Iterative searching in Binary Search Tree (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 30 Sep, 2024
Given a **Binary Search Tree and a **key, the task is to find if the node with a value key is **present in the BST or not.
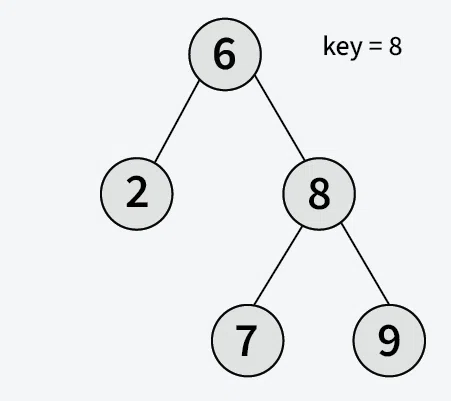
**Example:
**Input: Root of the below BST
**Output: True
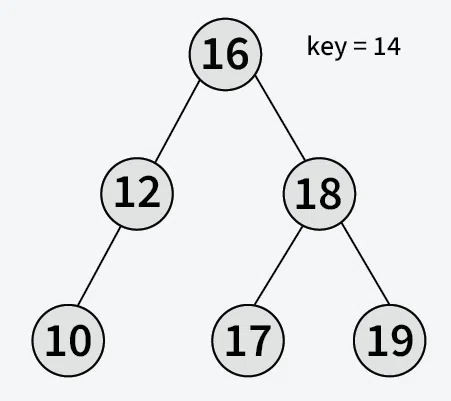
**Explanation: 8 is present in the BST as right child of root**Input: Root of the below BST
**Output: False
**Explanation: 14 is not present in the BST
**Approach:
The idea is to traverse the **Binary search tree, starting from the **root node. If the **current node's data is equal to **key, then **return true. If node's value is **less than key, then traverse the **right subtree by updateing current as current'right. Else, set current as current'left to travrese in left subtree. If current becomes NULL , key is **not present in the BST, return false.
Below is implementation of the above approach:
C++ `
// C++ program to search in // a BST. #include using namespace std;
class Node { public: int data; Node* left; Node* right; Node(int x) { data = x; left = nullptr; right = nullptr; } };
// Function to search in a bst. bool search(struct Node* root, int x) {
Node* curr = root;
while (curr != nullptr) {
// If curr node is x
if (curr->data == x)
return true;
// Search in right subtree
else if (curr->data < x)
curr = curr->right;
// Search in right subtree
else
curr = curr->left;
}
// If x is not found.
return false;}
int main() {
// Create a hard coded BST.
// 20
// / \
// 8 22
// / \
// 4 12
// / \
// 10 14
Node* root = new Node(20);
root->left = new Node(8);
root->left->left = new Node(4);
root->left->right = new Node(12);
root->left->right->left = new Node(10);
root->left->right->right = new Node(14);
root->right = new Node(22);
int x = 12;
if(search(root, x)) {
cout << "True";
}
else cout << "False";
return 0;}
C
// C program to search in // a BST. #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h>
struct Node { int data; struct Node* left; struct Node* right; };
// Function to search in a bst. int search(struct Node* root, int x) {
struct Node* curr = root;
while (curr != NULL) {
// If curr node is x
if (curr->data == x)
return 1;
// Search in right subtree
else if (curr->data < x)
curr = curr->right;
// Search in left subtree
else
curr = curr->left;
}
// If x is not found.
return 0;}
struct Node* createNode(int x) { struct Node* newNode = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); newNode->data = x; newNode->left = NULL; newNode->right = NULL; return newNode; }
int main() {
// Create a hard coded BST.
// 20
// / \
// 8 22
// / \
// 4 12
// / \
// 10 14
struct Node* root = createNode(20);
root->left = createNode(8);
root->left->left = createNode(4);
root->left->right = createNode(12);
root->left->right->left = createNode(10);
root->left->right->right = createNode(14);
root->right = createNode(22);
int x = 12;
if(search(root, x)) {
printf("True");
}
else printf("False");
return 0;}
Java
// Java program to search in // a BST. class Node { int data; Node left, right;
public Node(int x) {
data = x;
left = null;
right = null;
}}
class GfG {
// Function to search in a bst.
static boolean search(Node root, int x) {
Node curr = root;
while (curr != null) {
// If curr node is x
if (curr.data == x)
return true;
// Search in right subtree
else if (curr.data < x)
curr = curr.right;
// Search in left subtree
else
curr = curr.left;
}
// If x is not found.
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a hard coded BST.
// 20
// / \
// 8 22
// / \
// 4 12
// / \
// 10 14
Node root = new Node(20);
root.left = new Node(8);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(12);
root.left.right.left = new Node(10);
root.left.right.right = new Node(14);
root.right = new Node(22);
int x = 12;
System.out.println(search(root, x));
}}
Python
Python program to search in
a BST.
class Node: def init(self, x): self.data = x self.left = None self.right = None
Function to search in a bst.
def search(root, x):
curr = root
while curr is not None:
# If curr node is x
if curr.data == x:
return True
# Search in right subtree
elif curr.data < x:
curr = curr.right
# Search in left subtree
else:
curr = curr.left
# If x is not found.
return Falseif name == "main":
# Create a hard coded BST.
# 20
# / \
# 8 22
# / \
# 4 12
# / \
# 10 14
root = Node(20)
root.left = Node(8)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(12)
root.left.right.left = Node(10)
root.left.right.right = Node(14)
root.right = Node(22)
x = 12
print(search(root, x))C#
// C# program to search in // a BST. using System;
class Node { public int data; public Node left, right;
public Node(int x) {
data = x;
left = null;
right = null;
}}
class GfG {
// Function to search in a bst.
static bool search(Node root, int x) {
Node curr = root;
while (curr != null) {
// If curr node is x
if (curr.data == x)
return true;
// Search in right subtree
else if (curr.data < x)
curr = curr.right;
// Search in left subtree
else
curr = curr.left;
}
// If x is not found.
return false;
}
static void Main(string[] args) {
// Create a hard coded BST.
// 20
// / \
// 8 22
// / \
// 4 12
// / \
// 10 14
Node root = new Node(20);
root.left = new Node(8);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(12);
root.left.right.left = new Node(10);
root.left.right.right = new Node(14);
root.right = new Node(22);
int x = 12;
Console.WriteLine(search(root, x));
}}
JavaScript
// JavaScript program to search in // a BST. class Node { constructor(x) { this.data = x; this.left = null; this.right = null; } }
// Function to search in a bst. function search(root, x) {
let curr = root;
while (curr !== null) {
// If curr node is x
if (curr.data === x)
return true;
// Search in right subtree
else if (curr.data < x)
curr = curr.right;
// Search in left subtree
else
curr = curr.left;
}
// If x is not found.
return false;}
// Create a hard coded BST.
// 20
// /
// 8 22
// /
// 4 12
// /
// 10 14
let root = new Node(20);
root.left = new Node(8);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(12);
root.left.right.left = new Node(10);
root.left.right.right = new Node(14);
root.right = new Node(22);
let x = 12; console.log(search(root, x));
`
**Time Complexity: O(h), where **h is the height of the BST.
**Auxiliary Space: O(1)
**Related article: