Vector Class in Java (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 18 Nov, 2025
In Java, a Vector is a dynamic array that can grow or shrink in size as elements are added or removed. It is part of the java.util package and extends the AbstractList class.
- Maintains insertion order and allows duplicate and null values.
- Dynamically grows its size when capacity is exceeded.
- Implements List, RandomAccess, Cloneable, and Serializable interfaces.
- Vector is a Legacy class that was introduced in early versions of Java.
- Thread-safe: All methods are synchronized for safe multi-threaded access.
- ArrayList is preferred over vector in general when in-built thread synchronization is not required.. Java `
import java.util.Vector;
public class GFG{
public static void main(String[] args){
Vector<String> v = new Vector<>();
v.add("A");
v.add("B");
v.add("C");
System.out.println(v);
}}
`
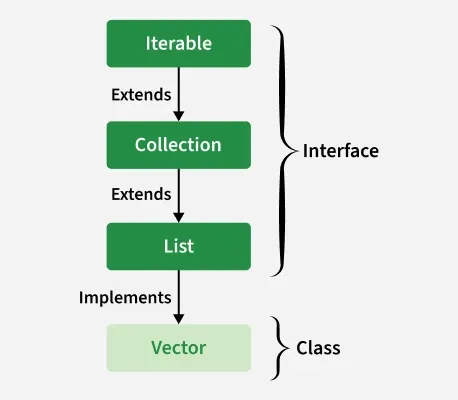
Hierarchy of Vector
It implements the List interface, which is a sub-interface of the Collection interface.
Constructors of Vector
In order to create a Vector, we need to create an object of the Vector class. The Vector class provides various constructors to create a vector in different ways.
1. Vector()
Creates an empty vector with a default initial capacity of 10.
Vector vector = new Vector<>();
2. Vector(int initialCapacity)
Creates a vector with the specified initial capacity.
Vector vector = new Vector<>(20);
3. Vector(int initialCapacity, int capacityIncrement)
Creates a vector with a specified initial capacity and capacity increment (amount by which the vector grows when full).
Vector vector = new Vector<>(10, 5);
4. Vector(Collection c)
Creates a vector containing all elements of the specified collection.
Vector vector = new Vector<>(collection);
Vector Capacity in Java
When a Vector is created using the default constructor, it is initialized with a default capacity of 10. This means it can hold up to 10 elements before needing to grow in size. If the number of elements exceeds the current capacity, the Vector automatically increases its capacity.
Vector vec = new Vector<>();
System.out.println("Default Capacity: " + vec.capacity()); // Output: 10
**Formula to calculate new capacity
newCapacity = oldCapacity * 2
Java `
import java.util.Vector;
public class VectorDoublingExample { public static void main(String[] args) { Vector vector = new Vector<>(2); // initial capacity = 2 System.out.println("Initial capacity: " + vector.capacity());
// Add elements to trigger capacity increase
vector.add(10);
vector.add(20);
System.out.println("Capacity after adding 2 elements: " + vector.capacity());
vector.add(30); // Triggers resize (2 → 4)
System.out.println("Capacity after adding 3rd element: " + vector.capacity());
vector.add(40);
vector.add(50); // Triggers resize again (4 → 8)
System.out.println("Capacity after adding 5 elements: " + vector.capacity());
}}
`
Output
Initial capacity: 2 Capacity after adding 2 elements: 2 Capacity after adding 3rd element: 4 Capacity after adding 5 elements: 8
Different Operations of Vector Class
1. Adding Elements
To add the elements to the Vector, we use the add() method. This method is overloaded to perform multiple operations based on different parameters. They are listed below as follows:
- **add(Object): This method is used to add an element at the end of the Vector.
- **add(int index, Object): This method is used to add an element at a specific index in the Vector. Java `
import java.io.; import java.util.;
class Geeks { public static void main(String[] arg) { // Creating a default vector Vector v1 = new Vector();
// Adding custom elements using add() method
v1.add(1);
v1.add(2);
v1.add("geeks");
v1.add("forGeeks");
v1.add(3);
System.out.println("Vector v1 is " + v1);
// Creating generic vector
Vector<Integer> v2 = new Vector<Integer>();
// Adding custom elements using add() method
v2.add(1);
v2.add(2);
v2.add(3);
System.out.println("Vector v2 is " + v2);
}}
`
Output
Vector v1 is [1, 2, geeks, forGeeks, 3] Vector v2 is [1, 2, 3]
2. Updating Elements
To update an element in a Vector, use the set() method. It takes the index and the new element to replace the existing one at that position.
Java `
import java.util.*;
public class Geeks {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Creating an empty Vector
Vector<Integer> v = new Vector<Integer>();
// Use add() method to add elements in the vector
v.add(12);
v.add(23);
v.add(22);
v.add(10);
v.add(20);
// Displaying the Vector
System.out.println("Vector: " + v);
// Using set() method to replace 12 with 21
System.out.println("The Object that is replaced is: "
+ v.set(0, 21));
// Using set() method to replace 20 with 50
System.out.println("The Object that is replaced is: "
+ v.set(4, 50));
System.out.println("The new Vector is:" + v);
} }
`
Output
Vector: [12, 23, 22, 10, 20] The Object that is replaced is: 12 The Object that is replaced is: 20 The new Vector is:[21, 23, 22, 10, 50]
3. Removing Elements
To remove an element from a Vector, we can use the remove() method. This method is overloaded to perform multiple operations based on different parameters. They are:
- **remove(Object): Removes the first occurrence of the specified object.
- **remove(int index): Removes the element at the given index and shifts remaining elements to the left. Java `
import java.util.; import java.io.;
class Geeks {
public static void main(String[] arg)
{
// Create default vector of capacity 10
Vector v = new Vector();
// Add elements using add() method
v.add(1);
v.add(2);
v.add("Geeks");
v.add("forGeeks");
v.add(4);
// Removing first occurrence element at 1
v.remove(1);
System.out.println("After removal: " + v);
}}
`
Output
After removal: [1, Geeks, forGeeks, 4]
4. Iterating the Vector
There are multiple ways to iterate through the Vector. The most famous ways are by using the basic for loop in combination with a get() method to get the element at a specific index and the advanced for a loop.
Java `
import java.util.*;
public class Geeks {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// create an instance of vector
Vector<String> v = new Vector<>();
// Add elements using add() method
v.add("Geeks");
v.add("Geeks");
v.add(1, "For");
// Using the Get method and the for loop
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++) {
System.out.print(v.get(i) + " ");
}
System.out.println();
for (String str : v)
System.out.print(str + " ");
}}
`
Output
Geeks For Geeks Geeks For Geeks
**Note: Please read to the ArrayList vs Vector class in Java to grasp it better.
Methods of Vector Class
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| add(E e) | Appends the specified element to the end of this Vector. |
| add(int index, E element) | Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this Vector. |
| addAll(Collection<?extends E> c) | Appends all elements from the given collection to the end of this Vector. |
| addAll(int index,Collection<? extends E> c) | Insert all of the elements in the specified Collection into this Vector at the specified position. |
| addElement(E obj) | Adds the specified element to the end, increasing size by one. |
| capacity() | Returns the current capacity of this vector. |
| clear() | Removes all of the elements from this Vector. |
| clone() | Returns a clone of this vector. |
| contains(Object o) | Returns true if this vector contains the specified element. |
| containsAll(Collection<?> c) | Returns true if this Vector contains all of the elements in the specified Collection. |
| copyInto(Object[] anArray) | Copies the components of this vector into the specified array. |
| elementAt(int index) | Returns the component at the specified index. |
| elements() | Returns an enumeration of the components of this vector. |
| ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) | Increases capacity to ensure it can hold at least the specified number of elements. |
| equals(Object o) | Compares the specified Object with this Vector for equality. |
| firstElement() | Returns the first component (the item at index 0) of this vector. |
| forEach(Consumer<?super E> action) | Performs the given action for each element of the Iterable until all elements have been processed or the action throws an exception. |
| get(int index) | Returns the element at the specified position in this Vector. |
| hashCode() | Returns the hash code value for this Vector. |
| indexOf(Object o) | Returns index of the first occurrence of the element or -1 if not found. |
| indexOf(Object o, int index) | Returns index of the first occurrence starting from the given index. |
| insertElementAt(E obj, int index) | Inserts the specified object as a component in this vector at the specified index. |
| isEmpty() | Tests if this vector has no components. |
| iterator() | Returns an iterator over the elements in this list in a proper sequence. |
| lastElement() | Returns the last component of the vector. |
| lastIndexOf(Object o) | Returns the index of the last occurrence of the element or -1 if not found. |
| lastIndexOf(Object o, int index) | Returns index of the last occurrence before the given index. |
| listIterator() | Returns a list iterator over the elements in this list (in proper sequence). |
| listIterator(int index) | Returns a list iterator over the elements in this list (in proper sequence), starting at the specified position in the list. |
| remove(int index) | Removes the element at the specified position in this Vector. |
| remove(Object o) | Removes the first occurrence of the specified element. |
| removeAll(Collection<?> c) | Removes from this Vector all of its elements contained in the specified Collection. |
| removeAllElements() | Removes all components from this vector and sets its size to zero. |
| removeElement(Object obj) | Removes the first (lowest-indexed) occurrence of the argument from this vector. |
| removeElementAt(int index) | Deletes the component at the specified index. |
| removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) | Removes all of the elements of this collection that satisfy the given predicate. |
| removeRange(int fromIndex,int toIndex) | Removes from this list all of the elements whose index is between fromIndex, inclusive and toIndex, exclusive. |
| replaceAll(UnaryOperator operator) | Replaces each element of this list with the result of applying the operator to that element. |
| retainAll(Collection<?> c) | Retains only the elements in this Vector contained in the specified Collection. |
| set(int index, E element) | Replaces the element at the specified position in this Vector with the specified element. |
| setElementAt(E obj, int index) | Sets the component at the specified index of this vector to be the specified object. |
| setSize(int newSize) | Sets the size of this vector. |
| size() | Returns the number of components in this vector. |
| sort(Comparator<? super E> c) | Sorts this list according to the order induced by the specified Comparator. |
| spliterator() | Creates a late-binding and fail-fast Spliterator over the elements in this list. |
| subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) | Returns a view of the portion of this List between fromIndex, inclusive and toIndex, exclusive. |
| toArray() | Returns an array containing all of the elements in this Vector in the correct order. |
| toArray(T[] a) | Returns an array containing all the elements. |
| toString() | Returns a string representation of this Vector, containing the String representation of each element. |
| trimToSize() | Trims the capacity of this vector to be the vector's current size. |
Which package contains the Vector class in Java?
- java.collection
- java.util
- java.list
- java.vector
Explanation:
The Vector class is part of the java.util package in Java.
What will be the output of the following code?
Java `
import java.util.*; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Vector vector = new Vector<>(2); vector.add(10); vector.add(20); vector.add(30); System.out.println(vector.capacity()); } }
`
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 10
Explanation:
The default growth strategy of Vector doubles its capacity when full. Since initial capacity is 2, adding a third element expands it to 4.
What is the default initial capacity of a Vector created using the no-argument constructor?
- 5
- 8
- 10
- 12
Explanation:
Vector starts with a default capacity of 10.

Quiz Completed Successfully
Your Score : 2/3
Accuracy : 0%
Login to View Explanation
1/3
1/3 < Previous Next >