Introduction to TypeScript (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 02 Apr, 2025
TypeScript is a syntactic superset of JavaScript that adds optional static typing, making it easier to write and maintain large-scale applications.
- Allows developers to catch errors during development rather than at runtime, improving code reliability.
- Enhances code readability and maintainability with features like type annotations and interfaces.
- Fully compatible with JavaScript, enabling seamless integration with existing projects.
- It is ideal for large-scale applications where strict type-checking and better tooling are essential.
What is TypeScript?
TypeScript is essentially JavaScript with additional features, most notably the ability to use type annotations. While JavaScript is dynamically typed, meaning types are determined at runtime, TypeScript allows developers to define types at compile time. This can help catch errors early in the development process and makes code easier to understand and maintain.
Key Features of TypeScript
1. Static Type Checking (Optional)
TypeScript allows you to check and assign types to variables, parameters, and function return values. While this step requires a little more effort, it significantly improves code quality. Optional static typing helps prevent bugs and makes your code more readable.
2. Class-Based Objects
One of TypeScript’s standout features is its support for **classes. Unlike JavaScript’s prototype-based approach, TypeScript lets you write true object-oriented code. You can create classes, define constructors, and use inheritance and access modifiers (public, private, protected).
3. Modularity
TypeScript promotes modularity. By using modules, you can organize your code into smaller, reusable pieces. This modularity enhances maintainability and collaboration among team members.
4. ES6 Features
TypeScript embraces **ECMAScript 6 (ES6) features. If you’re familiar with ES6 syntax (arrow functions, template literals, destructuring, etc.), you’ll feel right at home with TypeScript.
5. Syntactical Sugaring
TypeScript’s syntax is closer to that of high-level languages like Java. It’s like a sweetener for developers—more concise and expressive.
Structure of TypeScript
TypeScript Code cannot be interpreted by the Browser directly so there is a need to compile the TypeScript code into plain JavaScript Code, for this purpose we need the TypeScript Compiler (tsc).
TypeScript Compiler (tsc)
- Written in TypeScript itself.
- Compiles .ts files to .js files.
- Installed as an NPM package (NodeJS).
- Supports ES6 syntax.
TypeScript vs. JavaScript
| Feature | TypeScript | JavaScript |
|---|---|---|
| Typing | Statically Typed | Dynamically Typed |
| Object Orientation | Class-Based | Prototype-Based |
| Modules | Supports Modules | Does not Support Modules |
| Error Detection | Compile-Time Errors | Runtime Errors |
| Compilation | Requires Compilation | Interpreted by Browsers/Node.js |
| Code Maintainability | Easier due to static typing and interfaces | Can be harder in large codebases |
| Tooling Support | Advanced (autocompletion, refactoring) | Basic |
| Use Cases | Large projects, complex applications | Small to medium projects, quick prototyping |
Why TypeScript is Gaining Popularity ?
- **Enhanced Code Quality: Static typing and interfaces lead to more robust and maintainable code.
- **Developer Experience: Improved tooling support provides a richer environment for spotting errors during development.
- **Framework Adoption: Popular frameworks like Angular have adopted TypeScript, contributing to its rising popularity.
- **Active Community: Used by top tech companies, ensuring continuous improvement and support.
Why Do We Use TypeScript ?
- **Better developer experience - One of the biggest advantages of TypeScript is to enable IDEs to provide a richer environment for spotting common errors as you type the code. For a large scale project adopting TypeScript might result in more robust software, while still being deployable where a regular JavaScript application would run.
- **Code quality - Defining data structures in the beginning, using types and interfaces, forces you to think about your app’s data structure from the start and make better design decisions.
- **Prevents bugs - TypeScript won't make your software bug free. But it can prevent a lot of type-related errors. Along with the Clever IntelliSense many browsers and IDEs support direct debugging through Source Maps.
- **Active community - TypeScript is getting more and more popular. It’s used by the top tech companies like Google, Airbnb, Shopify, Asana, Adobe, and Mozilla so we can assume that it reaches their expectations in terms of scalability - as they are developing large and complex applications.
- **TypeScript Is Just JavaScript - TypeScript starts with JavaScript and ends with JavaScript. Typescript adopts the basic building blocks of your program from JavaScript. All TypeScript code is converted into its JavaScript equivalent for the purpose of execution.
How do I use TypeScript?
A common way to use TypeScript is by utilizing the official TypeScript compiler, which transpiles TypeScript code into JavaScript. To get started, you'll need to set up the compiler for your local project. Many popular code editors, such as Visual Studio Code, have built-in TypeScript support, providing real-time error detection and suggestions as you write your code. This integration makes it easier to work with TypeScript, ensuring you catch potential issues early in the development process.
Steps for Adding TypeScript File in HTML Code
1. Create the TypeScript File (types.ts)
JavaScript `
let myString; myString = 'Hello from ts'; console.log(myString);
`
- myString is declared as a string variable.
- It's assigned the value 'Hello from TypeScript'.
- The value is logged to the console.
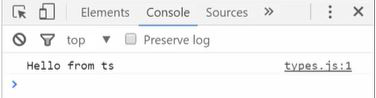
2. Compile TypeScript to JavaScript
Use the TypeScript compiler (tsc) to transpile types.ts into JavaScript. Open your terminal and run:
tsc types.ts
This command generates a types.js file containing the equivalent JavaScript code.
3. Create the HTML File (index.html)
HTML `
Welcome to GeeksforGeeks
Default code has been loaded into the Editor.
`
- A heading and a paragraph for content.
- A script tag that references the compiled JavaScript file types.js.
4. Run the HTML File
Open index.html in a web browser.