the linked list void printList(Node* head) { // Start from the head of the list Node* curr = head;
// Traverse the list
while (curr != nullptr) {
// Print the current node's data
cout << " " << curr->data;
// Move to the next node
curr = curr->next;
}
// Print a newline at the end
cout << endl;}
// Driver code to test the functions int main() { // Create the linked list 2->3->4->5 Node* head = new Node(2); head->next = new Node(3); head->next->next = new Node(4); head->next->next->next = new Node(5);
// Print the original list
cout << "Original Linked List:";
printList(head);
// Insert a new node at the front of the list
cout << "After inserting Nodes at the front:";
int data = 1;
head = insertAtFront(head, data);
// Print the updated list
printList(head);
return 0;}
C
// C Program to insert the node at the beginning of // Linked List
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h>
// Define a node in the linked list struct Node { int data; // Data stored in the node struct Node* next; // Pointer to the next node in the list };
// Function to create a new node with the given data struct Node* createNode(int new_data) { // Allocate memory for a new node struct Node* new_node = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
// Initialize the node's data
new_node->data = new_data;
// Set the next pointer to NULL
new_node->next = NULL;
// Return the newly created node
return new_node;}
// Function to insert a new node at the beginning of the // list struct Node* insertAtFront(struct Node* head, int new_data) { // Create a new node with the given data struct Node* new_node = createNode(new_data);
// Make the next of the new node point to the current
// head
new_node->next = head;
// Return the new node as the new head of the list
return new_node;}
// Function to print the contents of the linked list void printList(struct Node* head) { // Start from the head of the list struct Node* curr = head;
// Traverse the list
while (curr != NULL) {
// Print the current node's data
printf(" %d", curr->data);
// Move to the next node
curr = curr->next;
}
// Print a newline at the end
printf("\n");}
// Driver code to test the functions int main() { // Create the linked list 2->3->4->5 struct Node* head = createNode(2); head->next = createNode(3); head->next->next = createNode(4); head->next->next->next = createNode(5);
// Print the original list
printf("Original Linked List:");
printList(head);
// Insert a new node at the front of the list
printf("After inserting Nodes at the front:");
int data = 1;
head = insertAtFront(head, data);
// Print the updated list
printList(head);
return 0;}
Java
// Java Program to insert the node at the beginning of // Linked List
class Node { int data; // Data stored in the node Node next; // Pointer to the next node in the list
// Constructor to initialize the node
Node(int new_data) {
data = new_data;
next = null;
}}
public class GFG { // Function to insert a new node at the beginning of the list public static Node insertAtFront(Node head, int new_data) { // Create a new node with the given data Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
// Make the next of the new node point to the current head
new_node.next = head;
// Return the new node as the new head of the list
return new_node;
}
// Function to print the contents of the linked list
public static void printList(Node head) {
// Start from the head of the list
Node curr = head;
// Traverse the list
while (curr != null) {
// Print the current node's data
System.out.print(" " + curr.data);
// Move to the next node
curr = curr.next;
}
// Print a newline at the end
System.out.println();
}
// Driver code to test the functions
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create the linked list 2->3->4->5
Node head = new Node(2);
head.next = new Node(3);
head.next.next = new Node(4);
head.next.next.next = new Node(5);
// Print the original list
System.out.println("Original Linked List:");
printList(head);
// Insert a new node at the front of the list
System.out.println("After inserting Nodes at the front:");
int data = 1;
head = insertAtFront(head, data);
// Print the updated list
printList(head);
}}
Python
Python Program to insert the node at the beginning of
Linked List
class Node: def init(self, new_data): # Initialize the node's data self.data = new_data
# Set the next pointer to None
self.next = Nonedef insert_at_front(head, new_data): # Create a new node with the given data new_node = Node(new_data)
# Make the next of the new node point to the current head
new_node.next = head
# Return the new node as the new head of the list
return new_nodedef print_list(head): # Start from the head of the list curr = head
# Traverse the list
while curr is not None:
# Print the current node's data
print(f" {curr.data}", end="")
# Move to the next node
curr = curr.next
# Print a newline at the end
print()Driver code to test the functions
if name == "main": # Create the linked list 2->3->4->5 head = Node(2) head.next = Node(3) head.next.next = Node(4) head.next.next.next = Node(5)
# Print the original list
print("Original Linked List:", end="")
print_list(head)
# Insert a new node at the front of the list
print("After inserting Nodes at the front:", end="")
data = 1
head = insert_at_front(head, data)
# Print the updated list
print_list(head)JavaScript
// JavaScript Program to insert the node at the beginning of // Linked List
class Node { constructor(newData) { // Initialize the node's data this.data = newData;
// Set the next pointer to null
this.next = null;
}}
// Function to insert a new node at the beginning of the // list function insertAtFront(head, newData) { // Create a new node with the given data const newNode = new Node(newData);
// Make the next of the new node point to the current
// head
newNode.next = head;
// Return the new node as the new head of the list
return newNode;}
// Function to print the contents of the linked list function printList(head) { // Start from the head of the list let curr = head; let result = "";
// Traverse the list
while (curr !== null) {
// Append the current node's data to result
result += " " + curr.data;
// Move to the next node
curr = curr.next;
}
// Print the result
console.log(result);}
// Driver code to test the functions function main() { // Create the linked list 2->3->4->5 let head = new Node(2); head.next = new Node(3); head.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next = new Node(5);
// Print the original list
console.log("Original Linked List:");
printList(head);
// Insert a new node at the front of the list
console.log("After inserting Nodes at the front:");
const data = 1;
head = insertAtFront(head, data);
// Print the updated list
printList(head);}
main(); // Execute the driver code
`
Output
Original Linked List: 2 3 4 5 After inserting Nodes at the front: 1 2 3 4 5
**Time Complexity: O(1), We have a pointer to the head and we can directly attach a node and update the head pointer. So, the Time complexity of inserting a node at the head position is O(1).
**Auxiliary Space: O(1)
