Introduction to ElectronJS (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 12 Jul, 2025
Creating cross-platform applications often requires learning multiple programming languages and frameworks. However, Electron.js eliminates this complexity by allowing developers to build desktop applications using familiar web technologies like JavaScript, HTML, and CSS.
In this article, we will learn more about ElectronJS and also see how to implement it in our projects.
What is ElectronJS?
ElectronJS is the framework through which developers can build cross-platform desktop applications using web technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. It is open-source.
- **Cross-Platform Development: We can write the code of the ElectronJs once and can deploy it in any operating system.
- **Single Codebase for All Platforms: It maintains a single codebase for all platforms which reduces the time and development costs.
- **Automatic Updates: ElectronJs provides the features of built-in support for automatic updates so developers can easily deliver updates to users, without requiring them to download and install them manually.
- **NodeJS Backend: With the help of NodeJS Electronjs allows the application to access low-level operating system features, such as reading and writing files, and making network requests.
How Does ElectronJS Work?
ElectronJS works in two processes
Main Process
The main process in the ElectronJS is responsible for communicating with the operating system and managing the lifecycle, creating and managing application windows. It is written using NodeJS and for handling the system events they interact with the renderer processes.
Renderer Process
The renderer process is essentially a web page running inside a Chromium window, rendering the user interface using web technologies (HTML, CSS, and JavaScript). Each Electron window runs its renderer process, which can be used to display various views and components of the application.
Setting Up ElectronJS
Step 1: Install NodeJS
- Download and install NodeJS from nodejs.org.
- Make sure npm (Node Package Manager) is installed along with NodeJS.
Step 2: Create a New Project
mkdir electron-app cd electron-app npm init -y
This will generate a basic package.json file with default values.
electron-app
Step 3: Install Electron
Install Electron as a development dependency using npm:
npm install electron --save-dev
Folder Structure
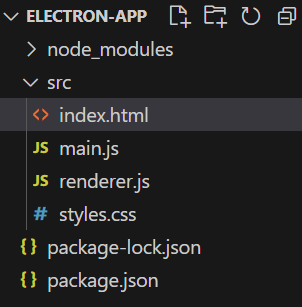
Folder structure
HTML `
Electron AppWelcome to Electron!
This is a basic Electron app.
Change TextCSS
/* src/styles.css */ body { font-family: Arial, sans-serif; background-color: #f4f4f9; display: flex; justify-content: center; align-items: center; height: 100vh; margin: 0; }
h1 { color: #333; }
button { padding: 10px 20px; font-size: 16px; cursor: pointer; margin-top: 20px; }
JavaScript
// src/main.js const { app, BrowserWindow } = require('electron'); let mainWindow;
function createWindow() { mainWindow = new BrowserWindow({ width: 800, height: 600 });
mainWindow.loadFile('index.html');
mainWindow.on('closed', () => {
mainWindow = null;
});}
app.on('ready', createWindow);
app.on('window-all-closed', () => { if (process.platform !== 'darwin') { app.quit(); } });
JavaScript
// src/renderer.js document.getElementById('changeTextButton').addEventListener('click', () => { document.querySelector('h1').innerText = 'Text Changed!'; });
`
**Start the app using the following command
npm start
**Output
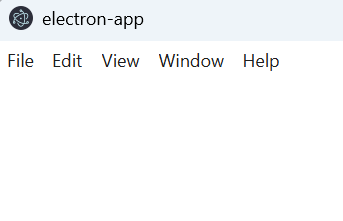
electron-app
Key Features of ElectronJS
- **Creating a Window with Local HTML: Instead of loading a webpage, you can load a local HTML file:
mainWindow.loadFile("index.html");
- **Adding a Custom Menu: Electron allows developers to create custom menus:
const { Menu } = require("electron");
const menuTemplate = [ { label: "File", submenu: [{ label: "Exit", role: "quit" }] } ];
const menu = Menu.buildFromTemplate(menuTemplate); Menu.setApplicationMenu(menu);
- **Using System Notifications: Electron provides native desktop notifications:
const { Notification } = require("electron");
new Notification({ title: "Hello!", body: "This is an Electron notification." }).show();
- **Creating a Tray Application: Electron supports tray icons for background applications:
const { Tray } = require("electron");
const tray = new Tray("icon.png"); tray.setToolTip("Electron App");
- **File System Access: You can read/write files using Node.js:
const fs = require("fs");
fs.writeFileSync("test.txt", "Hello Electron!");
**Electron vs Other Frameworks
| Feature | Electron.js | NW.js | Tauri | Flutter Desktop |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Language | JavaScript | JavaScript | Rust | Dart |
| Uses Chromium | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| System API Access | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| App Size | Large (~50MB) | Large (~50MB) | Small (~5MB) | Moderate (~10MB) |
| Cross-Platform | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Use Cases for ElectronJS
- **Cross-Platform Desktop Applications: Electron allows developers to create apps that can run across all operating systems.
- **Web-Based Apps: Applications like GitHub Desktop or WordPress Desktop that are essentially web-based apps but packaged as native desktop applications are great examples of how Electron can be used.
- **Development Tools: Electron is frequently used for building development tools, such as text editors (Visual Studio Code, Atom), IDEs, or version control clients.
- **Custom Dashboards: Electron is ideal for building custom dashboards, such as business or analytics dashboards that integrate with various data sources and provide real-time updates.
Limitations of ElectronJS
While Electron is powerful, it has some downsides
- **Large Application Size: Electron apps bundle Chromium + Node.js, leading to large package sizes (~50MB+).
- **High Memory Usage: Since each window runs in a separate process, RAM consumption is higher than native applications.
- **Security Concerns: Improper configurations can expose security risks like remote code execution (RCE)