Java if statement (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 22 Nov, 2024
The **Java if statement is the most simple decision-making statement. It is used to decide whether a certain statement or block of statements will be executed or not i.e. if a certain condition is true then a block of statements is executed otherwise not.
**Example:
Java `
// Java program to illustrate If statement class GfG { public static void main(String args[]) { int i = 10;
// using if statement
if (i < 15)
System.out.println("10 is less than 15");
System.out.println("Outside if-block");
// both statements will be printed
}}
`
Output
10 is less than 15 Outside if-block
**Dry-Running Above Example
- Program starts.
- i is initialized to 10.
- if-condition is checked. 10<15, yields true.
3.a) "10 is less than 15" gets printed. - "Outside if-block" is printed.
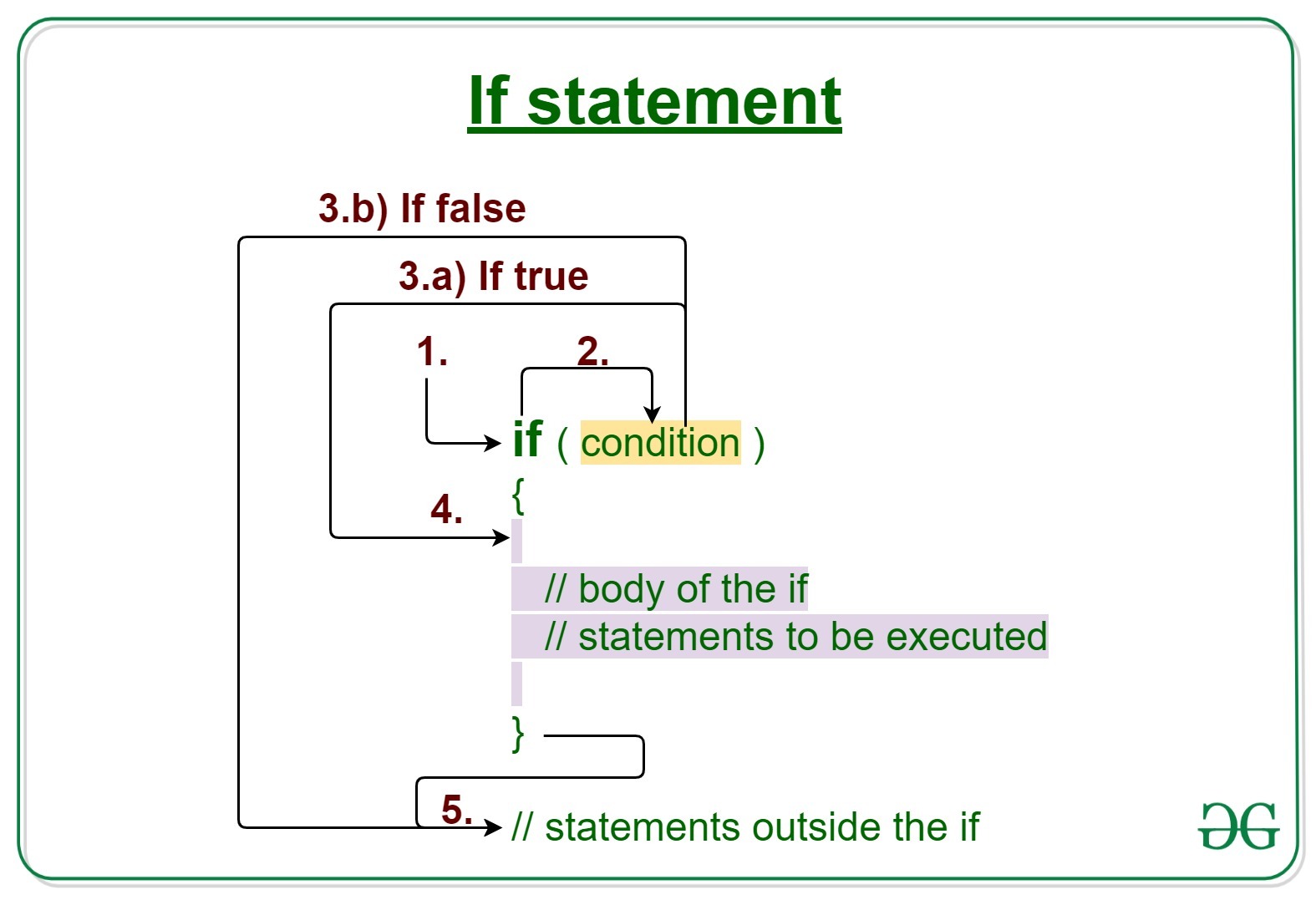
**Syntax:
if(condition)
{
// Statements to execute if
// condition is true
}
**Working of if statement:
- Control falls into the if block.
- The flow jumps to Condition.
- Condition is tested.
- If Condition yields true, goto Step 4.
- If Condition yields false, goto Step 5.
- The if-block or the body inside the if is executed.
- Flow steps out of the if block.
**Flowchart if statement:

**Operation: The condition after evaluation of if-statement will be either true or false. The if statement in Java accepts boolean values and if the value is true then it will execute the block of statements under it.
**Note: If we do not provide the curly braces ‘{‘ and ‘}’ after if( condition ) then by default if statement will consider the immediate one statement to be inside its block.
**Example:
if(condition)
statement1;
statement2;
// Here if the condition is true, if block will consider the statement
// under it, i.e statement1, and statement2 will not be considered in the if block, it will still be executed
// as it is not affected by any if condition.
**Example 1:
Java `
// Java program to illustrate If statement class GFG { public static void main(String args[]) { String str = "GeeksforGeeks"; int i = 4;
// if block
if (i == 4) {
i++;
System.out.println(str);
}
// Executed by default
System.out.println("i = " + i);
}}
`
Output
GeeksforGeeks i = 5
**Example 2: Implementing if else for Boolean values
I**nput:
boolean a = true;
boolean b = false;
Java `
// Java program to illustrate the if else statement public class IfElseExample { public static void main(String[] args) { boolean a = true; boolean b = false;
if (a) {
System.out.println("a is true");
} else {
System.out.println("a is false");
}
if (b) {
System.out.println("b is true");
} else {
System.out.println("b is false");
}
}}
`
Output
a is true b is false
**Explanation:
- The code starts with the declaration of two Boolean variables a and b, with a set to true and b set to false.
- The first if-else statement checks the value of a. If the value of a is true, the code inside the first set of curly braces {} is executed and the message "a is true" is printed to the console. If the value of a is false, the code inside the second set of curly braces {} is executed and the message "a is false" is printed to the console.
- The second if-else statement checks the value of b in the same way. If the value of b is true, the message "b is true" is printed to the console. If the value of b is false, the message "b is false" is printed to the console.
- This code demonstrates how to use an if-else statement to make decisions based on Boolean values. By using an if-else statement, you can control the flow of your program and execute code only under certain conditions. The use of Boolean values in an if-else statement provides a simple and flexible way to make these decisions.
Advantages of If else statement
- **Conditional execution: The if-else statement allows code to be executed conditionally based on the result of a Boolean expression. This provides a way to make decisions and control the flow of a program based on different inputs and conditions.
- **Readability: The if-else statement makes code more readable by clearly indicating when a particular block of code should be executed. This makes it easier for others to understand and maintain the code.
- **Reusability: By using if-else statements, developers can write code that can be reused in different parts of the program. This reduces the amount of code that needs to be written and maintained, making the development process more efficient.
- **Debugging: The if-else statement can help simplify the debugging process by making it easier to trace problems in the code. By clearly indicating when a particular block of code should be executed, it becomes easier to determine why a particular piece of code is not working as expected.
- **Flexibility: The if-else statement provides a flexible way to control the flow of a program. It allows developers to handle different scenarios and respond dynamically to changes in the program's inputs.
Overall, the if-else statement is a fundamental tool in programming that provides a way to control the flow of a program based on conditions. It helps to improve the readability, reusability, debuggability, and flexibility of the code.