JDK in Java (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 03 Jan, 2025
The Java Development Kit (JDK) is a cross-platformed software development environment that offers a collection of tools and libraries necessary for developing Java-based software applications and applets. It is a core package used in Java, along with the **JVM (Java Virtual Machine) and the JRE (Java Runtime Environment).
Beginners often get confused with JRE and JDK, if you are only interested in running Java programs on your machine then you can easily do it using Java Runtime Environment. However, if you would like to develop a Java-based software application then along with JRE you may need some additional necessary tools, which is called JDK.
**JDK=JRE+Development Tools
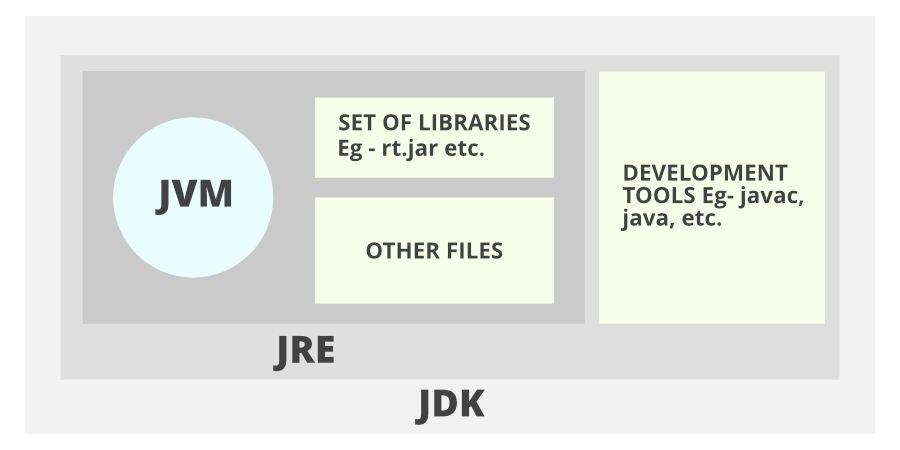
The Java Development Kit is an implementation of one of the Java Platform:
Contents of JDK
The JDK has a private Java Virtual Machine (JVM) and a few other resources necessary for the development of a Java Application.
**JDK contains:
- Java Runtime Environment (JRE),
- An interpreter/loader (Java),
- A compiler (javac),
- An archiver (jar) and many more.
The Java Runtime Environment in JDK is usually called Private Runtime because it is separated from the regular JRE and has extra content. The Private Runtime in JDK contains a JVM and all the class libraries present in the production environment, as well as additional libraries useful to developers, e.g, internationalization libraries and the IDL libraries.
**Most Popular JDKs:
- **Oracle JDK: the most popular JDK and the main distributor of Java11,
- **OpenJDK: Ready for use: JDK 15, JDK 14, and JMC,
- **Azul Systems Zing: efficient and low latency JDK for Linux os,
- **Azul Systems: based Zulu brand for Linux, Windows, Mac OS X,
- **IBM J9 JDK: for AIX, Linux, Windows, and many other OS,
- **Amazon Corretto: the newest option with the no-cost build of OpenJDK and long-term support.
Set-Up:
Setting up JDK in your development environment is super easy, just follow the below simple steps.
**Installation of JDK
- Go to this Oracle's official Download Page through this link
- Select the latest JDK version and click Download and add it to your classpath.
- Just check the JDK software is installed or not on your computer at the correct location, for example, at C:\Program Files\Java\jdk11.0.9.
**Set JAVA_HOME for Windows:
- Right-click My Computer and select Properties.
- Go to the Advanced tab and select Environment Variables, and then edit JAVA_HOME to point to the exact location where your JDK software is stored, for example, C:\Program Files\Java\jdk11.0.9 is the default location in windows.
Java maintains backward compatibility, so don't worry just download the latest release and you will get all the old and many new features. After Installing the JDK and JRE adds the java command to your command line. You can verify this through the command prompt by the **java -version command. In some cases, you need to restart your system after installing the JDK.
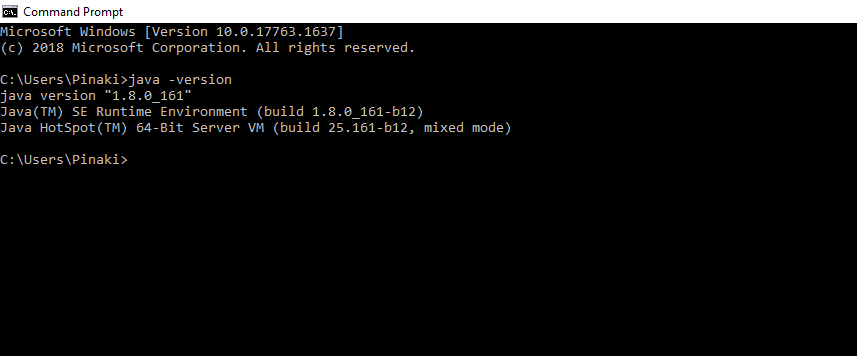
JDK Version
Compile and Run Java Code using JDK:
You can use the JDK compiler to convert your Java text file into an executable program. Your Java text segment is converted into **bytecode after compilation which carries the ****.class** extension.
First, create a Java text file and save it using a name. Here we are saving the file as Hello.java.
Java `
class Hello{ public static void main (String[] args) { System.out.println("Hello Geek!"); } }
`
After that just simply use the javac command, which is used for the compilation purpose in Java. Please don't forget to provide the full path of your java text file to the command line else you will get an error as "The system cannot find the path specified",
Your command should be similar to the given below example where Hello is the file name and the full path to the file is specified before the file name. The path and javac.exe should be inside the quotes.
"C:\Program Files\Java\jdk-11.0.9\bin\javac.exe" Hello.java
You can notice now that the _Hello.class file is being created in the same directory as Hello.java. Now you can run your code by simply using the java Hello command, which will give you the desired result according to your code. Please remember that you don't have to include the .class to run your code.
C:\Users\Pinaki\Documents>java Hello
(Output:) Hello Geek!
The Jar component:
JDK contains many useful tools and among them, the most popular after javac is the jar tool. The jar file is nothing but a full pack of Java classes. After creating the .class files, you can put them together in a .jar, which compresses and structures them in a predictable fashion. Now, let's convert our Hello.class to a jar file.
Before proceeding, please note that you should be in the same directory where the Hello.java file was saved. Now type the command given below in the command line.
**Creating a .jar file
C:\Users\Pinaki\Documents>"c:\Program Files\Java\jdk-11.0.9\bin\jar.exe" --create --file Hello.jar Hello.class
Now you can notice that Hello.jar file had been created in the same directory using Hello.class file and jar.exe. You can use the jar file by adding it to your classpath and executing the program inside it. Here the -cp stands for classpath which helps to add the jar to the same classpath.
**Executing the .jar file
java -cp hello_world.jar hello_world
Important Components of JDK
Below there is a comprehensive list of mostly used components of Jdk which are very useful during the development of a java application.
| Component | Use |
|---|---|
| javac | Java compiler converts source code into Java bytecode |
| java | The loader of the java apps. |
| javap | Class file disassembler, |
| javadoc | Documentation generator, |
| jar | Java Archiver helps manage JAR files. |
| appletviewer | Debugging of Java applets without a web browser, |
| xjc | Accepts an XML schema and generates Java classes, |
| apt | Annotation-processing tool, |
| jdb | Debugger, |
| jmc | Java Mission Control, |
| JConsole | Monitoring and Management Console, |
| pack200 | JAR compression tool, |
| extcheck | Utility tool to detects JAR file conflicts, |
| idlj | IDL-to-Java compiler, |
| keytool | The keystore manipulating tool, |
| jstatd | jstat daemon (experimental) |
| jstat | JVM statistics monitoring tool |
| jshell | jshell introduced in java 9. |
| jstack | Prints Java stack traces(experimental) |
| jrunscript | Java command-line script shell. |
| jhat | Java Heap Analysis Tool (experimental) |
| jpackage | Generate self-contained application bundles. |
| javaws | Web Start launcher for JNLP applications, |
| javah | C header and stub generator, |
| jarsigner | jar signing and verification tool |
| jinfo | configuration information(experimental) |
| javafxpackager | Package and sign JavaFX applications |