What is Array? (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 12 Apr, 2025
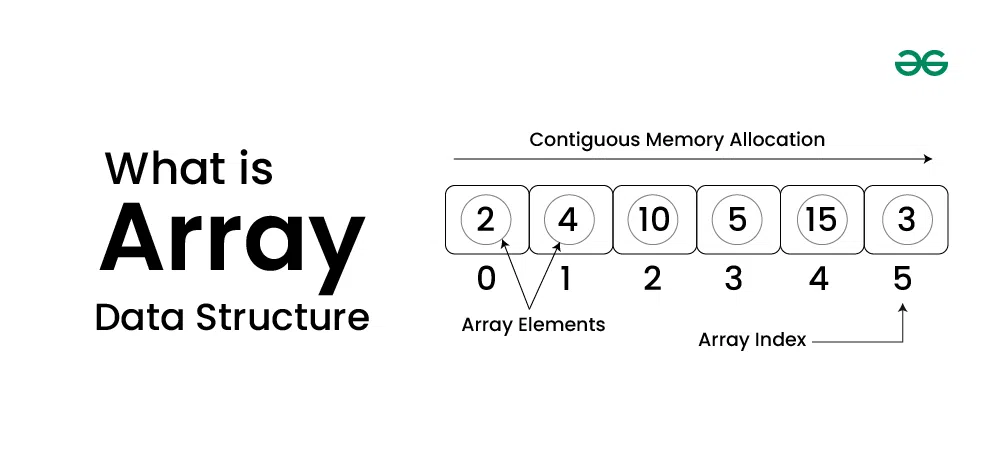
Array is a linear data structure where all elements are arranged sequentially. It is a collection of elements of **same data type stored at **contiguous memory locations.
For simplicity, we can think of an array as a flight of stairs where on each step is placed a value (let's say one of your friends). Here, you can identify the location of any of your friends by simply knowing the count of the step they are on.
This makes it easier to calculate the position of each element by simply adding an **offset to a base value, i.e., the memory location of the first element of the array (generally denoted by the name of the array). The base value is index 0 and the difference between the two indexes is the **offset.
**Is the array always of a fixed size?
Arrays at core are of fixed size only, but most of the languages provide dynamic sized arrays using the underlying fixed sized arrays. For example, vector in C++, ArrayList in Java and list in Python. In C language, the array has a fixed size meaning once the size is given to it, it cannot be changed i.e. you can’t shrink it nor can you expand it.
**Important Points to Note about Arrays
- Array is a fundamental data structure and used to implement other data structures like stack, queue, dequeue and heap.
- The main advantages of using array over other data structures are cache friendliness and random access memory. Please refer **Getting Started with Array Data Structure for more details.