Introduction to memory and memory units (original) (raw)
Memory is required to save data and instructions. Memory is divided into cells, and they are stored in the storage space present in the computer. Every cell has its unique location/address. Memory is very essential for a computer as this is the way it becomes somewhat more similar to a human brain. In this article, we are going to discuss memory and memory units in detail.
What is Memory?
Memory devices are digital systems that store data either temporarily or for a long term. Digital computers to hard disks have built-in memory devices that can store the data of users or manufacturers. The data either be in the form of control programs or programs that boot the system. Hence, to store such a huge amount of data the memory devices must have enormous capacity. The challenge is to build memory devices that have large capacities but are cost-effective. The memory devices must be capable of storing both permanent data and instantaneous data.
Memories are made up of registers. Each register in the memory is one storage location. The storage location is also called a memory location. Memory locations are identified using Address. The total number of bits a memory can store is its capacity. A storage element is called a Cell. Each register is made up of a storage element in which one bit of data is stored.
The data in a memory are stored and retrieved by the process called writing and reading respectively.
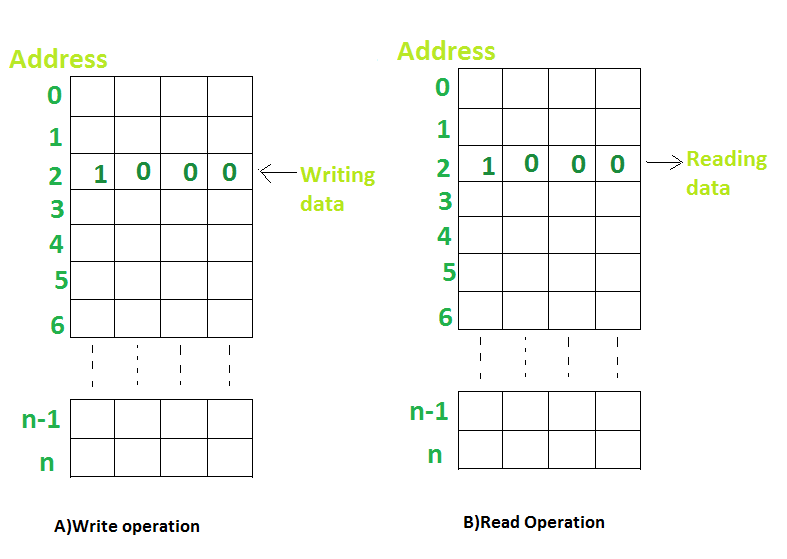
- A word is a group of bits where a memory unit stores binary information. A word with a group of 8 bits is called a byte.
- A memory unit consists of data lines, address selection lines, and control lines that specify the direction of transfer.
The block diagram of a memory unit is shown below:
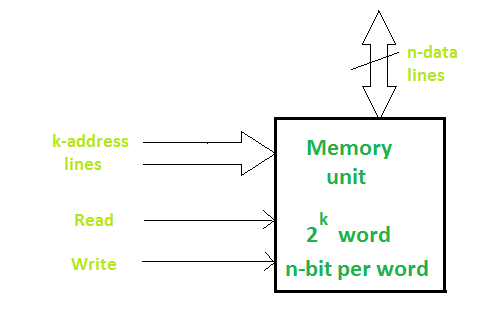
Data lines provide the information to be stored in memory. The control inputs specify the direct transfer. The k-address lines specify the word chosen.
When there are k address lines, 2k memory words can be accessed.
Types of Computer Memory
- **Cache Memory: This temporary storage area, known as a cache, is more readily available to the processor than the computer's main memory source. It is also called _CPU memory because it is typically integrated directly into the CPU chip or placed on a separate chip with a bus interconnect with the CPU.
- **RAM: It is one of the parts of the Main memory, also famously known as Read Write Memory. Random Access memory is present on the motherboard and the computer’s data is temporarily stored in RAM. As the name says, RAM can help in both Read and write.
- **D RAM (Dynamic RAM): D RAM uses capacitors and transistors and stores the data as a charge on the capacitors. They contain thousands of memory cells. It needs refreshing of charge on capacitor after a few milliseconds. This memory is slower than S RAM.
- **S RAM (Static RAM): S RAM uses transistors and the circuits of this memory are capable of retaining their state as long as the power is applied. This memory consists of the number of flip flops with each flip flop storing 1 bit. It has less access time and hence, it is faster.
- **ROM: ROM full form is Read Only Memory. ROM is a non volatile memory and it is used to store important information which is used to operate the system. We can only read the programs and data stored on it and can not modify of delete it.
- **MROM(Masked ROM): Hard-wired devices with a pre-programmed collection of data or instructions were the first ROMs. Masked ROMs are a type of low-cost ROM that works in this way.
- **PROM (Programmable Read Only Memory): This read-only memory is modifiable once by the user. The user purchases a blank PROM and uses a PROM program to put the required contents into the PROM. Its content can’t be erased once written.
- **EPROM (Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory): EPROM is an extension to PROM where you can erase the content of ROM by exposing it to Ultraviolet rays for nearly 40 minutes.
- **EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory): Here the written contents can be erased electrically. You can delete and reprogram EEPROM up to 10,000 times. Erasing and programming take very little time, i.e., nearly 4 -10ms(milliseconds). Any area in an EEPROM can be wiped and programmed selectively.
- **Virtual memory: A memory management technique where secondary memory can be used as if it were a part of the main memory. Virtual memory uses hardware and software to enable a computer to compensate for physical memory shortages by temporarily transferring data from RAM to disk storage.
**What is Primary Memory?
It is also referred to as main memory or internal memory. It is a computer system's temporary storage component which is directly accessible by the central processing unit (CPU). It houses data for immediate processing.
Characteristics
- volatile: Data is lost upon power loss.
- High-speed access.
- Limited capacity relative to secondary storage.
- Examples: Random Access Memory(RAM), Read-Only Memory, Cache memory.
Advantages
- **High-speed access: Data can be retrieved and stored very quickly.
- **Directly accessible by CPU: No intermediate steps are required for data transfer.
Disadvantages
- **Volatile: Data is lost when power is turned off.
- **Limited storage capacity: compared to secondary storage, primary memory is relatively small.
- **Expensive: Cost per unit is higher than secondary storage.
Different Applications of Primary Memory are:
- Temporary storage
- Multitasking
- Buffering
- Caching
**What is Secondary Memory?
Secondary memory or external memory serves as long-term storge for data and programs. Unlike primary memory, it is not directly accessible by the CPU and requires input/output operations.
Characteristics
- Non-volatile: Data persists even when the system is powered off.
- slower access speeds compared to primary memory.
- High storage capacity.
- Examples: Hard Disk Drives(HDD), Solid-State Drives(SSD), Optical drives(CD, DVD, Blu-ray).
Advantages
- **Non-volatile: Data persists even when the power is turned off.
- **Large storage capacity: can store vast amount of data.
- **Relatively Inexpensive: cost-effective for storing large volumes of data.
Disadvantages
- **Slower access time: Data retrieval is slower compared to primary memory.
- **Requires input/output operations: Data transfer involves additional steps.
Different Applications of Primary Memory are:
- Long-term storage
- Operating system installation
- Software installation
- Data backup
- Media storage
read more about - Difference between Primary and Secondary Memory
Units of Memory
Memory units are used to measure the size and represent data. Some of the commonly used memory units are:
1. Bit
The first memory location in a computer is bit. The smallest measurement unit for data held in primary memory and storage devices is a bit. Out of the binary values 0 and 1, a bit can only have one.
- The smallest measurement unit for data in primary memory and storage devices.
- Represents binary values 0 and 1.
2. Nibble
- It means the group of 4 bits.
3. Word
It is a fixed number of bits, it is different from computer to computer, but the same for each device. Compute store information in the form of words.
- A fixed number of bits that varies across computers but remains consistent within each device.
- Used to store information in computers.
4. Bytes
The fundamental unit used to measure data is the byte. It has 8 bits in it. A byte can therefore represent 2 * 8 or 256 values. They determine the size of files, documents, photos, and other kinds of data.
- The fundamental unit for measuring data, consisting of 8 bits.
- Represents 256 values and determines file, document, photo, and data sizes.
5. Kilobyte
1024 bytes is equal to one kilobyte. It is widely used to denote small file sizes and data storage capacities. One kilobyte can hold a small image or around 1024 characters of text. It frequently shows up in text documents, spreadsheets, and small image files.
- Equal to 1024 bytes.
- Denotes small file sizes and storage capacities.
- Can hold small images or around 1024 characters of text.
6. Megabyte
A megabyte is 1024 kilobytes in size. It contains more info as compared to a kilobyte. A megabyte can hold longer texts, high-resolution images, and short audio clips. It is used to calculate the size of files comprising music and short films, software packages, and documents. Megabytes are still important and frequently used, even though larger units of measurement are being used more frequently as a result of the growing number of data files.
- Comprising 1024 kilobytes.
- Contains more information compared to a kilobyte.
- Holds longer texts, high-resolution images, and short audio clips.
- Measures file sizes of music, short films, software packages, and documents.
7. Gigabyte
1024 megabytes is equal to one gigabyte. It has a substantial amount of data storage space. Larger files, such full photo albums, high-definition movies, and software programs can fit within a gigabit. The storage capabilities of hard drives, solid-state drives, and other forms of data storage devices are routinely assessed utilizing this technique.
- Equal to 1024 megabytes.
- Offers substantial data storage space.
- Suitable for larger files, such as full photo albums, high-definition movies, and software programs.
8. Terabyte
A terabyte is made up of 1024 gigabytes. It has a substantial amount of data storing capacity. A terabyte can hold a lot of data in large databases, massive media collections, and enterprise-level storage systems. It is frequently used by data centers, cloud storage services, and external hard drives with large storage capacities. As the demand for large-scale data processing and storage grows, terabytes are becoming more and more important.
- Comprising 1024 gigabytes.
- Provides substantial data storing capacity.
- Holds large databases, media collections, and enterprise-level storage systems.
9. Petabyte
A petabyte is a colossal unit of data storage capacity. A petabyte may hold massive amounts of data, including significant video libraries, sizable databases, and sizable collections of high-resolution pictures. It is often used in data centers, cloud storage, and scientific research that uses a lot of data.
- A colossal unit of data storage capacity.
- Stores massive data quantities, like video libraries and large databases.
10. Exabyte (1024 petabytes)
An exabyte is equal to one EB. It has a substantial amount of data storage space. Exabytes can store vast film archives, massive data warehouses, and global internet traffic. It is extensively used in large-scale scientific simulations, cloud computing infrastructures, and enterprise-level storage systems.
- Equal to 1024 petabytes.
- Holds vast film archives, data warehouses, and global internet traffic.
11. Zettabyte (1024 exabytes)
A zettabyte. It represents a capacity for data storage that is almost unimaginable. Zettabytes have the capacity to store unfathomably large amounts of data, including worldwide internet content, long-term archival storage, and in-depth global data analysis.
- Represents an almost unimaginable data storage capacity.
- Stores worldwide internet content, long-term archival data, and extensive global analysis.
12. Yottabyte
1024 zettabytes make up a yottabyte (abbreviated YB). It stands for an incredible amount of data storage. Unimaginable amounts of data, such as the equivalent of storing all of the material on the internet numerous times or tracking vast amounts, may be stored in yottabytes.
- Comprising 1024 zettabytes.
- Stands for an incredible amount of data storage.
- Can hold vast amounts equivalent to storing internet content numerous times.
Functions of Memory Unit
The memory unit of a computer has several functions:
- **Stores Data and Instructions: The memory unit stores data and instructions needed by the **CPU to perform tasks efficiently. This includes data related to operations to be performed and data related to the program.
- **Tracks Interim Results: The memory unit keeps track of the interim results of processing.
- **Saves Final Results: The memory unit saves the final processing results before sending them to an output device.
- **Receives And Transmits Inputs And Outputs: The memory unit receives and transmits all inputs and outputs.
The size of the memory unit affects its speed, power, and capabilities. without a memory unit, the processor would have to wait longer for data retrieval.
Conversions of Units
| Name | Equal To | Size (In Bytes) |
|---|---|---|
| Bit | 1 Bit | 1/8 |
| Nibble | 4 Bits | 1/2 (rare) |
| Byte | 8 Bits | 1 |
| Kilobyte | 1024 Bytes | 1024 |
| Megabyte | 1024 Kilobytes | 1, 048, 576 |
| Gigabyte | 1024 Megabytes | 1, 073, 741, 824 |
| Terabyte | 1024 Gigabytes | 1, 099, 511, 627, 776 |
| Petabyte | 1024 Terabytes | 1, 125, 899, 906, 842, 624 |
| Exabyte | 1024 Petabytes | 1, 152, 921, 504, 606, 846, 976 |
| Zettabyte | 1024 Exabytes | 1, 180, 591, 620, 717, 411, 303, 424 |
| Yottabyte | 1024 Zettabytes | 1, 208, 925, 819, 614, 629, 174, 706, 176 |
Memory Hierarchy
Memory hierarchy is the organization of different types of memory in a computer system based on their speed, cost, and size. Faster and more expensive memory, like registers and cache, is placed closer to the CPU, while slower and larger memory, like RAM and hard drives, is further away. This arrangement helps the computer work efficiently by storing frequently used data in faster memory and less-used data in slower memory.
read more about - Memory Hierarchy Design and its Characteristics
Conclusion
Memory is the vital component of a computer system that stores data and instructions for processing. It is divided into various types, each with its specific characteristics and purpose. From the rapid access of **RAM to the persistent storage of ROM and the vast capacities of secondary storage, memory units are fundamental to the operation of modern computers.