Introduction to Graph Data Structure (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 24 Nov, 2025
A graph is a non-linear data structure made up of vertices (nodes) and edges (connections) that represent relationships between objects. Unlike arrays or linked lists, graphs do not follow a sequential order.
Example: On a map, each city is a vertex, and each road connecting two cities is an edge. This way, a graph represents how cities are linked.
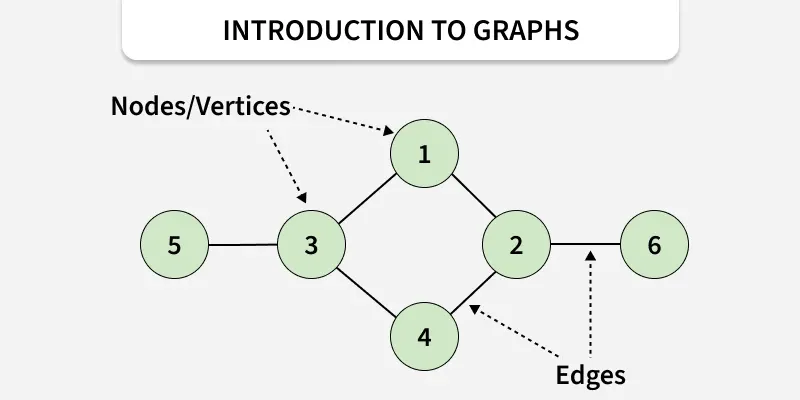
Components of Graph Data Structure
- **Vertices: Vertices are the fundamental units of the graph. Sometimes, vertices are also known as vertex or nodes. Every node/vertex can be labeled or unlabelled.
- **Edges: Edges are drawn or used to connect two nodes of the graph. It can be ordered pair of nodes in a directed graph. Edges can connect any two nodes in any possible way. There are no rules. Sometimes, edges are also known as arcs. Every edge can be labelled/unlabelled.
Types OfGraphs in Data Structure and Algorithms
A graph can be divided into multiple categories based on different properties such as edges, direction, connectivity and many others.
Based on weight :
1. Weighted Graphs
A weighted graph is a graph where each edge has a number (weight) that represents distance, cost, or time.
2. Unweighted Graphs
An **unweighted graph is a graph where all edges are treated equally, with no extra values like distance or cost.

Based on Edge Direction:
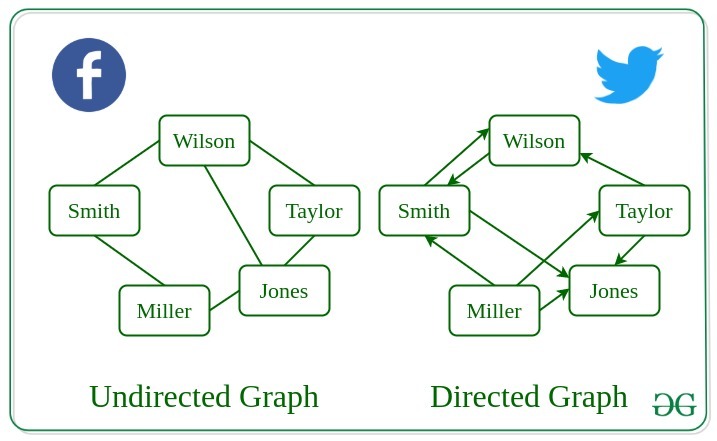
3. Undirected Graph
A graph in which edges do not have any direction. That is the nodes are unordered pairs in the definition of every edge.
4. Directed Graph
A graph in which edge has direction. That is the nodes are ordered pairs in the definition of every edge.
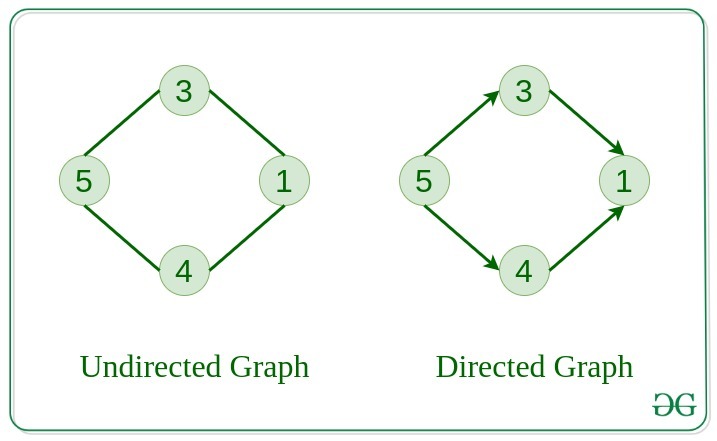
**For More Refer this Article: Types Of Graph
Representation of Graph Data Structure:
There are multiple ways to store a graph: The following are the most common representations.
- Adjacency Matrix
- Adjacency List
Adjacency Matrix Representation of Graph Data Structure:
In this method, the graph is stored in the form of the 2D matrix where rows and columns denote vertices. Each entry in the matrix represents the weight of the edge between those vertices.
matrix[i][j] = 1 if there is an edge between vertex i and vertex j.
matrix[i][j] = 0 if there is no edge.
-copy.webp)
Adjacency List Representation of Graph:
This graph is represented as a collection of array lists. There is an array of pointer which points to the edges connected to that vertex.
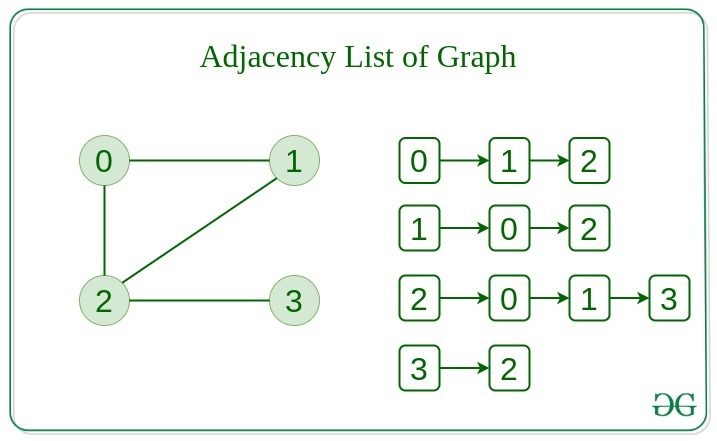
**For More Refer this Article : Represent graph using adj list and mat
Difference between Tree and Graph:
Tree is a restricted type of Graph Data Structure, just with some more rules. Every tree will always be a graph but not all graphs will be trees. Linked List, Trees, and Heaps all are special cases of graphs.
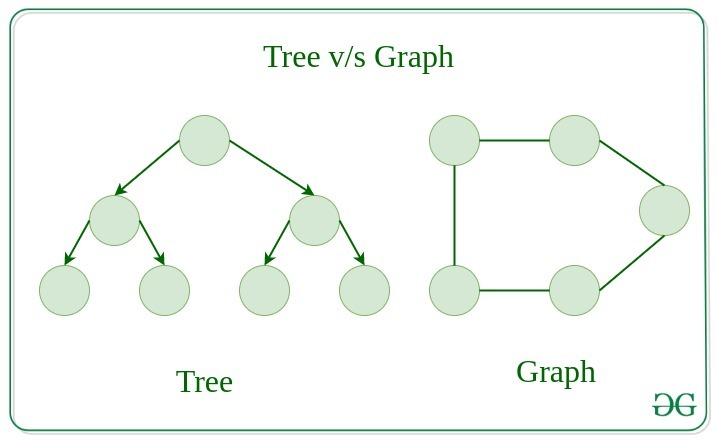
**For More Refer this Article : Trees vs Graph
Traversal Technique of Graph:
Traversal techniques are used to visit all the vertices of a graph systematically. These methods help to explore the graph completely and are useful for solving many graph-related problems.
Depth First Search (DFS):
- Explores as far as possible along each branch before backtracking.
- Uses a stack (or recursion).
**For More Refer this Article : Depth First Search
Breadth First Search (BFS)
- Explores all neighbors of a vertex before moving to the next level.
- Uses a queue.
**For More Refer this Article : Breadth First Search
Real-Life Applications of Graph Data Structure:
Graph Data Structure has numerous real-life applications across various fields. Some of them are listed below:
- **Social Networks: Represent users and their connections; used to find mutual friends, suggest new connections, and detect communities.
- **Computer Networks: Model routers and data links; used for efficient routing, fault detection, and network optimization.
- **Transportation Networks: Represent cities and routes; used to find shortest or fastest paths and plan optimal travel routes.
- **Neural Networks: Represent neurons and synapses; used to simulate learning, brain behavior, and data processing.
- **Compilers: Represent data dependencies and control flows; used for optimization, register allocation, and code analysis.
- **Robot Path Planning: Represent states and transitions; used to compute the safest or shortest route for autonomous movement.
- **Project Dependencies: Represent tasks and dependencies; used in topological sorting to determine the correct execution order.
- **Network Optimization: Represent network nodes and links; used to minimize cost, reduce latency, and improve efficiency.
Advantages of Graph Data Structure:
- **Graphs are flexible: Unlike arrays, linked lists, or trees, graphs have no restrictions and can represent any type of relationship.
- **Model real-world problems: Useful for pathfinding, data clustering, network analysis, and machine learning.
- **Represent items and relationships: Any set of items and their connections can be modeled as a graph.
- **Simplifies complex data: Graphs make complex relationships easy to visualize and understand.