MySQL DELETE JOIN (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 14 Jun, 2024
MySQL is an open-source, user-friendly, powerful, and popular choice, relational database management system. When maintaining and modifying data, tables usually interact in a complex way.
MySQL's DELETE JOIN function is one of its most powerful functions. MySQL DELETE JOIN is explored in detail in this article, which also offers examples to help visualize its capabilities with **Right Join, **Left Join, **Inner Join, and Subqueries.
MySQL DELETE JOIN
With the help of the MySQL **DELETE JOIN function, we can delete row entries from one table in response to a condition related to another table. This is very useful when we need to delete rows based on specific conditions from data that exists across many linked tables.
**Syntax:
DELETE target_table FROM table1
JOIN table2 ON table1.joining_column = table2.joining_column
WHERE some_condition;
Examples of MySQL DELETE JOIN
Let's have two tables, the first is **employees and the other is **salaries, those contain the following data:
Example 1
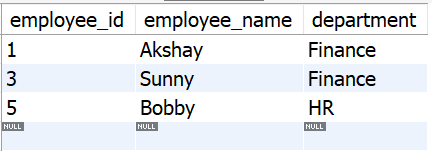
Table **employees:
tbl_employees
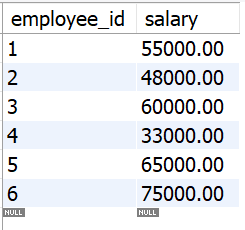
Table **salaries:
tbl_salaries
**In this example:
- The **employees table has columns **employee_id, **employee_name, and **department.
- The **salaries table has columns **employee_id and **salary.
- The **employee_id column is used as a common column to link the two tables.
Now, if we execute the DELETE JOIN query from the previous response:
DELETE emp FROM employees emp
JOIN salaries sal ON emp.employee_id = sal.employee_id
WHERE sal.salary < 50000;
It will delete the rows corresponding to the records from the **employees table, as the salary is below **50,000.
After the deletion, the **employees table will look like this -
**Output:
output_tbl_employees
Example 2
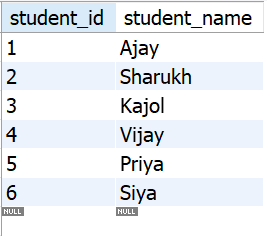
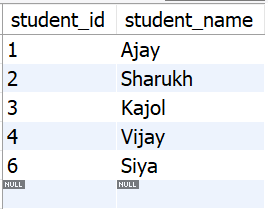
Let's have some tables, **students, **courses, **enrollments, and **grades, that contain the following data:
Table **students:
tbl_students
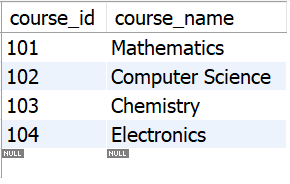
Table **courses:
tbl_courses
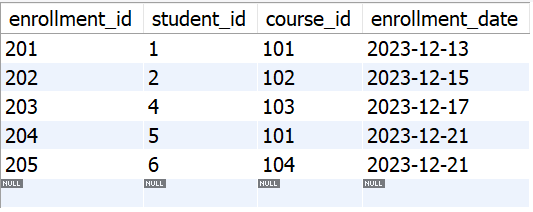
Table **enrollments:
tbl_enrollments
Table **grades:
tbl_grades
Now, if we execute the **DELETE JOIN query from the Example 2 tables:
DELETE st FROM students st
RIGHT JOIN enrollments en ON st.student_id = en.student_id
LEFT JOIN grades gd ON en.enrollment_id = gd.enrollment_id
WHERE gd.grade_id IS NULL;
It will delete those rows corresponding to students with neither enrollment nor grades.
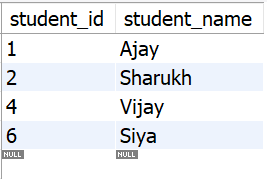
After the deletion, the employees table will look like this -
**Output:
output_tbl_students
**DELETE Statement with INNER JOIN
Now, if we again execute the **DELETE INNER JOIN query from the Example 2 tables:
DELETE FROM students
WHERE NOT EXISTS (
SELECT 1
FROM enrollments en
INNER JOIN grades gd ON en.enrollment_id = gd.enrollment_id
WHERE students.student_id = en.student_id
);
It will delete those rows from the students table with no associated enrollments and grades.
After the deletion, the employees table will look like this -
**Output:
output_tbl_students
Using Subquery With INNER JOIN
Now, if we again execute the **DELETE JOIN in subquery from the Example 2 tables:
DELETE FROM students
WHERE student_id IN (
SELECT student_id
FROM (
SELECT st.student_id
FROM students st
LEFT JOIN enrollments en ON st.student_id = en.student_id
LEFT JOIN grades gd ON en.enrollment_id = gd.enrollment_id
WHERE en.enrollment_id IS NULL AND gd.grade_id IS NULL
) AS subquery
);
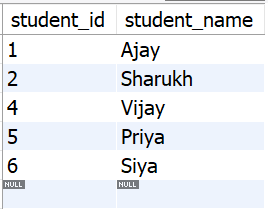
It will delete those rows from the students table who do not have any associated enrollments and grades.
After the **deletion, the employees table will look like this -
**Output:
output_tbl_students
Conclusion
MySQL **DELETE JOIN is a strong feature for maintaining data security and cleanliness in complex database structures. Whether using Left Join for inclusive **deletions or **Inner Join for exact deletions or Right Join for accurate deletions, understanding this operation is important for effective database management. Always exercise caution when performing **DELETE operations, especially in complex scenarios, to avoid accidental data loss. Testing on a small dataset or a backup copy of the database is suggested.