MySQL BEFORE DELETE Trigger (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 07 Aug, 2024
**MySQL BEFORE DELETE trigger is a powerful tool that automatically performs specific actions before an **DELETE**operation is executed on a table. This feature allows us to handle tasks such as logging deleted records, enforcing business rules or validating data before it is removed from the **database.
In this article, we will How the **BEFORE DELETE trigger in **MySQL works, including its syntax, usage, and practical examples.
MySQL BEFORE DELETE Trigger
- A **MySQL
BEFORE DELETEtrigger is a special type of trigger that automatically executes a specified set of operations before aDELETEoperation is carried out on a table. - This allows us to perform actions such as logging changes, validating data, or enforcing business rules before the actual deletion of records occurs.
**Syntax
A **BEFORE DELETE trigger is created using the **CREATE TRIGGER statement.
The syntax is as follows:
CREATE TRIGGER trigger_name
BEFORE DELETE
ON table_name
FOR EACH ROW
BEGIN
-- trigger logic
END;
**Explanation:
- **trigger_name: The name of the trigger.
- **table_name: The name of the table on which the trigger is applied.
- **BEGIN ... END;: The block where the trigger logic is written.
Example 1: Logging Deleted Records
Lets, we have a table named **employees and we want to log the details of any deleted employee into another table deleted_employees.
/* creating table for employess */
CREATE TABLE emp(
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(100),
position VARCHAR(100)
);
/* creating table from deleted employees */
CREATE TABLE del_emp (
id INT,
name VARCHAR(100),
position VARCHAR(100),
deleted_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
);
**Creating trigger:
CREATE TRIGGER trig_del_emp
BEFORE DELETE ON employees
FOR EACH ROW
BEGIN
INSERT INTO del_emp (id, name, position)
VALUES (OLD.id, OLD.name, OLD.position);
END;
**Explanation:
- When an **employee record is deleted from the **employees table, the trigger **trig_del_employee inserts the deleted record's details into the **deleted_employees table.
- **The OLD keyword enable you to access columns in the rows affected by the delete trigger.
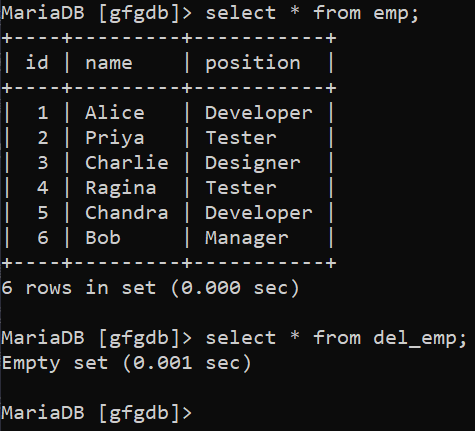
See all data of the tables,
select * from emp;
select * from del_emp;
**Output:
fetching all the data
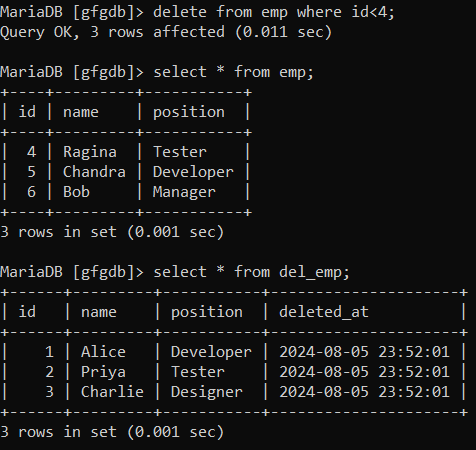
Now lets delete some data,
delete from emp where id<4;
Let's verify both the tables.
select * from emp;
select * from del_emp;
**Output:
fetch data after delete
Example 2: Preventing Deletion of Certain Records
Now we want to prevent the deletion of those employees who hold the position '**Manager'.
Creating trigger:
CREATE TRIGGER trig_del_prev
BEFORE DELETE ON employees
FOR EACH ROW
BEGIN
IF OLD.position = 'Manager' THEN
SIGNAL SQLSTATE '45000'
SET MESSAGE_TEXT = 'Managers cannot be deleted.';
END IF;
END;
**Explanation:
If an attempt is made to delete an employee with the position '**Manager', the trigger will raise an error and prevent the deletion.
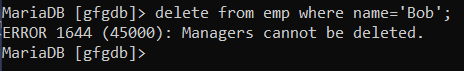
lets try to **delete that **employee who is manager.
delete from emp where name='Bob';
**Output:
deleteding data
Conclusion
The BEFORE DELETE trigger in MySQL offers a versatile way to control and monitor data deletion activities. By using this trigger, you can ensure that important data is preserved in audit logs or prevent certain deletions based on business rules. Mastering the use of BEFORE DELETE triggers can significantly enhance data integrity and provide greater control over database operations.