Javascript Program For Inserting A Node In A Linked List (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 06 Sep, 2024
We have introduced Linked Lists in the previous post. We also created a simple linked list with 3 nodes and discussed linked list traversal.
All programs discussed in this post consider the following representations of the linked list.
JavaScript `
// Linked List Class
// Head of list let head;
// Node Class class Node { // Constructor to create // a new node constructor(d) { this.data = d; this.next = null; } } // This code is contributed by todaysgaurav
`
In this post, methods to insert a new node in linked list are discussed. A node can be added in three ways
**1) At the front of the linked list
**2) After a given node.
**3) At the end of the linked list.
**Add a node at the front: (4 steps process)
The new node is always added before the head of the given Linked List. And newly added node becomes the new head of the Linked List. For example, if the given Linked List is 10->15->20->25 and we add an item 5 at the front, then the Linked List becomes 5->10->15->20->25. Let us call the function that adds at the front of the list is push(). The push() must receive a pointer to the head pointer, because push must change the head pointer to point to the new node (See this)
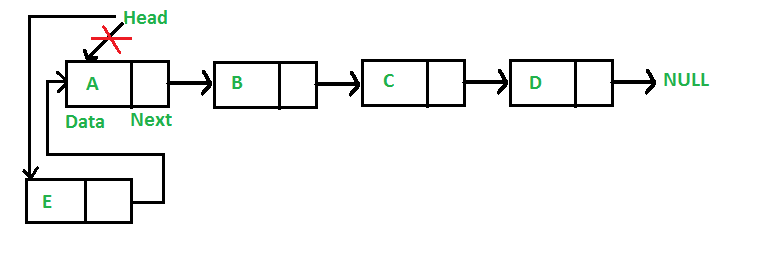
Following are the 4 steps to add a node at the front.
JavaScript `
/* This function is in LinkedList class. Inserts a new Node at front of the list. This method is defined inside LinkedList class shown above / function push(new_data) { / 1 & 2: Allocate the Node & Put in the data*/ let new_node = new Node(new_data);
// Make next of new Node as head
new_node.next = head;
// 4. Move the head to point to new Node
head = new_node;} // This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
`
Time complexity of push() is O(1) as it does a constant amount of work.
**Add a node after a given node: (5 steps process)
We are given a pointer to a node, and the new node is inserted after the given node.
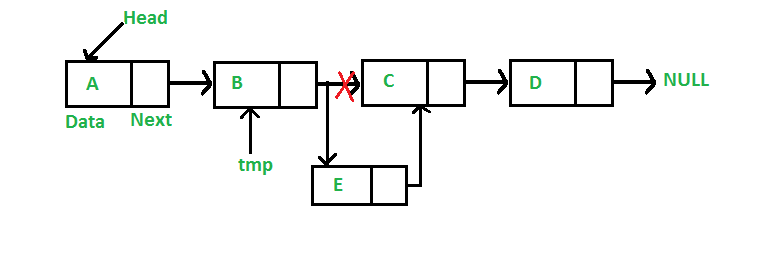
JavaScript `
/* This function is in LinkedList class. Inserts a new node after the given prev_node. This method is defined inside LinkedList class shown above */ function insertAfter(prev_node, new_data) { // 1. Check if the given Node is null if (prev_node == null) { console.log("The given previous node cannot be null"); return; }
/* 2. Allocate the Node &
3. Put in the data*/
let new_node = new Node(new_data);
// 4. Make next of new Node as next
// of prev_node
new_node.next = prev_node.next;
// 5. make next of prev_node as new_node
prev_node.next = new_node;} // This code is contributed by aashish1995
`
Time complexity of insertAfter() is O(1) as it does a constant amount of work.
**Add a node at the end: (6 steps process)
The new node is always added after the last node of the given Linked List. For example if the given Linked List is 5->10->15->20->25 and we add an item 30 at the end, then the Linked List becomes 5->10->15->20->25->30.
Since a Linked List is typically represented by the head of it, we have to traverse the list till the end and then change the next to last node to a new node.
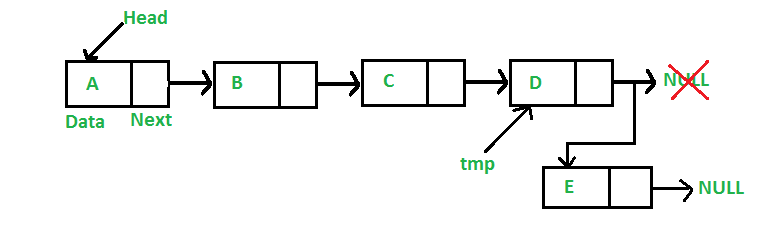
Following are the 6 steps to add node at the end.
JavaScript `
/* Appends a new node at the end. This method is defined inside LinkedList class shown above / function append(new_data) { / 1. Allocate the Node & 2. Put in the data 3. Set next as null */ let new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* 4. If the Linked List is empty, then
make the new node as head */
if (head == null) {
head = new Node(new_data);
return;
}
/* 4. This new node is going to be the
last node, so make next of it as null */
new_node.next = null;
// 5. Else traverse till the last node
let last = head;
while (last.next != null)
last = last.next;
// 6. Change the next of last node
last.next = new_node;
return;} // This code is contributed by aashish1995>
`
Time complexity of append is O(n) where n is the number of nodes in the linked list. Since there is a loop from head to end, the function does O(n) work.
This method can also be optimized to work in O(1) by keeping an extra pointer to the tail of the linked list/
Following is a complete program that uses all of the above methods to create a linked list.
JavaScript `
// A complete working javascript program // to demonstrate all insertion methods // on linked list
// Head of list let head;
// Linked list Node class Node { constructor(val) { this.data = val; this.next = null; } }
// Inserts a new Node at front // of the list. function push(new_data) { /* 1 & 2: Allocate the Node & Put in the data */ let new_node = new Node(new_data);
// 3. Make next of new Node as head
new_node.next = head;
// 4. Move the head to point
// to new Node
head = new_node;}
// Inserts a new node after the given // prev_node. function insertAfter(prev_node, new_data) { // 1. Check if the given Node is null if (prev_node == null) { console.log("The given previous node cannot be null"); return; }
/* 2 & 3: Allocate the Node &
Put in the data */
let new_node = new Node(new_data);
// 4. Make next of new Node as next
// of prev_node
new_node.next = prev_node.next;
// 5. make next of prev_node as new_node
prev_node.next = new_node;}
/* Appends a new node at the end. This method is defined inside LinkedList class shown above / function append(new_data) { / 1. Allocate the Node & 2. Put in the data 3. Set next as null */ let new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* 4. If the Linked List is empty,
then make the new node as head */
if (head == null) {
head = new Node(new_data);
return;
}
/* 4. This new node is going to be the
last node, so make next of it as null */
new_node.next = null;
// 5. Else traverse till the last node
let last = head;
while (last.next != null)
last = last.next;
// 6. Change the next of last node
last.next = new_node;
return;}
/* This function prints contents of linked list starting from the given node */ function printList() { let tnode = head; while (tnode != null) { console.log(tnode.data + " "); tnode = tnode.next; } }
// Driver code
// Start with the empty list
// Insert 6. So linked list becomes // 6->NUllist append(6);
// Insert 7 at the beginning. So // linked list becomes 7->6->NUllist push(7);
// Insert 1 at the beginning. So // linked list becomes 1->7->6->NUllist push(1);
// Insert 4 at the end. So linked list // becomes 1->7->6->4->NUllist append(4);
// Insert 8, after 7. So linked list // becomes 1->7->8->6->4->NUllist insertAfter(head.next, 8);
console.log("Created Linked list is: "); printList(); // This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
`
Output
Created Linked list is: 1 7 8 6 4
Complexity Analysis:
- **Time complexity: O(N) where N is no of the nodes in linked list
- **Auxiliary space: O(1) because using constant space
Please refer complete article on Linked List | Set 2 (Inserting a node) for more details!
Similar Reads
- Learn Data Structures with Javascript | DSA using JavaScript Tutorial JavaScript (JS) is the most popular lightweight, interpreted programming language, and might be your first preference for Client-side as well as Server-side developments. But have you thought about using JavaScript for DSA? Learning Data Structures and Algorithms can be difficult when combined with 7 min read
- Learn Algorithms with Javascript | DSA using JavaScript Tutorial This Algorithms with Javascript tutorial is designed to help you understand and implement fundamental algorithms using the versatile JavaScript programming language. Whether you are a beginner in programming or looking to enhance your algorithmic skills, this guide will walk you through essential co 15+ min read