Next.js Nested Routes (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 30 Jul, 2024
Next.js is a popular React framework that enables server-side rendering and static site generation. One of the key features that enhance the development experience in Next.js is its routing system.
While Next.js provides a file-based routing mechanism, implementing nested routes requires some additional understanding. This article will guide you through the process of creating nested routes in Next.js.
**What are nested routes?
In Next.js, routing is based on the file system. Each file in the pages directory corresponds to a route in the application. For example, pages/index.js maps to the root URL (/), and pages/about.js maps to the /about URL.
**Implementation of nested routes in Next.js
Next.js implements routing in the form of a **file system where the ****'pages'** directory is the root directory which corresponds to the path ****'/'**. Nested routes can be introduced in this file system by creating **sub-directories inside the 'pages' directory. In the same way, multiple sub-directories can be created within a sub-directory. Thus, the nesting of multiple directories and their routes can be achieved in this way.
**Steps To Implement Nested Routes in Next.js
**Step 1: Create a next application using the following command.
npx create-next-app@latest
The placeholder '<>' specifies the name of the application to be created.
Change the directory to your application directory.
cd
**Step 2: Install all the required npm dependencies.
npm install
**Initial Project Structure: The file structure of our project will look like the following image once the application has been created. Observation of project structure is crucial for our example since Next.js implements file structure-based routing.

initial file structure
Dependencies
dependencies :
{
"react": "^18",
"react-dom": "^18",
"next": "14.2.4"
}
**Example 1: Let's take a basic example to implement nested routing.
**Step 1: Create a new directory called ****'nested'** inside the 'pages' directory.
**Step 2: Create a new page called ****'index.js'** inside the newly created 'nested' directory which will be the root page for the 'nested' directory.
**index.js
JavaScript `
export default function nested(){
return(
<div>
<h1 style={{color: "green"}}>
Geeks for Geeks
</h1>
<h1> Let's learn nested routing! </h1>
</div>
);}
`
**Step 3: Create a new page called ****'nested_page.js'** inside the 'nested' directory.
**nested_page.js
JavaScript `
export default function nested(){
return(
<div>
<h1 style={{color: "green"}}>
Geeks for Geeks
</h1>
<h1> Nested routing is simple! </h1>
</div>
);}
`
After creating nested routes, the project structure will look like this.

project structure after creating a nested route
**Output:
The URL ****"http://localhost:3000/nested/"** will load the root page of the 'nested' directory which is 'index.js'.
The URL ****"http://localhost:3000/nested/nested\_page"** will load the page we have nested, inside the 'nested' directory, which is 'nested_page.js'.
**Example 2: To get a better understanding of the implementation of nested routing in Next.js, let us take another example of a primitive website of GeeksforGeeks which has a home page (**index.js).
**Step 1: Replace the content of index.js. For simplicity, let's replace the default index page with a simple GeeksforGeeks home page.
index.js
JavaScript `
export default function home(){ return(
Geeks for Geeks home page !!!
`
**Step 2: Create a new page - articles.js (http://localhost:3000/articles)
Let's now create a page for articles on our primitive GeeksforGeeks website. To achieve this, we don't need to implement nested routing since we just need to create the required page under the root directory - 'pages'. So, let's create a page called ****'articles.js'** under the 'pages' directory.
**articles.js
JavaScript `
export default function articles(){ return(
Articles page of GeeksforGeeks
`
Now the file structure looks like this.
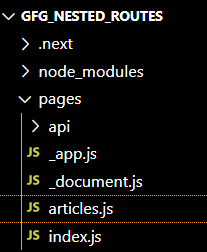
file structure after creating articles.js
Till this point, regular routing was able to satisfy our needs.
**Step 3: First nested route (http://localhost:3000/articles/dsa). Articles do not come under a single category. Technical articles need to be categorized based on their topics. To achieve this, we need to implement nested routing. This can be done by creating a directory called ****'articles'** inside the root directory- 'pages' and creating different categories of articles such as '**dsa.js' within the 'articles' directory. The nested route corresponding to the nested directory will be automatically generated by Next.js.
**dsa.js
JavaScript `
export default function articles(){ return(
Articles page of GeeksforGeeks
`
The file structure after the creation of our first nested route can be seen below.

first nested route
**Step 4: Second nested route (http://localhost:3000/articles/dsa/post1)
Now that we have created a sample category in our project, It's time to add sample posts to it. To do so, we need to create a directory called ****'dsa' within** the 'articles' directory. Inside the 'DSA' directory, we are going to create our sample post - ****'post1.js'.**
**post1.js
JavaScript `
export default function post1(){ return(
Sample post of GeeksforGeeks
`
The file structure will now look like the one shown below.

NextJs Nested routes
**Output:
**Steps to run the application: Enter the following command in the terminal to start the development server.
npm run dev
**Visit the below URL using a browser: http://localhost:3000/