Nested Loops in C (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 28 May, 2025
A nested loop means a loop statement inside another loop statement. That is why nested loops are also called "**loop inside loops". We can define any number of loops inside another loop.
For a nested loop, the inner loop performs all of its iterations for each iteration of the outer loop.
**Example: If the outer loop is running from i = 1 to 5 and the inner loop is running from a to e. Then, for each value of the outer loop variable (i), the inner loop will run from a to e.
Types of Nested Loops in C
We can create nested loops use any loop available in C language whether it be a for loop or a do while loop. We can also combine different type of loops to create nested loops.
Example: for loop inside a do while loop or a while loop in side a for loop etc.
1. Nested for Loop
Nested for loop refers to any type of loop that is defined inside a 'for' loop. Below is the equivalent flow diagram for nested 'for' loops:
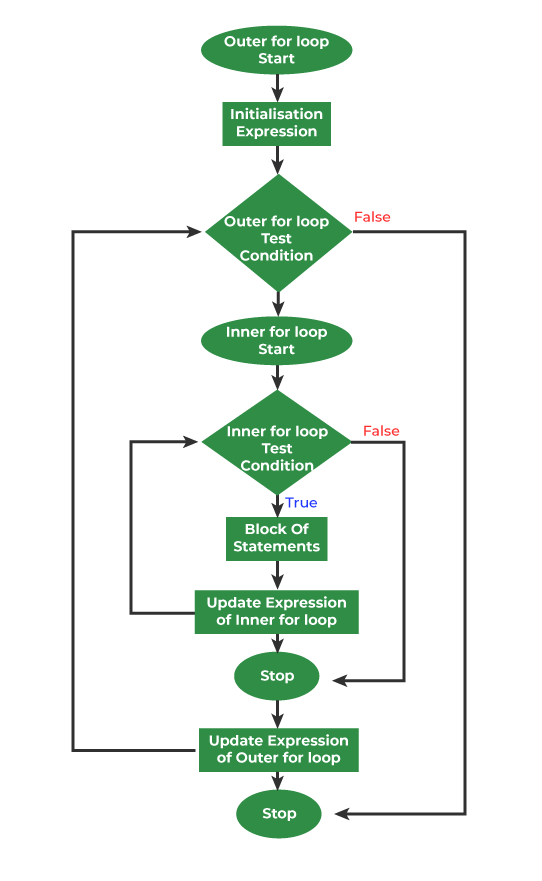
Flowchart for nested for loop in C
**Syntax:
C `
for ( initialization; condition; increment ) { for ( initialization; condition; increment ) { // statement of inside loop } // statement of outer loop }
`
**Example: Below program uses a nested for loop to print a 3D matrix of 2x3x2.
C `
#include <stdio.h>
int main() { // initializing the 3-D array int arr[2][3][2] = { { { 0, 6 }, { 1, 7 }, { 2, 8 } }, { { 3, 9 }, { 4, 10 }, { 5, 11 } } };
// Printing values of 3-D array
for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; ++j) {
for (int k = 0; k < 2; ++k) {
printf("Element at arr[%i][%i][%i] = %d\n",
i, j, k, arr[i][j][k]);
}
}
}
return 0;}
`
Output
Element at arr[0][0][0] = 0 Element at arr[0][0][1] = 6 Element at arr[0][1][0] = 1 Element at arr[0][1][1] = 7 Element at arr[0][2][0] = 2 Element at arr[0][2][1] = 8 Element at arr[1][0][0] = 3 Element at arr[1][0][1] = 9 Element at arr[1][1][0] = 4 Element at arr[1][1][1] = 10 Element at arr[1][2][0] = 5 Element at arr[1][2][1] = 11
**2. Nested while Loop
A nested while loop refers to any type of loop that is defined inside a 'while' loop. Below is the equivalent flow diagram for nested 'while' loops:
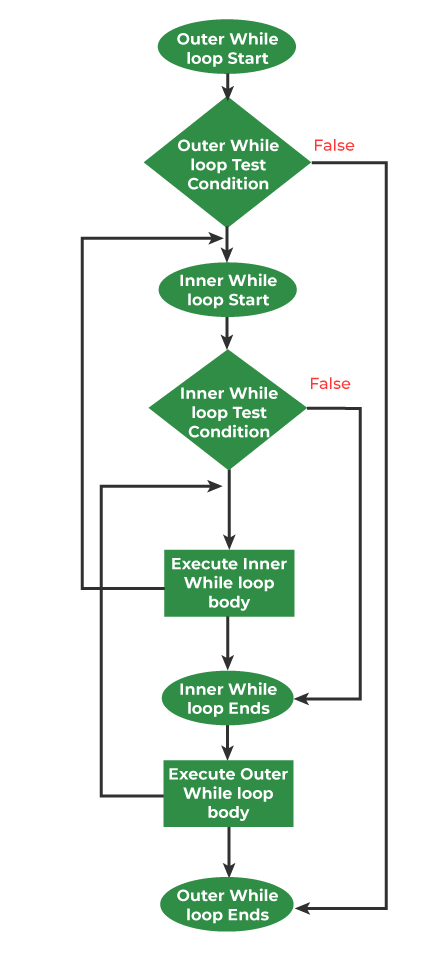
Flowchart for a nested while loop in C
**Syntax:
C `
while(condition) { while(condition) { // statement of inside loop } // statement of outer loop }
`
**Example: Print Pattern using nested while loops
C `
#include <stdio.h>
int main() { int end = 5;
printf("Pattern Printing using Nested While loop");
int i = 1;
while (i <= end) {
printf("\n");
int j = 1;
while (j <= i) {
printf("%d ", j);
j = j + 1;
}
i = i + 1;
}
return 0;}
`
Output
Pattern Printing using Nested While loop 1 1 2 1 2 3 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 5
3. Nested do-while Loop
A nested do-while loop refers to any type of loop that is defined inside a do-while loop. Below is the equivalent flow diagram for nested 'do-while' loops:
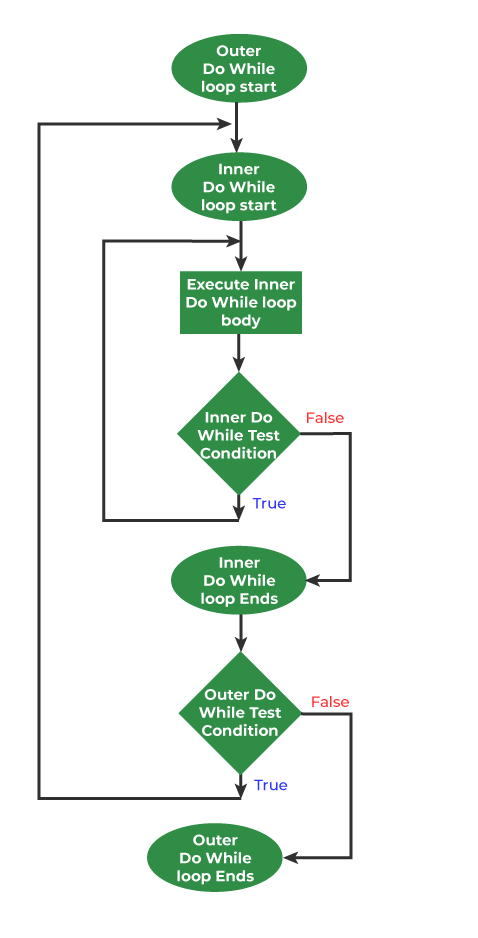
flowchart for do while loop in C
**Syntax:
C `
do{ do{ // statement of inside loop }while(condition); // statement of outer loop }while(condition);
`
**Note: There is no rule that a loop must be nested inside its own type. In fact, there can be any type of loop nested inside any type and to any level.
**Syntax:
C `
do{ while(condition) { for ( initialization; condition; increment ) { // statement of inside for loop } // statement of inside while loop } // statement of outer do-while loop }while(condition);
`
**Example: Below program uses a nested for loop to print all prime factors of a number.
C `
#include <math.h> #include <stdio.h>
// A function to print all prime factors of a given number n void primeFactors(int n) { // Print the number of 2s that divide n while (n % 2 == 0) { printf("%d ", 2); n = n / 2; }
// n must be odd at this point. So we can skip
// one element (Note i = i +2)
for (int i = 3; i <= sqrt(n); i = i + 2) {
// While i divides n, print i and divide n
while (n % i == 0) {
printf("%d ", i);
n = n / i;
}
}
// to handle the case when n
// is prime number greater than 2
if (n > 2)
printf("%d ", n);} int main() { int n = 315; primeFactors(n); return 0; }
`
Break Inside Nested Loops
Whenever we use a break statement inside the nested loops it breaks the innermost loop only and program control goes to the outer loop. Breaking the inner loop does not affects the outer loops.
**Example:
C `
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int i = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
// This inner loop will break when i==3
if (i == 3) {
break;
}
printf("* ");
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;}
`
Output
In the above program, the first loop will iterate from 0 to 5 but here if i will be equal to 3 it will break and will not print the * as shown in the output.
Continue Inside Nested loops
Whenever we use a continue statement inside the nested loops it skips the iteration of the innermost loop only. The outer loop remains unaffected.
**Example:
C `
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int i = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
// This inner loop will skip when j==2
if (j==2) {
continue;
}
printf("%d ",j);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;}
`
In the above program, the inner loop will be skipped when j will be equal to 2. The outer loop will remain unaffected.
Uses of Nested Loops
- **Printing Patterns: Nested loops are often used to print complex patterns such as printing shapes, grids, or tables.
- **Searching and Sorting: Nested loops are used in algorithms that involve searching for or sorting elements like bubble sort, insertion sort, matrix searching etc.
- **Multi-Dimensional Data: Nested loops are useful when dealing with multidimensional data structures like 2D or 3D arrays, matrices, list of lists.
- Dynamic Programming: Nested loops are commonly used in dynamic Programming for solving problems like knapsack problem or longest common subsequence.