Introduction to Java Servlets (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 17 Apr, 2025
**Java Servlet is a Java program that runs on a Java-enabled web server or application server. It handles client requests, processes them, and generates responses dynamically. Servlets are the backbone of many server-side Java applications due to their efficiency and scalability.
**Key Features:
- Servlets work on the server side.
- Servlets are capable of handling complex requests obtained from the web server.
- Generate dynamic responses efficiently.
Creating a Basic Servlet
**Example: Here's a simple example of how a servlet works:
Java `
// Basic Java Servlet Demonstration import java.io.; import jakarta.servlet.; import jakarta.servlet.http.*;
public class HelloWorldServlet extends HttpServlet { protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { response.setContentType("text/html"); PrintWriter out = response.getWriter(); out.println("
Hello, World!
"); } }`
Configuring a Servlet
To deploy a servlet, you need to configure it in the web.xml file. This file maps URLs to servlets. For example,
XML `
<servlet>
<servlet-name>HelloWorldServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>HelloWorldServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>HelloWorldServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/hello</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>`
Modern Servlet Configuration (Annotation-Based)
From **Servlet 3.0, servlet configuration can also be done using **annotations. Instead of using **web.xml, we can configure the servlet using the ****@WebServlet annotations.**
Java `
// This annotation replaces the need for // configuring the servlet in web.xml @WebServlet("/hello") public class HelloWorldServlet extends HttpServlet { protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { response.setContentType("text/html"); PrintWriter out = response.getWriter(); out.println("
Hello, World!
"); } }`
Why Choose Java Servlet over other Technologies?
Dynamic web content requires server-side technologies. While there are many options, Java Servlet stand out due to their advantages over alternatives like Common Gateway Interface (CGI)
**Limitations of CGI:
- Process Overhead: CGI creates and destroys a process for every client request, leading to high resource consumption.
- Scalability Issues: Poor performance with increased client requests.
**Benefits of Java Servlets:
- Faster execution as Servlets do not create new processes for each request.
- Write-once, run-anywhere feature of Java.
- Single instance handles multiple requests.
- Easily integrates with databases using JDBC.
- It inherits robust security features from web servers.
- Many web servers like Apache Tomcat are free to use with Java Servlets.
Java Servlets Architecture
Java servlets container play a very important role. It is responsible for handling important tasks like load balancing, session management and resource allocation, it make sure that all the requests are process efficiently under high traffic. The container distribute requests accross multiple instances, which helps improve the system performance.
Servlet Architecture can be depicted from the image itself as provided below as follows:
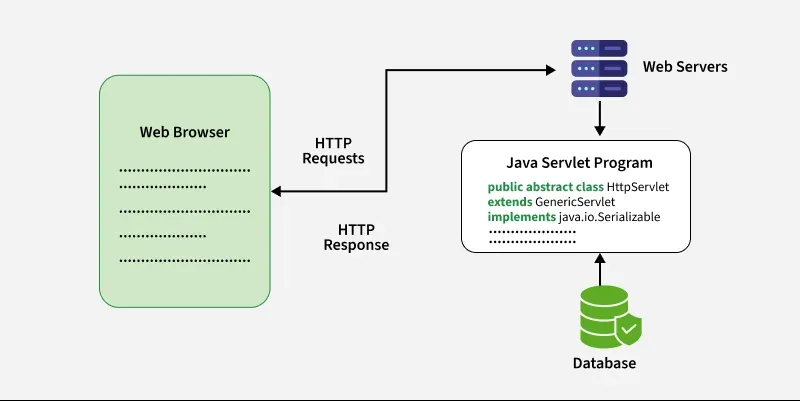
Execution of Java Servlets
Execution of Servlets basically involves Six basic steps:
- The Clients send the request to the Web Server.
- The Web Server receives the request.
- The Web Server passes the request to the corresponding servlet.
- The Servlet processes the request and generates the response in the form of output.
- The Servlet sends the response back to the webserver.
- The Web Server sends the response back to the client and the client browser displays it on the screen.
Java Servlet LifeCycle Methods
**1. init(): This method itializes the Servlet instance.
Java `
@Override public void init() throws ServletException {
// Initialization: Called once when the servlet is loaded into memory
System.out.println("Servlet initialized");}
`
**2. service(): This method Processes requests and invokes either doGet() and doPost() based on the request type.
Java `
@Override protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
// Request handling: Called each time a request is made
String method = request.getMethod();
if ("GET".equalsIgnoreCase(method)) {
doGet(request, response);
} else if ("POST".equalsIgnoreCase(method)) {
doPost(request, response);
}}
`
**3. destroy(): This method cleans up resources when the servlet is terminated.
Java `
@Override public void destroy() {
// Cleanup: Called once when the servlet is being destroyed
System.out.println("Servlet destroyed");}
`
**Need of Server-Side Extensions
The Server-Side Extensions are nothing but the technologies that are used to create dynamic Web pages. To enable dynamic web pages, a web server or container is required. To meet this requirement, independent Web server providers offer some proprietary solutions in the form of APIs (Application Programming Interface).
These APIs allow us to build programs that can run with a Web server. In this case, Java Servlet is also one of the component APIs of Java Servlets are part of Jakarta EE (formerly Java EE). which sets standards for creating dynamic Web applications in Java.
Before learning about something, it's important to know the need for that something, it's not like that this is the only technology available for creating Dynamic Web Pages. The Servlet technology is similar to other Web server extensions such as Common Gateway Interface (CGI) scripts and Hypertext Preprocessor (PHP). However, Java Servlets are more acceptable since they solve the limitations of CGI such as low performance and low degree scalability.
What is CGI (Common Gateway Interface)?
CGI is actually an external application that is written by using any of the programming languages like C or C++ and this is responsible for processing client requests and generating dynamic content.
In CGI application, when a client makes a request to access dynamic Web pages, the Web server performs the following operations:
- It first locates the requested web page i.e the required CGI application using URL.
- It then creates a new process to service the client's request.
- Invokes the CGI application within the process and passes the request information to the application.
- Collects the response from the CGI application.
- Destroys the process, prepares the HTTP response, and sends it to the client.
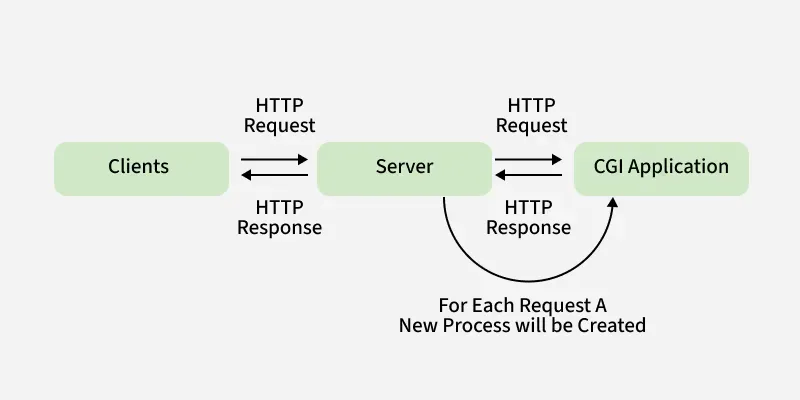
So, in CGI server has to create and destroy the process for every request. It's easy to understand that this approach is applicable for handling few clients but as the number of clients increases, the workload on the server increases and so the time is taken to process requests increases.
Difference Between Java Servlets and CGI
The table below demonstrates the difference between servlet and CGI
| Servlet | CGI (Common Gateway Interface) |
|---|---|
| Servlets are portable and efficient. | CGI is not portable. |
| In Servlets, sharing data is possible. | In CGI, sharing data is not possible. |
| Servlets can directly communicate with the webserver. | CGI cannot directly communicate with the webserver. |
| Servlets are less expensive than CGI. | CGI is more expensive than Servlets. |
| Servlets can handle the cookies. | CGI cannot handle the cookies. |
Servlets APIs and Packages
Servlets are built from two packages:
- **jakarta.servlet(Basic): Provides basic Servlet classes and interfaces.
- **jakarta.servlet.http(Advance): Advanced classes for handling HTTP-specific requests.
Key Classes and Interfaces
Various classes and interfaces present in these packages are:
| Component | Type | Package |
|---|---|---|
| Servlet | Interface | javax.servlet.* |
| ServletRequest | Interface | javax.servlet.* |
| ServletResponse | Interface | javax.servlet.* |
| GenericServlet | Class | javax.servlet.* |
| HttpServlet | Class | javax.servlet.http.* |
| HttpServletRequest | Interface | javax.servlet.http.* |
| HttpServletResponse | Interface | javax.servlet.http.* |
| Filter | Interface | javax.servlet.* |
| ServletConfig | Interface | javax.servlet.* |
Servlet Container
Servlet container, also known as Servlet engine, is an integrated set of objects that provide a run time environment for Java Servlet components. In simple words, it is a system that manages Java Servlet components on top of the Web server to handle the Web client requests.
Services provided by the Servlet container:
- **Network Services: Loads a Servlet class. The loading may be from a local file system, a remote file system or other network services. The Servlet container provides the network services over which the request and response are sent.
- **Decode and Encode MIME-based messages: Provides the service of decoding and encoding MIME-based messages.
- **Manage Servlet container: Manages the lifecycle of a Servlet.
- **Resource management: Manages the static and dynamic resources, such as HTML files, Servlets, and JSP pages.
- **Security Service: Handles authorization and authentication of resource access.
- **Session Management: Maintains a session by appending a session ID to the URL path
Real-World Use Cases of Java Servlets
- **E-Commerce Platforms: Dynamic catalog generation and order processing.
- **Banking Applications: Secure user sessions and real-time transaction processing.
- **Content Management Systems: Handling file uploads and dynamic content delivery.