MongoDB insertOne() Method db.Collection.insertOne() (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 28 Feb, 2025
MongoDB is a powerful NoSQL database known for its **flexibility, **scalability, and **performance. When working with MongoDB, one of the most common tasks is inserting data into collections. The insertOne() method is an essential tool in this process.
In this article, We will learn about the **MongoDB insertOne() Method, explain how to use it effectively, and showcase several examples. Whether you’re using MongoDB in the shell, Node.js, or Python, you’ll find this guide helpful.
What is the MongoDB insertOne() Method?
The MongoDBinsertOne() method is used to add a single document to a collection. It adds the document to the specified collection and assigns it a unique **_id**if one is not provided. This**insertOne() method is part of the MongoDB driver for various programming languages and can be used in MongoDB Shell, Node.js, Python and other environments.
- We can insert documents with or without the **_id field. If we insert a document in the collection without the _id field, MongoDB will automatically add an _id field and assign it with a unique **ObjectId.
- if we insert a document with the _id field, then the value of the _id field must be unique to avoid the **duplicate key error.
- This method can also throw either **writeError or **writeConcernError exception.
- This method can also be used inside multi-document transactions.
**Syntax:
db.Collection_name.insertOne(
,
{
writeConcern:
}
)
**Key Terms
<document>: The document we want to insert. A document is a set of key-value pairs similar to a JSON object.writeConcern(optional): If we need to specify a custom write concern (e.g., to ensure the data is written to multiple nodes), you can include this option.
Return Value of insertOne()
The insertOne() method returns the following:
- **Acknowledgement: It returns
acknowledged: trueif the write concern was enabled. - **InsertedId: This field contains the
_idvalue of the inserted document
**Examples of MongoDB insertOne()
Let’s go over a few examples to understand how insertOne() works in MongoDB. In the following examples, we are working with:
- **Database: gfg
- **Collection: student
- **Document: No document but, we want to insert in the form of the student name and student marks.

**Example 1: Insert a Document without Specifying an _id Field
Here, we are inserting the document whose name is Akshay and marks is 500 in the student collection. MongoDB will automatically assign a unique _id field to this document.
**Query:
db.student.insertOne({Name: "Akshay", Marks: 500})
**Output:

**Explanation: As shown above, MongoDB has inserted the document with a new ObjectId automatically generated for the _id field.
**Example 2: Insert a Document Specifying an _id Field
Here, we are inserting a document whose unique id is Stu102, name is Vishal, and marks is 230 in the student collection
**Query:
db.student.insertOne({_id: "Stu102", Name: "Vishal", Marks: 230})
**Output:
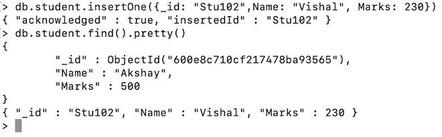
**Explanation: Here, we specified the _id as "Stu102", and MongoDB inserts the document successfully.
Example 3: Handling Write Concern with insertOne()
If we want to specify a custom write concern, we can add an optional writeConcern parameter. For instance, this can be useful when we want to ensure data is written to multiple nodes before considering it committed.
**Query:
db.student.insertOne(
{ Name: "John", Marks: 420 },
{ writeConcern: { w: 1, j: true, wtimeout: 5000 } }
)
Common Errors with insertOne()
While the insertOne() method is quite efficient, you might encounter some errors when:
- **Duplicate _id: If the
_idfield is already present in the collection, MongoDB will throw aDuplicateKeyError. Always ensure the_idfield is unique unless you’re ok with the default behavior of automatic_idgeneration. - **Write Concern Errors: If you’ve set a custom write concern and it cannot be satisfied (e.g., not enough replicas), you might get a
WriteConcernError.
Best Practices for Using insertOne()
- **Ensure Unique _id: While MongoDB auto-generates the
_id, if you provide a custom_id, make sure it’s unique to avoid conflicts. - **Batch Insertions: If you need to insert multiple documents, consider using
insertMany()for better performance. - **Use Write Concerns Appropriately: When writing to a replica set, always consider setting a custom write concern to ensure the durability of your data.
**Conclusion
The insertOne() method in MongoDB is essential for adding single documents to a collection, offering features such as automatic _id generation, write concern options, and support for multi-document transactions. By understanding its syntax and parameters, users can efficiently insert data while ensuring its uniqueness and integrity within the collection.