Insertion in an empty List in the circular linked list (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 08 Aug, 2024
A circular linked list is a type of data structure where each node points to the **next one, and the **last node connects back to the first, forming a circle. This setup allows you to loop through the list without stopping. Knowing how to **insert a node into an empty circular linked list is important in creating circular linked list.
Insertion in an empty List in the circular linked list
To insert a node in empty circular linked list, creates a new node with the given data, sets its next pointer to point to itself, and updates the **last pointer to reference this **new node.
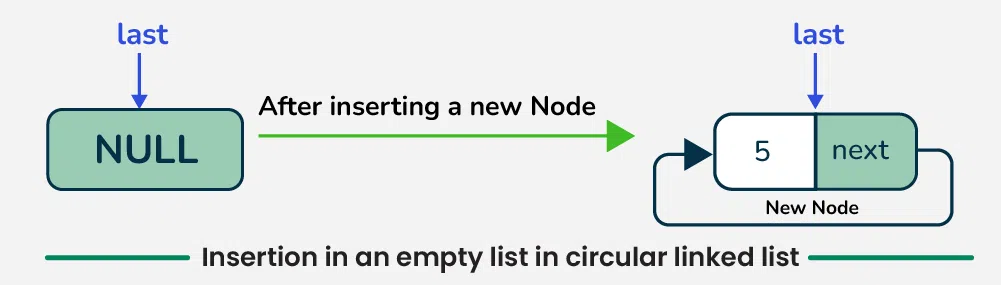
Insertion in an empty List
Step-by-step approach:
- Check if **last is not **nullptr. If **true, return **last (the list is not empty).
- Otherwise, Create a **new node with the provided data.
- Set the **new node’s next pointer to point to itself (circular link).
- Update **last to point to the **new node and return it.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++ `
#include using namespace std;
struct Node{ int data; Node *next; Node(int value){ data = value; next = nullptr; } };
// Function to insert a node into an empty circular singly linked list Node *insertInEmptyList(Node *last, int data){ if (last != nullptr) return last;
// Create a new node
Node *newNode = new Node(data);
// Point newNode to itself
newNode->next = newNode;
// Update last to point to the new node
last = newNode;
return last;}
void printList(Node* last){ if(last == NULL) return;
// Start from the head node
Node* head = last->next;
while (true) {
cout << head->data << " ";
head = head->next;
if (head == last->next) break;
}
cout << endl;}
int main(){ Node *last = nullptr;
// Insert a node into the empty list
last = insertInEmptyList(last, 1);
// Print the list
cout << "List after insertion: ";
printList(last);
return 0;}
C
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h>
// Define the Node structure struct Node { int data; struct Node* next; };
struct Node* createNode(int value);
// Function to insert a node into an empty // circular singly linked list struct Node* insertInEmptyList(struct Node* last, int data) { if (last != NULL) return last;
// Create a new node
struct Node* newNode = createNode(data);
// Update last to point to the new node
last = newNode;
return last;}
void printList(struct Node* last) { if (last == NULL) return;
// Start from the head node
struct Node* head = last->next;
while (1) {
printf("%d ", head->data);
head = head->next;
if (head == last->next) break;
}
printf("\n");}
struct Node* createNode(int value) { struct Node* newNode = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); newNode->data = value; newNode->next = newNode; return newNode; }
int main() { struct Node* last = NULL;
// Insert a node into the empty list
last = insertInEmptyList(last, 1);
// Print the list
printf("List after insertion: ");
printList(last);
return 0;}
Java
class Node { int data; Node next;
Node(int value) {
data = value;
next = null;
}}
public class Main { // Function to insert a node into an empty // circular singly linked list static Node insertInEmptyList(Node last, int data) { if (last != null) return last;
// Create a new node
Node newNode = new Node(data);
// Point newNode to itself
newNode.next = newNode;
// Update last to point to the new node
last = newNode;
return last;
}
// Function to print the list
static void printList(Node last) {
if (last == null) return;
// Start from the head node
Node head = last.next;
while (true) {
System.out.print(head.data + " ");
head = head.next;
if (head == last.next) break;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node last = null;
// Insert a node into the empty list
last = insertInEmptyList(last, 1);
// Print the list
System.out.print("List after insertion: ");
printList(last);
}}
Python
class Node: def init(self, value): self.data = value self.next = self # Point to itself
def insertInEmptyList(last, data): if last is not None: return last
# Create a new node
new_node = Node(data)
# Update last to point to the new node
last = new_node
return lastdef printList(last): if last is None: return
# Start from the head node
head = last.next
while True:
print(head.data, end=" ")
head = head.next
if head == last.next:
break
print()if name == "main": last = None
# Insert a node into the empty list
last = insertInEmptyList(last, 1)
# Print the list
print("List after insertion: ", end="")
printList(last)JavaScript
class Node { constructor(value) { this.data = value; this.next = null; } }
function insertInEmptyList(last, data) { if (last !== null) return last;
// Create a new node
let newNode = new Node(data);
// Point newNode to itself
newNode.next = newNode;
// Update last to point to the new node
last = newNode;
return last;}
function printList(last) { if (last === null) return;
// Start from the head node
let head = last.next;
while (true) {
console.log(head.data);
head = head.next;
if (head === last.next)
break;
}}
// Main function
let last = null;
// Insert a node into the empty list last = insertInEmptyList(last, 1);
// Print the list console.log("List after insertion:"); printList(last);
`
Output
List after insertion: 1
**Time Complexity: O(1)
**Auxiliary Space: O(1)
