Introduction to Linked List Data Structure and Algorithm Tutorials (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 22 Oct, 2024
**Linked List is basically chains of nodes where each node contains information such as **data and a **pointer to the next node in the chain. It is a popular data structure with a wide range of real-world applications. Unlike Arrays, Linked List elements are not stored at a contiguous location. In the linked list there is a **head pointer, which points to the first element of the linked list, and if the list is empty then it simply points to null or nothing.
In this article, we will provide a complete introduction of Linked List, which will help you tackle any problem based on Linked List.
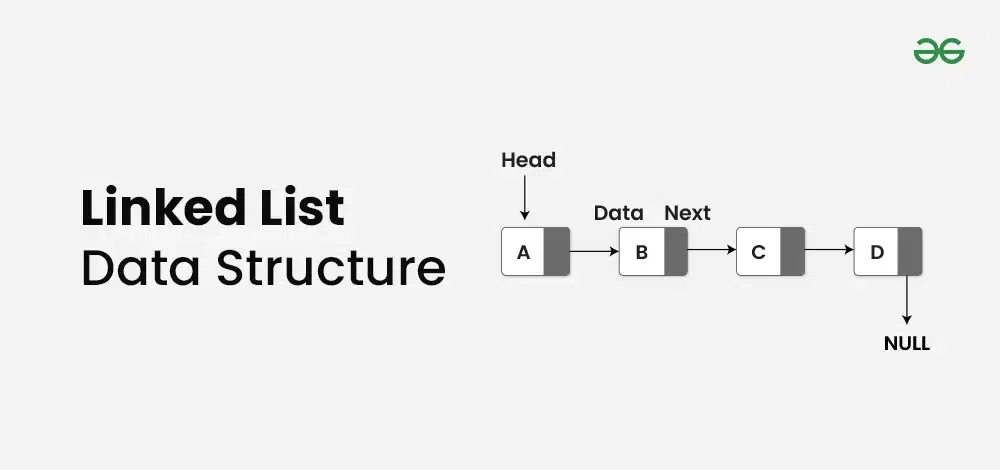
Basic Terminologies of Linked List
- **Head: The Head of a linked list is a pointer to the first node or reference of the first node of linked list. This pointer marks the beginning of the linked list.
- **Node: Linked List consists of a series of nodes where each node has two parts: **data and **next pointer.
- **Data: Data is the part of node which stores the information in the linked list.
- **Next pointer: Next pointer is the part of the node which points to the next node of the linked list.
Importance of Linked List
Here are a few advantages of a linked list that is listed below, it will help you understand why it is necessary to know.
- **Dynamic Data structure: The size of memory can be allocated or de-allocated at run time based on the operation insertion or deletion.
- **Ease of Insertion/Deletion: The insertion and deletion of elements are simpler than arrays since no elements need to be shifted after insertion and deletion, Just the address needed to be updated.
- **Efficient Memory Utilization: As we know Linked List is a dynamic data structure the size increases or decreases as per the requirement so this avoids the wastage of memory.
- **Implementation: Various advanced data structures can be implemented using a linked list like a stack, queue, graph, hash maps, etc.
Implementations of Basic Operations on Different Types of List
Basic Operations on Singly Linked List
The following are some basic operations performed on a Single Linked List:
- **Insertion: The insertion operation can be performed in three ways. They are as follows:
- **Deletion: The deletion operation can be performed in three ways. They are as follows:
- **Traverse****:** This process displays the elements of a Single-linked list.
- **Search:It is a process of determining and retrieving a specific node either from the front, the end or anywhere in the list.
**Operations on Doubly Linked List:
In a doubly linked list, we perform the following operations...
- **Insertion: The insertion operation can be performed in three ways as follows:
- **Deletion: The deletion operation can be performed in three ways as follows...
- Deleting from the Beginning of the list
- Deleting from the End of the list
- Deleting a Specific Node
- **Display: This process displays the elements of a double-linked list.
**Commonly used operations on Circular Linked List:
The following operations are performed on a Circular Linked List
- **Insertion: The insertion operation can be performed in three ways:
- **Deletion: The deletion operation can be performed in three ways:
- **Display: This process displays the elements of a Circular linked list.
Linked List vs. Array:
| Array | Linked List |
|---|---|
| Arrays are stored in contiguous location. | Linked Lists are not stored in contiguous location. |
| Fixed size (Dynamic Sized Arrays also internally use fixed sized arrays) | Dynamic Size |
| Only store elements no extra reference / pointer. | It stores both data and address of next node. |
| Elements can be accessed easily in O(1) time. | Elements can be access by traversing through all the nodes till we reach the required node. |
| Insertion and deletion operation is slower than Linked List. | Insertion and deletion operation is faster than Array. |
Time Complexity Analysis of Linked List and Array:
| Operation | Linked list | Array |
|---|---|---|
| Random Access | O(N) | O(1) |
| Insertion and deletion at beginning | O(1) | O(N) |
| Insertion and deletion at end | O(N) (If we maintain only head) | O(1) |
| Insertion and deletion at a random position | O(N) | O(N) |
Please refer Applications, Advantages and Disadvantages of Linked List for more details
Conclusion:
There are many advantages of the linked list compared to array, despite the fact that they solve the similar problem to arrays, we have also discussed the advantage, disadvantages, and its application, and we concluded the fact that we can use a linked list if we need the dynamic size of storage and list are good for adding and removing items quickly or for tasks that require sequence but are not suitable for querying or search elements in a large collection of data.
So, it becomes important that we should always keep in mind the **positive and **negative aspects of a **data structure and how they relate to the problem you are trying to solve.
**Related articles:
- Top 50 Problems on Linked List Data Structure asked in SDE Interviews
- Understanding the basics of Linked List
- SDE SHEET – A Complete Guide for SDE Preparation
- Amazon SDE Sheet – A Guide for Amazon SDE Interview Preparation
- Google Interview Preparation For Software Engineer – A Complete Guide
- 100 Days of Code – A Complete Guide For Beginners and Experienced