java.lang.Character Class Methods | Set 1 (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 10 Jan, 2025
**java.lang.Character Class wraps the value of a primitive data type **char to an object of datatype Character. This object contains a single field having the data type **char. This class provides several methods regarding character manipulations like converting them from lowercase to uppercase. Character Class is based on Unicode Standards to provide character information.
**Class Declaration
public final class Character
extends Object
implements Serializable, Comparable
Character Class Methods
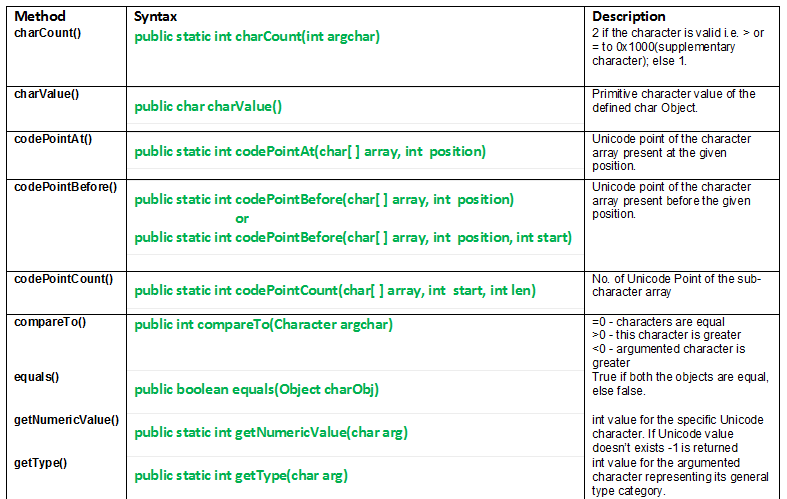
**1. charCount()
**java.lang.charCount() method uses Unicode point to return the number of char values to represent the argument char values. A **Unicode code point is used for character values in the range between U+0000 and U+10FFFF and for 16-bit char values that are code units of the UTF-16 encoding.
**Syntax:
public static int charCount(int argchar)
- **Parameters: argchar: Unicode point of the character to be counted.
- **Return: 2 if the character is valid i.e. > or = to 0X1000 (supplementary character); else 1
**2. charValue()
The charValue() method returns primitive char value of defined Character Object.
**Syntax:
public char charValue()
**Return Value: The primitive char value of the specified Character object.
**3. codePointAt()
The codePointAt(char[ ] array, int position) method returns Unicode Point of the character array present at the argumented position.
**Syntax:
public static int codePointAt(char[] array, int position)
**Parameters:
- array: The character array.
- position: The index of the character whose Unicode code point you need.
**Return Value: The Unicode point of the character at the specified position
**Examples Using charCount() , charValue() , and codePointAt() Methods:
JAVA `
// Java program explaining Character class methods // charCount(), charValue(), codePointat() import java.lang.Character;
public class Geeks { public static void check(int ele) {
// Checking for geek
if (ele == 2)
System.out.println("Valid Character geek");
else
System.out.println("Invalid Character geek");
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Use of charCount() method
int geek = 0x9999,
geek1 = 0x10000,
geek2 = 0x10001;
int c = Character.charCount(geek);
int c1 = Character.charCount(geek1);
int c2 = Character.charCount(geek2);
check(c);
check(c1);
check(c2);
System.out.println();
// Character object m
Character m;
// Assigning value g to m;
m = new Character('g');
char gfg;
// Use of charValue() method
gfg = m.charValue();
System.out.println("Primitive value of gfg : "+ gfg);
System.out.println();
// Use of codePointAt()
char[] arg = new char[] { 'g', 'e', 'e', 'k', 's' };
int val, val1, position = 3;
val = Character.codePointAt(arg, position);
val1 = Character.codePointAt(arg, 0);
System.out.println("Unicode code point at "
+ position + " : " + val);
System.out.println("Unicode code point at 0 : "
+ val1);
}}
`
Output
Invalid Character geek Valid Character geek Valid Character geek
Primitive value of gfg : g
Unicode code point at 3 : 107 Unicode code point at 0 : 103
**4. codePointBefore()
The codePointBefore(char[ ] array, int position) method returns Unicode Point of the character array present before the argumented position.
**Syntax:
public static int codePointBefore(char[] array, int position)
or
public static int codePointBefore(char[] array, int position, int start)
**Parameters:
- array: The character array.
- position: The index of the character whose preceding Unicode point is needed.
- start: The start index of the character array (optional).
**Return Value: The Unicode point of the character before the specified position.
**5. codePointCount()
The codePointCount() method returns number of Unicode Point of the sub-character array.
**Syntax:
public static int codePointCount(char[] array, int start, int len)
**Parameters:
- array: The character array.
- start: The starting index of the sub-array.
- len: The length of the sub-array.
**Return Value: The number of Unicode code points in the sub-array.
**Exceptions:
- NullPointerException: If the character array is null.
- IndexOutOfBoundsException: If the specified range is invalid.
**6. compareTo()
The compareTo(Character argChar) method compares given character with argumented character.
**Syntax:
public int compareTo(Character argChar)
**Parameters: argChar: character to be compared with.
**Return Values:
- **= 0: if both characters are equal
- **> 0: if given this character is greater
- ****< 0:** if argumented character is greater
**Examples Using codePointBefore() , codePointCount() , and compareTo() Methods:
JAVA `
// Java program explaining Character class methods // codePointBefore(), codePointCount(), compareTo() import java.lang.Character;
public class Geeks { public static void main(String[] args) { // Use of codePointBefore() char[] arg = new char[] { 'g', 'e', 'e', 'k', 's' }; int position = 4;
int val = Character.codePointBefore(arg, position);
int val1 = Character.codePointBefore(arg, 1);
int val2 = Character.codePointBefore(arg, 3, 1);
System.out.println( "Unicode code point before "
+ position + " : " + val );
System.out.println( "Unicode code point before 1 : "
+ val1 );
System.out.println( "Unicode code point before 3"
+" to 1 : " + val2);
System.out.println();
// Use of codePointCount()
int count = Character.codePointCount(arg, 1,3 );
System.out.println("No. of Unicode points : " + count);
System.out.println();
// Use of compareTo()
Character g1 = new Character('g');
Character g2 = new Character('o');
int check = g1.compareTo(g2);
System.out.println("g1 < g2 : " + check);
int check1 = g2.compareTo(g1);
System.out.println("g2 > g1 : " + check1);
int check2 = g2.compareTo(g2);
System.out.println("g2 = g2 : " + check2);
}}
`
Output
Unicode code point before 4 : 107 Unicode code point before 1 : 103 Unicode code point before 3 to 1 : 101
No. of Unicode points : 3
g1 < g2 : -8 g2 > g1 : 8 g2 = g2 : 0
**7. equals()
The equals() method compares the present char object with the argumented char object.
**Syntax:
public boolean equals(Object charObj)
- **Parameter: charObj: char object to compare with.
- **Returns: true if both the objects are equal, else false.
**8. getNumericValue()
The getNumericValue(char arg) method returns int value for the specific Unicode character. A - Z value ranges u0041 to u005A a -z value ranges u0061 to u007A
**Syntax:
public static int getNumericValue(char arg)
- **Parameters: arg: The char whose numeric value is to be retrieved.
- **Return Value: The integer value of the specified Unicode character. If the character does not have a numeric value, -1 is returned.
**9. getType()
The getType(char arg) method identifies the general type of character A - Z value ranges u0041 to u005A a -z value ranges u0061 to u007A.
**Syntax:
public static int getType(char arg)
- **Parameter: arg: The char whose type category is to be identified.
- **Return Value: An integer value representing the character's general type.
**Example: Using equals(), getNumericValue(), and getType() Methods:
JAVA `
// Java program explaining Character class methods // equals(), getNumericValue(), getType() import java.lang.Character;
public class Geeks { public static void main(String[] args) { // Use of equals() method Character g1 = new Character('g'); Character g2 = new Character('O');
boolean check = g1.equals(g2);
boolean check1 = g1.equals(g1);
System.out.println("Are g and o equal?: " + check);
System.out.println("Are g and g equal?: " + check1);
System.out.println();
// Use of getNumericValue() method
int c = Character.getNumericValue(g1);
int c1 = Character.getNumericValue(g2);
System.out.println("Int value for g: " + c);
System.out.println("Int value for A: " + c1);
System.out.println();
// Use of getType() method
Character g3 = new Character('$');
Character g4 = new Character('6');
int r1 = Character.getType(g1);
int r2 = Character.getType(g2);
int r3 = Character.getType(g3);
int r4 = Character.getType(g4);
System.out.println("Type for lowercase: " + r1);
System.out.println("Type for uppercase: " + r2);
System.out.println("Type for currency: " + r3);
System.out.println("Type for numeric: " + r4);
}}
`
Output
Are g and o equal?: false Are g and g equal?: true
Int value for g: 16 Int value for A: 24
Type for lowercase: 2 Type for uppercase: 1 Type for currency: 26 Type for numeric: 9