Insertion in Binary Search Tree (BST) (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 23 Jul, 2025
Given a **BST, the task is to insert a new node in this **BST.
**Example:
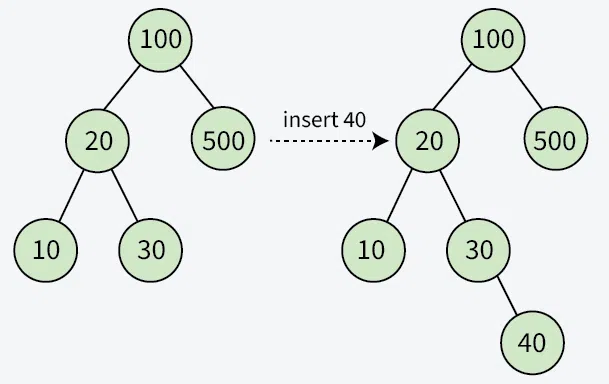
How to Insert a value in a Binary Search Tree:
A new key is always inserted at the leaf by maintaining the property of the binary search tree. We start searching for a key from the root until we hit a leaf node. Once a leaf node is found, the new node is added as a child of the leaf node. The below steps are followed while we try to insert a node into a binary search tree:
- Initilize the current node (say, **currNode or node) with root node
- Compare the **key with the current node.
- **Move left if the **key is less than or equal to the current node value.
- **Move right if the **key is greater than current node value.
- Repeat steps 2 and 3 until you reach a leaf node.
- Attach the new key as a left or right child based on the comparison with the leaf node's value.
Follow the below illustration for a better understanding:
**Insertion in Binary Search Tree using Recursion:
Below is the implementation of the insertion operation using recursion.
C++14 `
#include using namespace std;
struct Node {
int key;
Node* left;
Node* right;
Node(int item) {
key = item;
left = NULL;
right = NULL;
}
};
// A utility function to insert a new node with // the given key Node* insert(Node* node, int key) {
// If the tree is empty, return a new node
if (node == NULL)
return new Node(key);
// If the key is already present in the tree,
// return the node
if (node->key == key)
return node;
// Otherwise, recur down the tree/ If the key
// to be inserted is greater than the node's key,
// insert it in the right subtree
if (node->key < key)
node->right = insert(node->right, key);
// If the key to be inserted is smaller than
// the node's key,insert it in the left subtree
else
node->left = insert(node->left, key);
// Return the (unchanged) node pointer
return node;}
// A utility function to do inorder tree traversal void inorder(Node* root) { if (root != NULL) { inorder(root->left); cout << root->key << " "; inorder(root->right); } }
// Driver program to test the above functions
int main() {
// Creating the following BST
// 50
// /
// 30 70
// / \ /
// 20 40 60 80
Node* root = new Node(50);
root = insert(root, 30);
root = insert(root, 20);
root = insert(root, 40);
root = insert(root, 70);
root = insert(root, 60);
root = insert(root, 80);
// Print inorder traversal of the BST
inorder(root);
return 0;}
C
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h>
// Define the structure for a BST node struct Node { int key; struct Node* left; struct Node* right; };
// Function to create a new BST node struct Node* newNode(int item) { struct Node* temp = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); temp->key = item; temp->left = temp->right = NULL; return temp; }
// Function to insert a new node with the given key struct Node* insert(struct Node* node, int key) {
// If the tree is empty, return a new node
if (node == NULL)
return newNode(key);
// If the key is already present in the tree,
// return the node
if (node->key == key)
return node;
// Otherwise, recur down the tree. If the key
// to be inserted is greater than the node's key,
// insert it in the right subtree
if (node->key < key)
node->right = insert(node->right, key);
// If the key to be inserted is smaller than
// the node's key,insert it in the left subtree
else
node->left = insert(node->left, key);
// Return the (unchanged) node pointer
return node;}
// Function to perform inorder tree traversal void inorder(struct Node* root) { if (root != NULL) { inorder(root->left); printf("%d ", root->key); inorder(root->right); } }
// Driver program to test the above functions
int main() {
// Creating the following BST
// 50
// /
// 30 70
// / \ /
// 20 40 60 80
struct Node* root = newNode(50);
root = insert(root, 30);
root = insert(root, 20);
root = insert(root, 40);
root = insert(root, 70);
root = insert(root, 60);
root = insert(root, 80);
// Print inorder traversal of the BST
inorder(root);
return 0;}
Java
class Node { int key; Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
key = item;
left = right = null;
}}
class GfG {
// A utility function to insert a new node
// with the given key
static Node insert(Node root, int key)
{
// If the tree is empty, return a new node
if (root == null)
return new Node(key);
// If the key is already present in the tree,
// return the node
if (root.key == key)
return root;
// Otherwise, recur down the tree
if (key < root.key)
root.left = insert(root.left, key);
else
root.right = insert(root.right, key);
// Return the (unchanged) node pointer
return root;
}
// A utility function to do inorder tree traversal
static void inorder(Node root)
{
if (root != null) {
inorder(root.left);
System.out.print(root.key + " ");
inorder(root.right);
}
}
// Driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Node root = null;
// Creating the following BST
// 50
// / \
// 30 70
// / \ / \
// 20 40 60 80
root = insert(root, 50);
root = insert(root, 30);
root = insert(root, 20);
root = insert(root, 40);
root = insert(root, 70);
root = insert(root, 60);
root = insert(root, 80);
// Print inorder traversal of the BST
inorder(root);
}}
Python
Python program to demonstrate
insert operation in binary search tree
class Node: def init(self, key): self.left = None self.right = None self.val = key
A utility function to insert
a new node with the given key
def insert(root, key): if root is None: return Node(key) if root.val == key: return root if root.val < key: root.right = insert(root.right, key) else: root.left = insert(root.left, key) return root
A utility function to do inorder tree traversal
def inorder(root): if root: inorder(root.left) print(root.val, end=" ") inorder(root.right)
Creating the following BST
50
/ \
30 70
/ \ / \
20 40 60 80
r = Node(50) r = insert(r, 30) r = insert(r, 20) r = insert(r, 40) r = insert(r, 70) r = insert(r, 60) r = insert(r, 80)
Print inorder traversal of the BST
inorder(r)
C#
using System;
class Node { public int key; public Node left, right;
public Node(int item) {
key = item;
left = right = null;
}}
class GfG {
// A function to insert a new node with the given key
public static Node Insert(Node node, int key) {
if (node == null)
return new Node(key);
// Duplicates not allowed
if (key == node.key)
return node;
if (key < node.key)
node.left = Insert(node.left, key);
else if (key > node.key)
node.right = Insert(node.right, key);
return node;
}
// A utility function to do inorder tree traversal
public static void Inorder(Node root) {
if (root != null) {
Inorder(root.left);
Console.Write(root.key + " ");
Inorder(root.right);
}
}
// Driver method
public static void Main() {
// Creating the following BST
// 50
// / \
// 30 70
// / \ / \
// 20 40 60 80
Node root = new Node(50);
root = Insert(root, 30);
root = Insert(root, 20);
root = Insert(root, 40);
root = Insert(root, 70);
root = Insert(root, 60);
root = Insert(root, 80);
// Print inorder traversal of the BST
Inorder(root);
}}
JavaScript
class Node { constructor(key) { this.key = key; this.left = null; this.right = null; } }
// A utility function to insert a new // node with the given key function insert(root, key) {
if (root === null)
return new Node(key);
// Duplicates not allowed
if (root.key === key)
return root;
if (key < root.key)
root.left = insert(root.left, key);
else if (key > root.key)
root.right = insert(root.right, key);
return root;}
// A utility function to do inorder // tree traversal function inorder(root) { if (root !== null) { inorder(root.left); console.log(root.key + " "); inorder(root.right); } }
// Creating the following BST
// 50
// /
// 30 70
// / \ /
// 20 40 60 80
let root = new Node(50); root = insert(root, 30); root = insert(root, 20); root = insert(root, 40); root = insert(root, 70); root = insert(root, 60); root = insert(root, 80);
// Print inorder traversal of the BST inorder(root);
`
Output
20 30 40 50 60 70 80
**Time Complexity:
- The worst-case time complexity of insert operations is O(h) where **h is the height of the Binary Search Tree.
- In the worst case, we may have to travel from the root to the deepest leaf node. The height of a skewed tree may become **n and the time complexity of insertion operation may become O(n).
**Auxiliary Space: The auxiliaryspace complexity of insertion into a binary search tree is O(h), due to recursive stack.
**Insertion in Binary Search Tree using Iterative approach:
Instead of using recursion, we can also implement the insertion operation iteratively using a **while loop. Below is the implementation using a while loop.
C++ `
#include using namespace std;
struct Node { int key; Node* left; Node* right; Node(int item) { key = item; left = NULL; right = NULL; } };
Node* insert(Node* root, int x) {
Node* temp = new Node(x);
// If tree is empty
if (root == NULL)
return temp;
// Find the node who is going
// to have the new node temp as
// it child. The parent node is
// mainly going to be a leaf node
Node *parent = NULL, *curr = root;
while (curr != NULL) {
parent = curr;
if (curr->key > x)
curr = curr->left;
else if (curr->key < x)
curr = curr->right;
else
return root;
}
// If x is smaller, make it
// left child, else right child
if (parent->key > x)
parent->left = temp;
else
parent->right = temp;
return root;}
// A utility function to do inorder // tree traversal void inorder(Node* root) { if (root != NULL) { inorder(root->left); cout << root->key << " "; inorder(root->right); } }
// Driver program
int main()
{
// Creating the following BST
// 50
// /
// 30 70
// / \ /
// 20 40 60 80
Node* root = new Node(50);
root = insert(root, 30);
root = insert(root, 20);
root = insert(root, 40);
root = insert(root, 70);
root = insert(root, 60);
root = insert(root, 80);
// Print inorder traversal of the BST
inorder(root);
return 0;}
C
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h>
// Define the structure for a BST node struct Node { int key; struct Node* left; struct Node* right; };
// Function to create a new BST node struct Node* newNode(int item) { struct Node* temp = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); temp->key = item; temp->left = temp->right = NULL; return temp; }
struct Node* insert(struct Node* root, int x) {
struct Node* temp = newNode(x);
// If tree is empty
if (root == NULL)
return temp;
// Find the node who is going
// to have the new node temp as
// it child. The parent node is
// mainly going to be a leaf node
struct Node *parent = NULL, *curr = root;
while (curr != NULL) {
parent = curr;
if (curr->key > x)
curr = curr->left;
else if (curr->key < x)
curr = curr->right;
else
return root;
}
// If x is smaller, make it
// left child, else right child
if (parent->key > x)
parent->left = temp;
else
parent->right = temp;
return root;}
// Function to perform inorder tree traversal void inorder(struct Node* root) { if (root != NULL) { inorder(root->left); printf("%d ", root->key); inorder(root->right); } }
// Driver program to test the above functions
int main() {
// Creating the following BST
// 50
// /
// 30 70
// / \ /
// 20 40 60 80
struct Node* root = newNode(50);
root = insert(root, 30);
root = insert(root, 20);
root = insert(root, 40);
root = insert(root, 70);
root = insert(root, 60);
root = insert(root, 80);
// Print inorder traversal of the BST
inorder(root);
return 0;}
Java
class Node { int key; Node left, right; public Node(int item) { key = item; left = right = null; } }
class GfG {
// Function to insert a new node with
// the given key
static Node insert(Node root, int x) {
Node temp = new Node(x);
// If tree is empty
if (root == null) {
return temp;
}
// Find the node who is going to have
// the new node temp as its child
Node parent = null;
Node curr = root;
while (curr != null) {
parent = curr;
if (curr.key > x) {
curr = curr.left;
} else if (curr.key < x) {
curr = curr.right;
} else {
return root; // Key already exists
}
}
// If x is smaller, make it left
// child, else right child
if (parent.key > x) {
parent.left = temp;
} else {
parent.right = temp;
}
return root;
}
// A utility function to do inorder tree traversal
static void inorder(Node root)
{
if (root != null) {
inorder(root.left);
System.out.print(root.key + " ");
inorder(root.right);
}
}
// Driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Node root = null;
// Creating the following BST
// 50
// / \
// 30 70
// / \ / \
// 20 40 60 80
root = insert(root, 50);
root = insert(root, 30);
root = insert(root, 20);
root = insert(root, 40);
root = insert(root, 70);
root = insert(root, 60);
root = insert(root, 80);
// Print inorder traversal of the BST
inorder(root);
}}
Python
Python program to demonstrate
insert operation in binary search tree
class Node: def init(self, key): self.left = None self.right = None self.key = key
def insert(root, key): temp = Node(key)
# If tree is empty
if root is None:
return temp
# Find the node who is going to
# have the new node temp as its child
parent = None
curr = root
while curr is not None:
parent = curr
if curr.key > key:
curr = curr.left
elif curr.key < key:
curr = curr.right
else:
return root # Key already exists
# If key is smaller, make it left
# child, else right child
if parent.key > key:
parent.left = temp
else:
parent.right = temp
return rootA utility function to do inorder tree traversal
def inorder(root): if root: inorder(root.left) print(root.key, end=" ") inorder(root.right)
Creating the following BST
50
/ \
30 70
/ \ / \
20 40 60 80
r = Node(50) r = insert(r, 30) r = insert(r, 20) r = insert(r, 40) r = insert(r, 70) r = insert(r, 60) r = insert(r, 80)
Print inorder traversal of the BST
inorder(r)
C#
using System;
class Node { public int key; public Node left, right;
public Node(int item) {
key = item;
left = right = null;
}}
class GfG {
// Function to insert a new node with the given key
public static Node Insert(Node root, int x)
{
Node temp = new Node(x);
// If tree is empty
if (root == null)
return temp;
// Find the node who is going to
// have the new node temp as its child
Node parent = null;
Node curr = root;
while (curr != null)
{
parent = curr;
if (curr.key > x)
curr = curr.left;
else if (curr.key < x)
curr = curr.right;
else
return root; // Key already exists
}
// If x is smaller, make it left
// child, else right child
if (parent.key > x)
parent.left = temp;
else
parent.right = temp;
return root;
}
// A utility function to do inorder tree traversal
public static void Inorder(Node root) {
if (root != null) {
Inorder(root.left);
Console.Write(root.key + " ");
Inorder(root.right);
}
}
// Driver method
public static void Main() {
// Creating the following BST
// 50
// / \
// 30 70
// / \ / \
// 20 40 60 80
Node root = new Node(50);
root = Insert(root, 30);
root = Insert(root, 20);
root = Insert(root, 40);
root = Insert(root, 70);
root = Insert(root, 60);
root = Insert(root, 80);
// Print inorder traversal of the BST
Inorder(root);
}}
JavaScript
class Node { constructor(key) { this.key = key; this.left = null; this.right = null; } }
// Function to insert a new node with the given key function insert(root, x) { const temp = new Node(x);
// If tree is empty
if (root === null)
return temp;
// Find the node who is going to have
// the new node temp as its child
let parent = null;
let curr = root;
while (curr !== null) {
parent = curr;
if (curr.key > x)
curr = curr.left;
else if (curr.key < x)
curr = curr.right;
else
return root; // Key already exists
}
// If x is smaller, make it left
// child, else right child
if (parent.key > x)
parent.left = temp;
else
parent.right = temp;
return root;}
// A utility function to do inorder tree traversal function inorder(root) { if (root !== null) { inorder(root.left); console.log(root.key + " "); inorder(root.right); } }
// Creating the following BST
// 50
// /
// 30 70
// / \ /
// 20 40 60 80
let root = new Node(50); root = insert(root, 30); root = insert(root, 20); root = insert(root, 40); root = insert(root, 70); root = insert(root, 60); root = insert(root, 80);
// Print inorder traversal of the BST inorder(root);
`
Output
20 30 40 50 60 70 80
The **time complexity of **inorder traversal is **O(h), where h is the height of the tree.
The **Auxiliary space is **O(1)
**Related Links: