Java ifelseif ladder with Examples (original) (raw)
Java if-else-if ladder with Examples
Last Updated : 05 Dec, 2024
The **Java if-else-if ladder is used to evaluate multiple conditions sequentially. It allows a program to check several conditions and execute the block of code associated with the first true condition. If none of the conditions are true, an optional else block can execute as a fallback.
**Example: The below example demonstrates a straightforward **if-else-if **ladder structure. It evaluates a number and prints the corresponding message based on the condition.
Java `
// Java program to demonstrate // a simple if-else-if ladder class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 20;
// if-else-if ladder to check the value of i
if (i == 10)
System.out.println("i is 10");
else if (i == 20)
System.out.println("i is 20");
else
System.out.println("i is neither 10 nor 20");
}}
`
**Dry-Running Above Example
- Program starts.
iis initialized to20.- The first
ifconditioni == 10is checked:- It evaluates to
falsebecauseiis20.
- It evaluates to
- The second
else ifconditioni == 20is checked:- It evaluates to
truebecauseiis20. - 4.a)
"i is 20"gets printed.
- It evaluates to
- The
elseblock is skipped since a condition was satisfied. - Program ends.
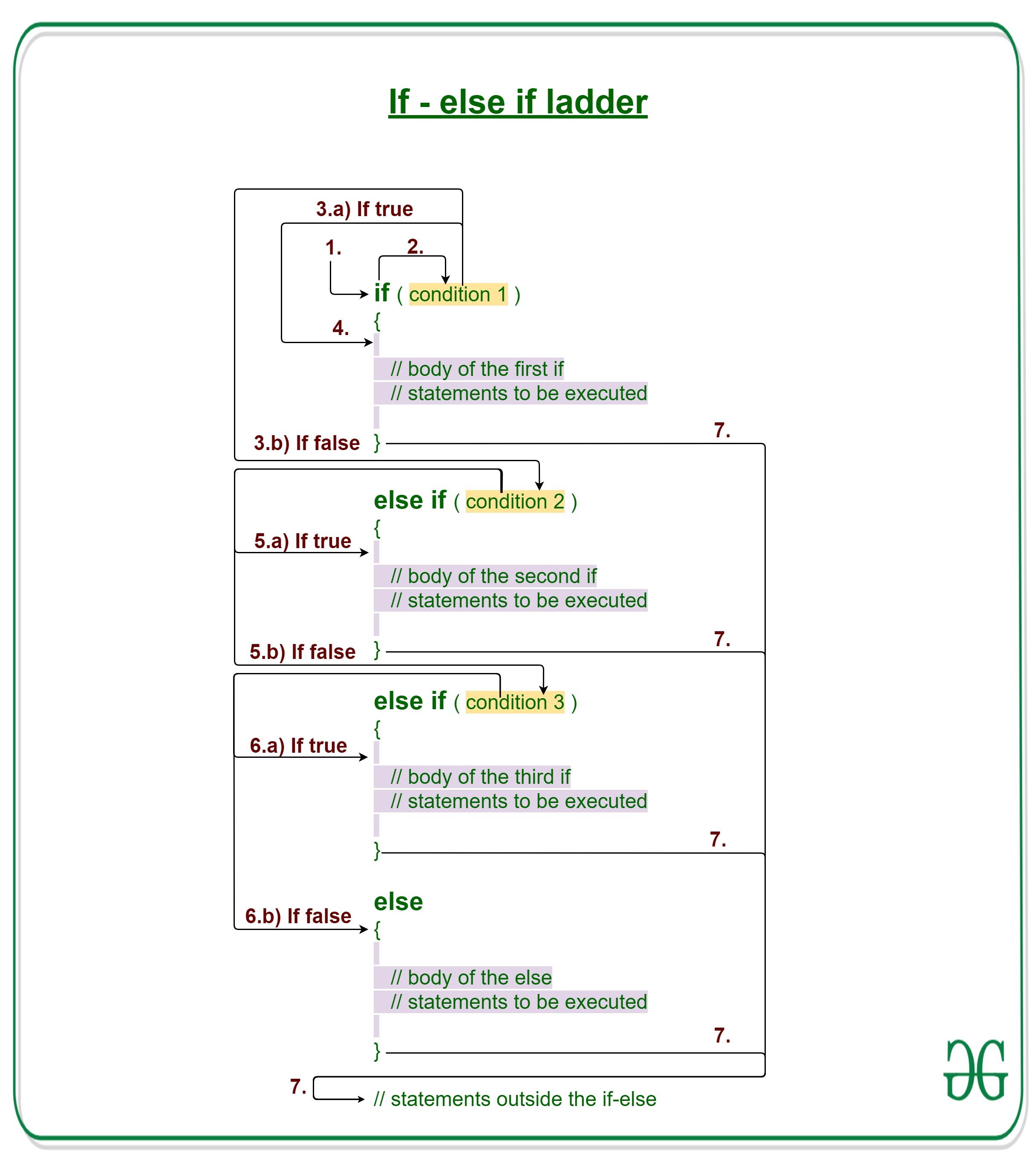
**Syntax of if-else-if ladder:
if (condition)
statement 1;
else if (condition)
statement 2;
.
.
else
statement;
**Working of the if-else-if ladder:
- Control falls into the if block.
- The flow jumps to Condition 1.
- Condition is tested.
- If Condition yields true, go to Step 4.
- If Condition yields false, go to Step 5.
- The present block is executed. Go to Step 7.
- The flow jumps to Condition 2.
- If Condition yields true, go to step 4.
- If Condition yields false, go to Step 6.
- The flow jumps to Condition 3.
- If Condition yields true, go to step 4.
- If Condition yields false, execute else block.
Go to Step 7.
- Exit the if-else-if ladder.
**Flowchart if-else-if ladder:
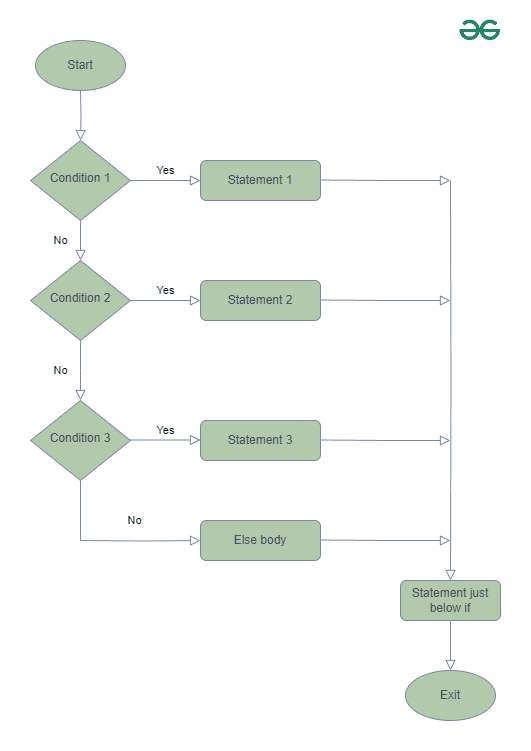
The above flowchart represents the working of an **if-else-if ladder in a program. It evaluates conditions sequentially and executes the corresponding statement or the else block if none of the conditions are true.
**Example 1:
Java `
// Java program to illustrate if-else-if ladder import java.io.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// initializing expression
int i = 20;
// condition 1
if (i == 10)
System.out.println("i is 10\n");
// condition 2
else if (i == 15)
System.out.println("i is 15\n");
// condition 3
else if (i == 20)
System.out.println("i is 20\n");
else
System.out.println("i is not present\n");
System.out.println("Outside if-else-if");
}}
`
Output
i is 20
Outside if-else-if
**Explanation: The above example demonstrates an **if-else-if ladder to check the value of "i" against multiple conditions. It prints the matching condition's output or a default message.
Advantages of Java if-else-if Ladder
- **Sequential Condition Checking: It allows multiple conditions to be evaluated in order by making it useful for handling a range of scenarios.
- **Readability: It is easy to read and understand for simple decision-making logic.
- **Fallback Mechanism: This provides an optional else block to handle cases where none of the conditions are met.
- **Versatile: This can be used for both numerical and logical comparisons.
- **Simpler Alternative: It is suitable for situations where using switch is not feasible, such as complex conditions.